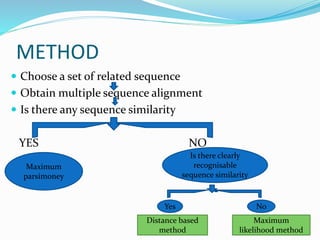
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a taxonomic group as represented by a phylogenetic tree. The goals of phylogeny are to show relationships between species based on evolutionary time. There are several tools and methods used to build phylogenetic trees, including distance-based methods like UPGMA and neighbor joining which use sequence similarities, and character-based methods like maximum parsimony. Software like MEGA, Dendroscope, and Phylotree.js can be used to construct and visualize phylogenetic trees.