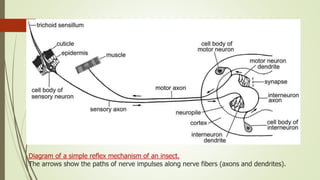
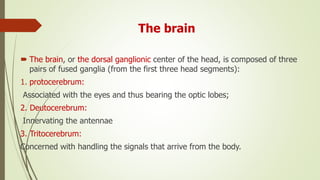
The insect nervous system consists of three main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), the visceral nervous system, and the peripheral nervous system. The CNS contains a brain and a ventral nerve cord made up of fused ganglia. It receives and processes sensory information. The visceral nervous system innervates internal organs. The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS and visceral nervous system to muscles and sense organs via motor and sensory neurons. Together these systems allow insects to respond to their environment and control bodily functions through neural pathways and chemical signaling between different neuron types.