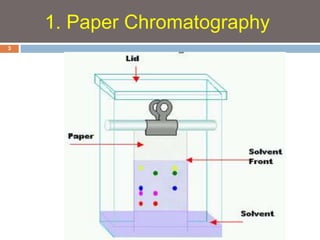
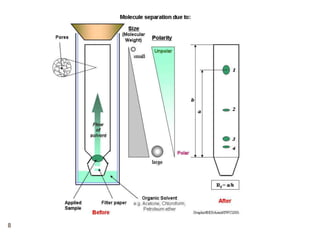
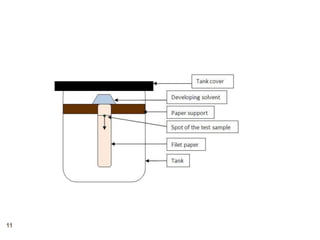
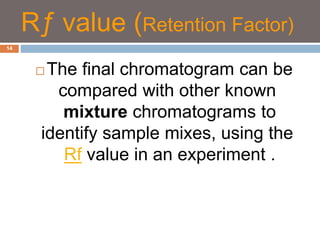
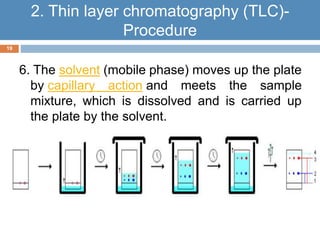
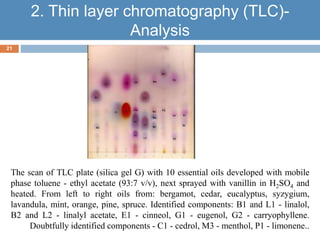
Paper chromatography and thin layer chromatography are techniques used to separate mixtures. In paper chromatography, a sample is placed on chromatography paper and placed in a solvent, allowing different compounds to travel up the paper at different rates based on their interactions with the paper and solvent. Thin layer chromatography uses a thin layer of adsorbent, like silica gel, coated on a plate as the stationary phase, and a solvent to separate compounds based on polarity. Both methods allow visualization and quantification of separated compounds through calculation of Rf values and use of detection reagents.