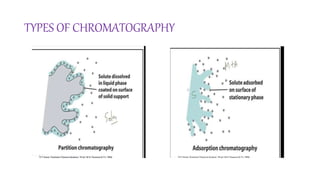
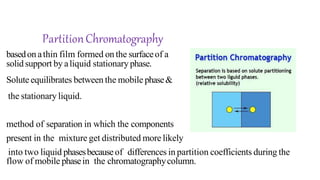
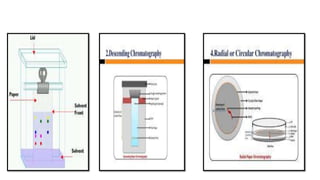
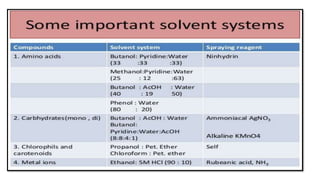
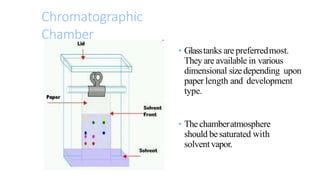
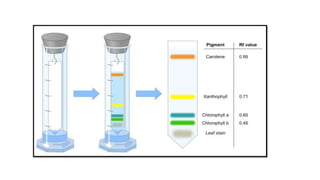
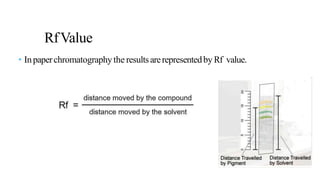
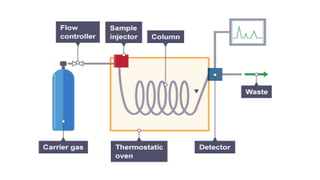
This document provides an overview of partition chromatography. It defines partition chromatography as a method of separation where components in a mixture distribute between two immiscible liquid phases due to differences in their partition coefficients. The document discusses the history of chromatography and describes partition chromatography techniques like paper chromatography and gas-liquid chromatography. It explains the basic principles, procedures, factors affecting separation, and applications of partition chromatography.