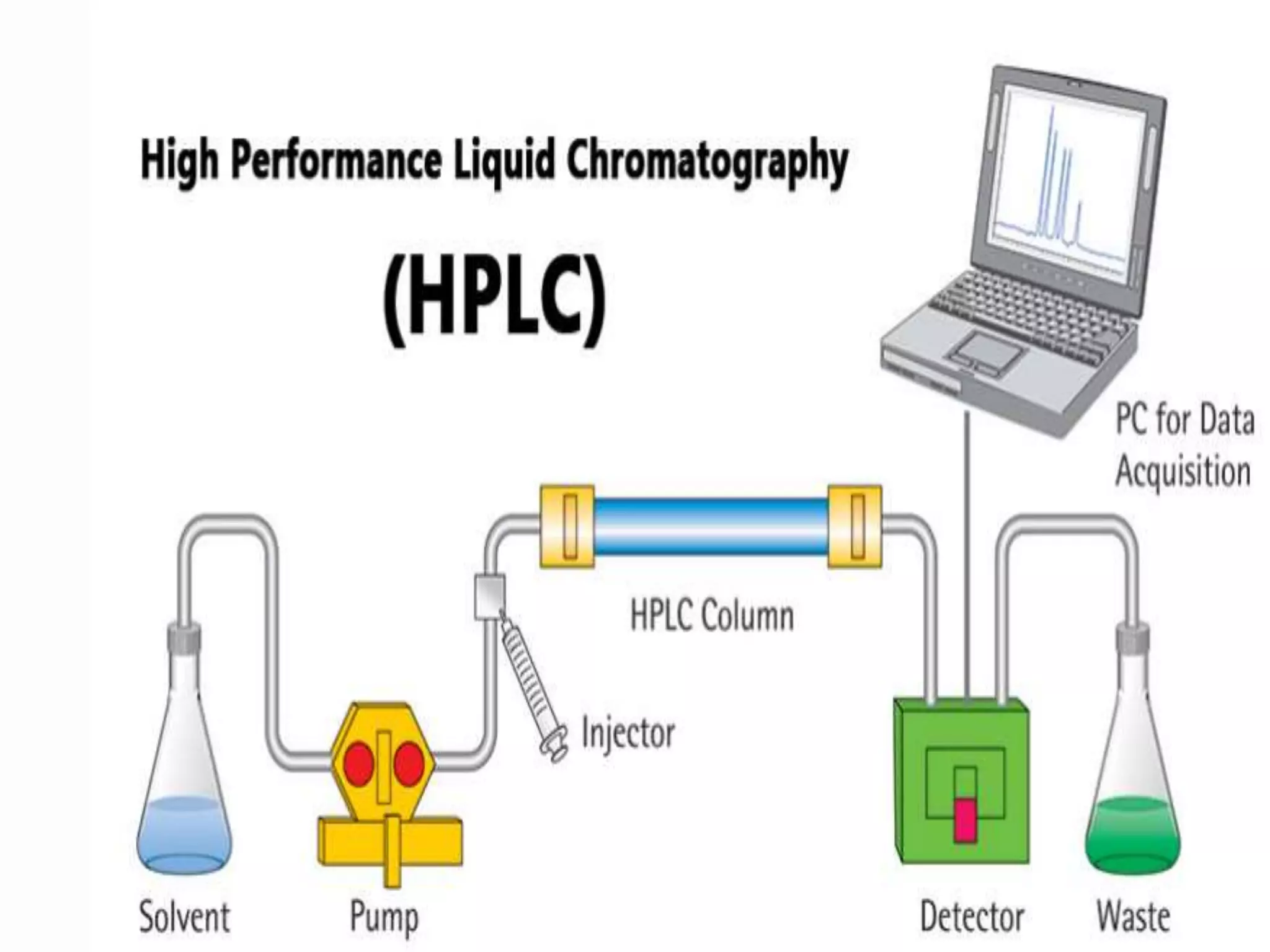
HPLC, or high-performance liquid chromatography, is an analytical technique used to separate, identify, and quantify components in a mixture. It works by pumping a pressurized mobile liquid phase through a column containing a stationary phase, which causes the components in a sample to separate as they migrate through the column at different rates. Common components of an HPLC system include the pump, injector, column, detector, and recorder or computer system. HPLC has advantages of speed, efficiency, accuracy, and versatility in chemical analysis. It is used in various applications such as drug analysis, environmental analysis, and industrial quality control.