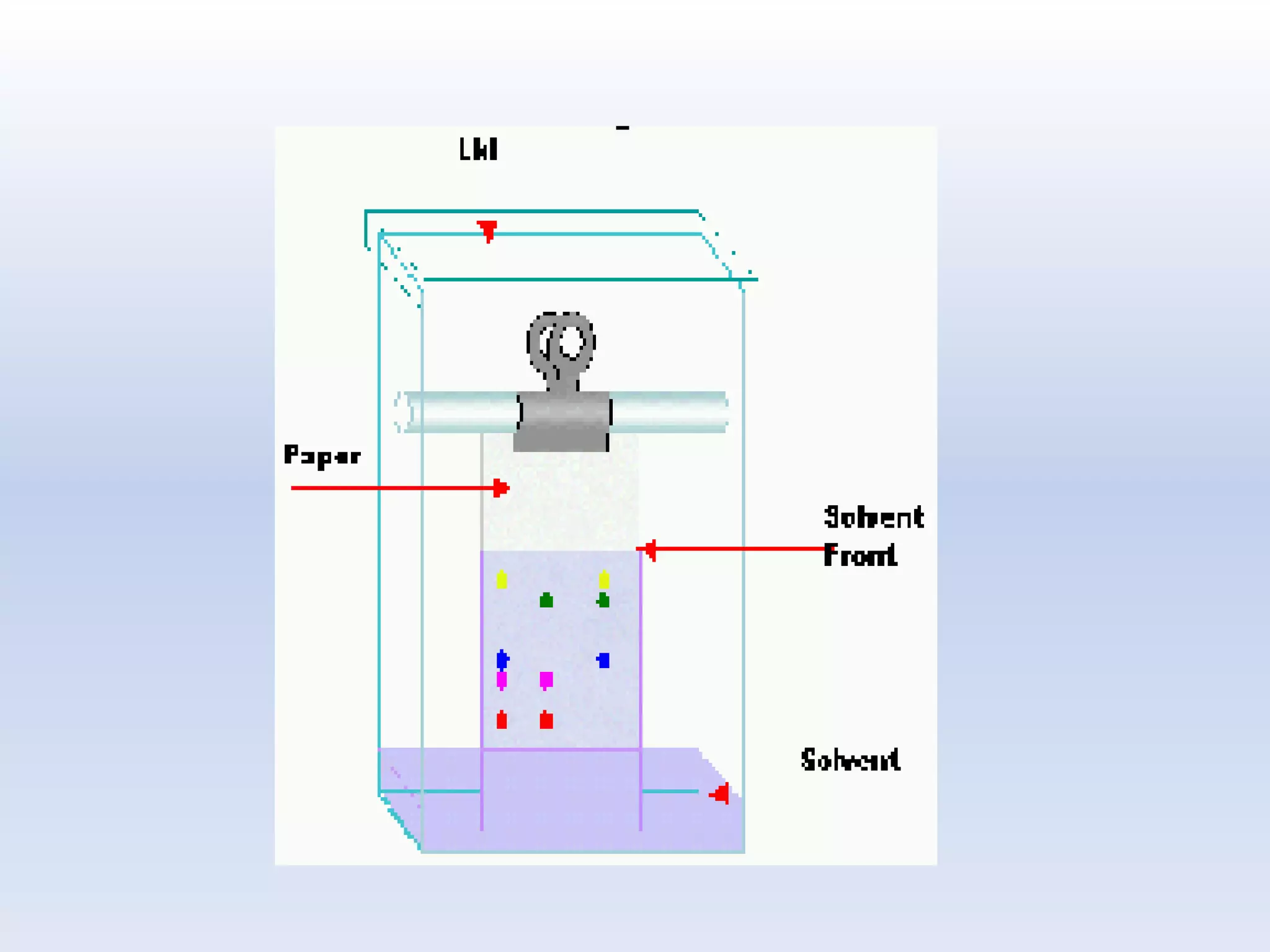
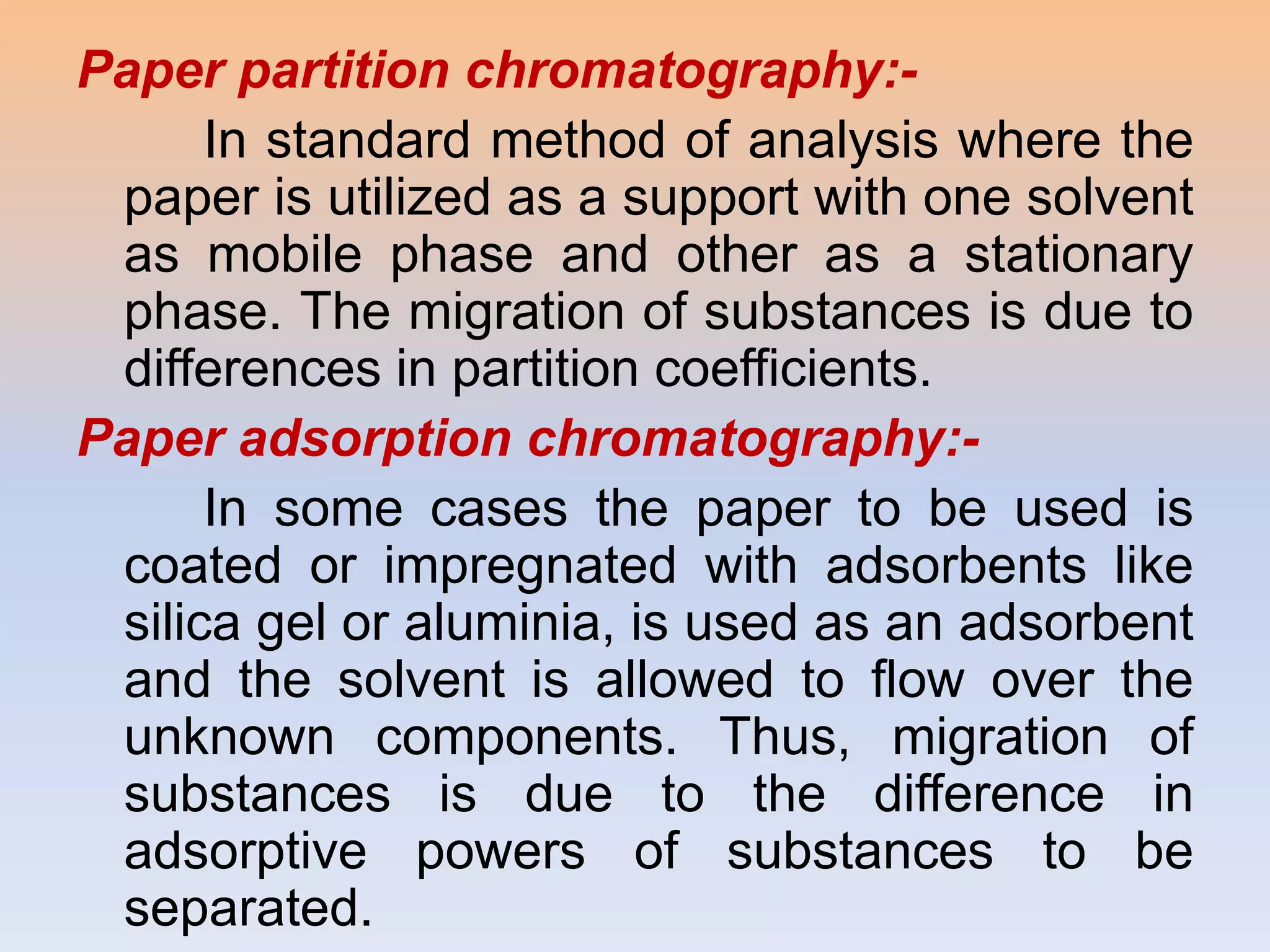
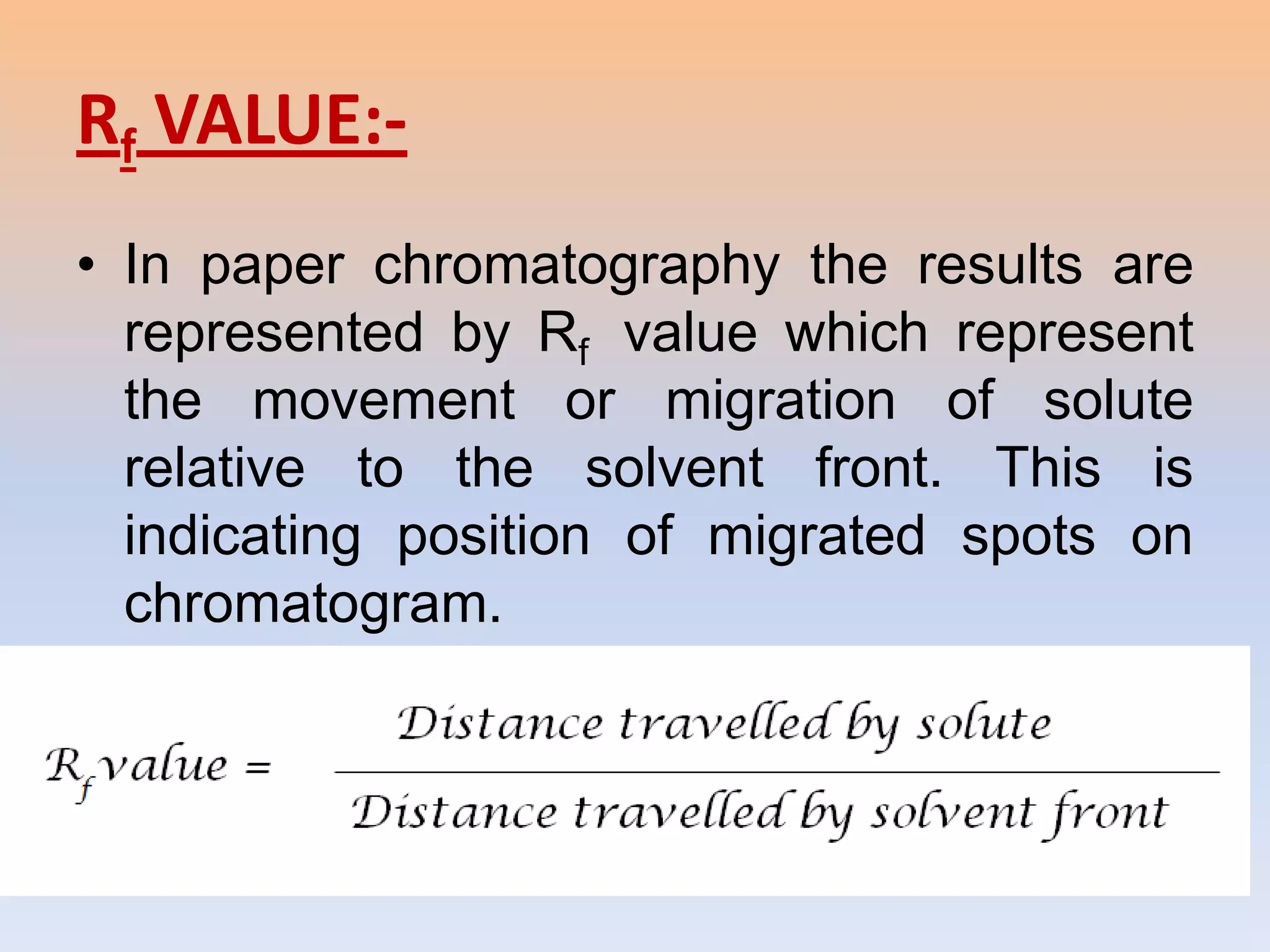
This presentation discusses paper chromatography, including its principle, types, advantages, and calculation of Rf values. Paper chromatography separates compounds based on their differential partitioning between a stationary phase (paper) and mobile phase (solvent). It has advantages like simple equipment and ability to separate closely related compounds. The distance migrated by a compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front gives the retention factor (Rf value), which is useful for identification. Factors like solvent composition, temperature, paper quality can influence Rf values.