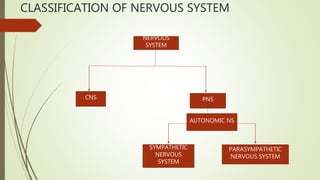
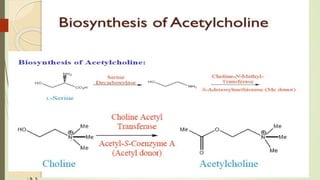
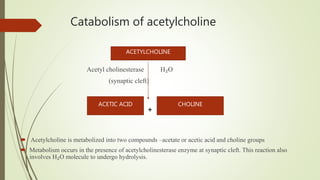
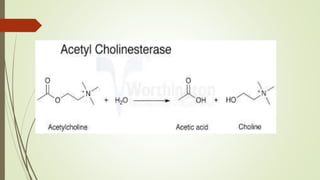
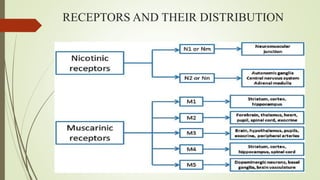
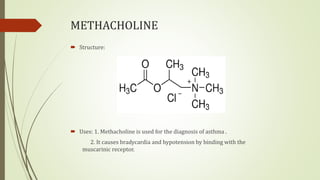
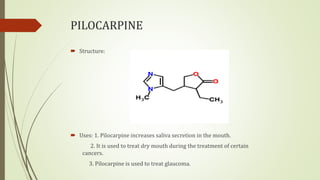
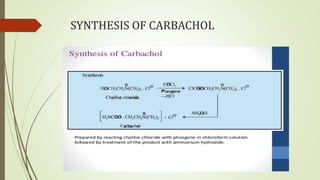
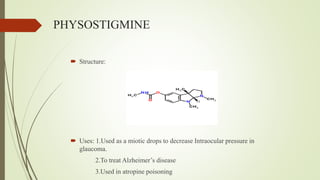
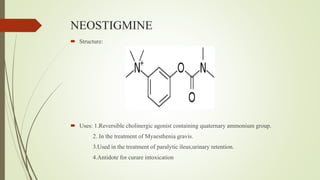
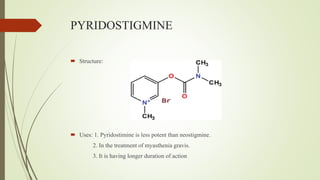
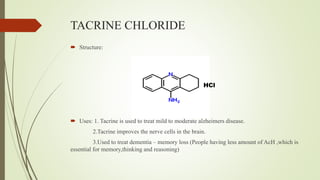
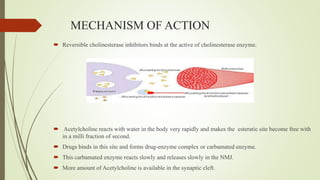
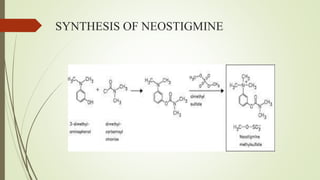
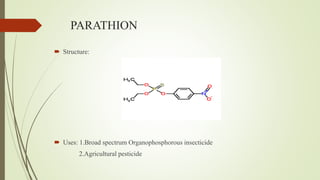
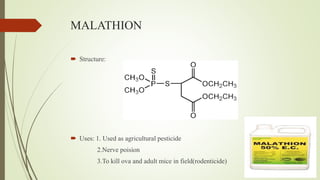
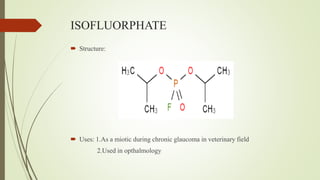
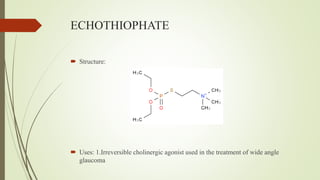
This document summarizes parasympathomimetics (cholinergic agonists). It discusses how the parasympathetic nervous system uses acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter and how cholinergic agonists mimic acetylcholine's actions. It classifies cholinergic agonists into direct-acting and indirect-acting types. Direct agonists bind receptors, while indirect agonists inhibit acetylcholinesterase to increase acetylcholine levels. Examples of both types are provided along with their structures, mechanisms of action, and uses. The document also covers acetylcholine synthesis and catabolism as well as structure-activity relationships of parasympathomimetics.