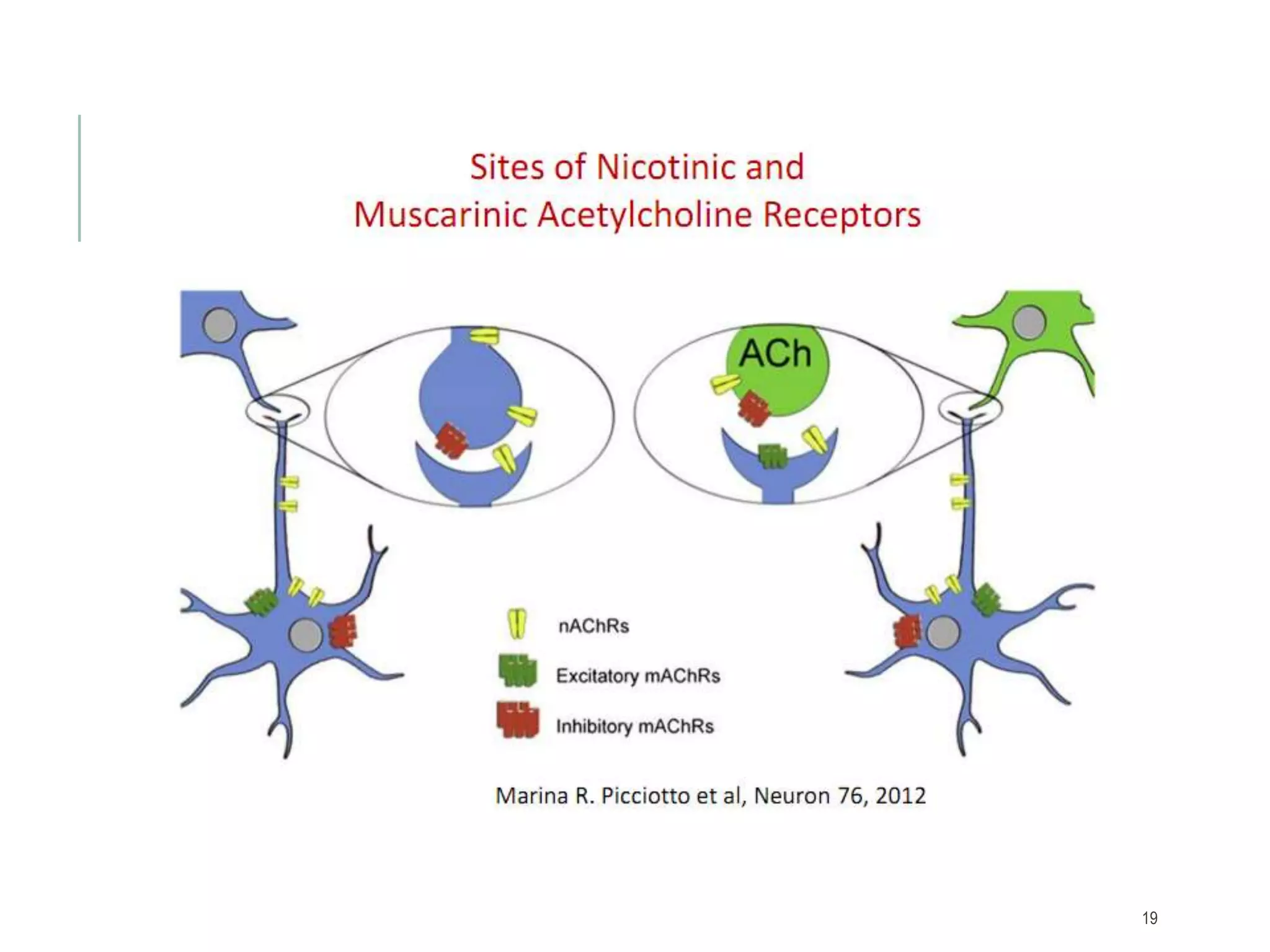
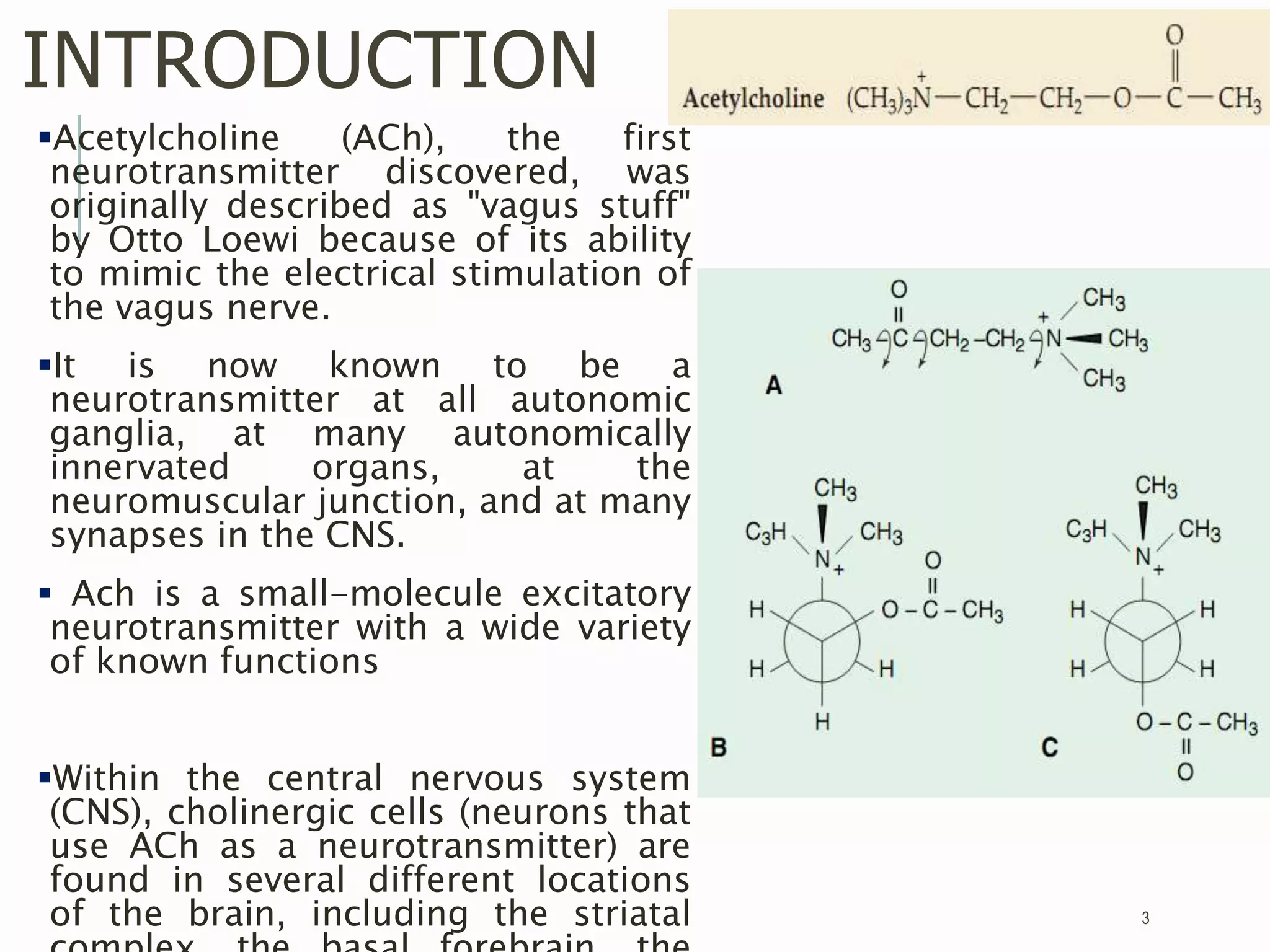
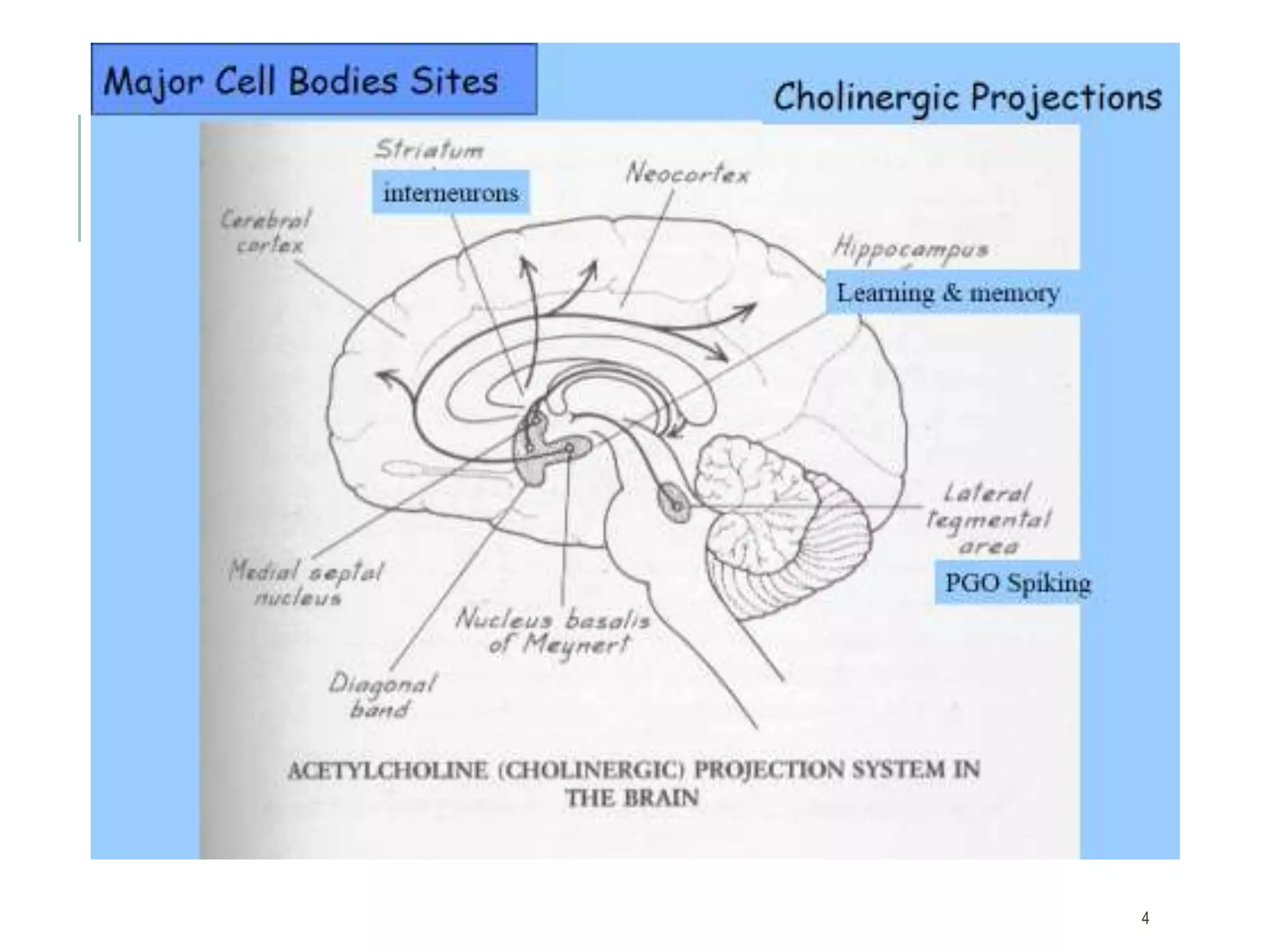
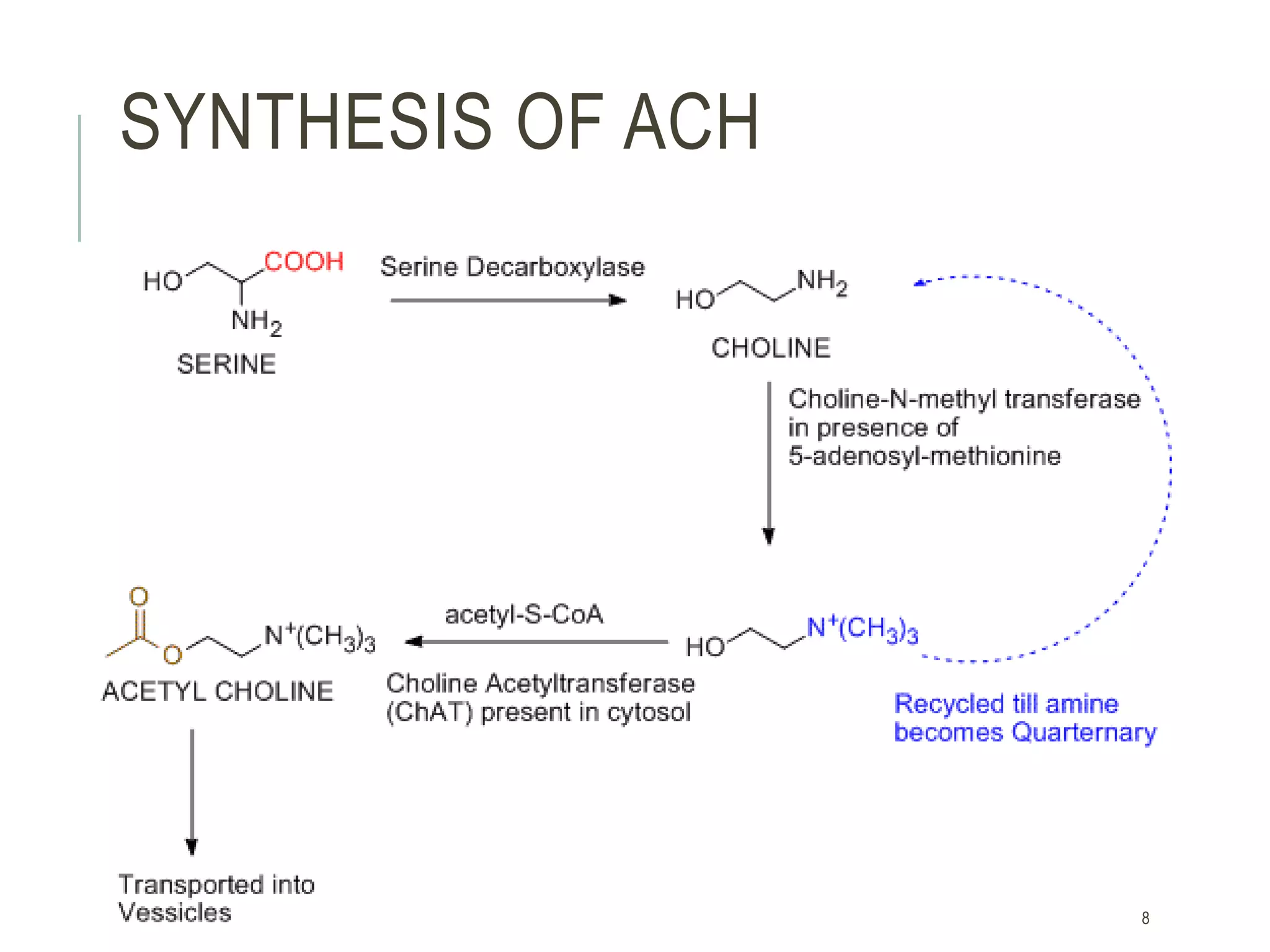
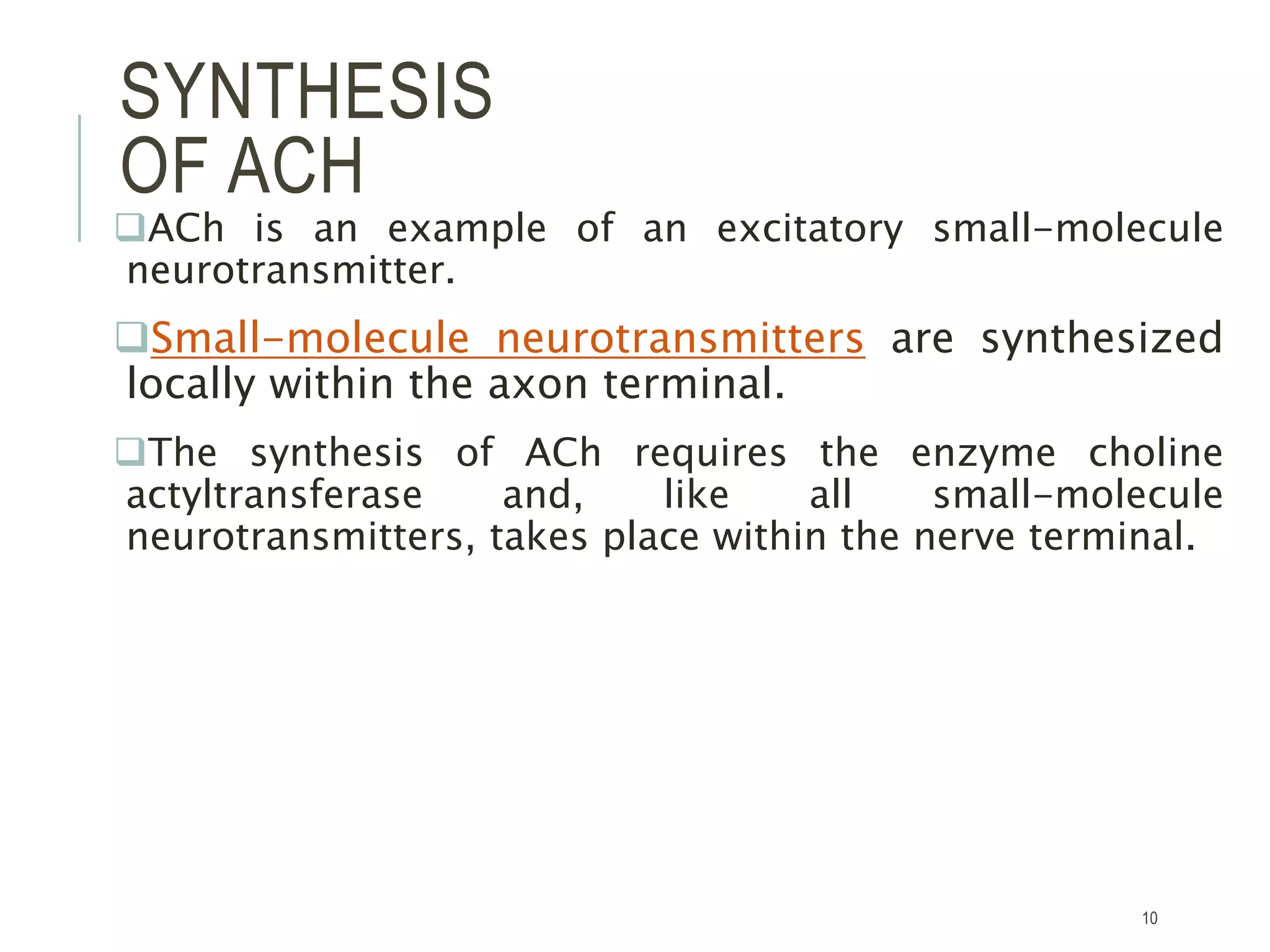
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter synthesized locally within cholinergic neurons from choline and acetyl-CoA. During neurotransmission, an action potential causes calcium influx and vesicle fusion, releasing ACh into the synaptic cleft. ACh then binds post-synaptic nicotinic or muscarinic receptors, opening ion channels and continuing the action potential in the next neuron. In the central nervous system, ACh is involved in processes like learning, memory, and sleep regulation. Deficiencies in central cholinergic systems are implicated in Alzheimer's disease.



![CHOLINERGIC
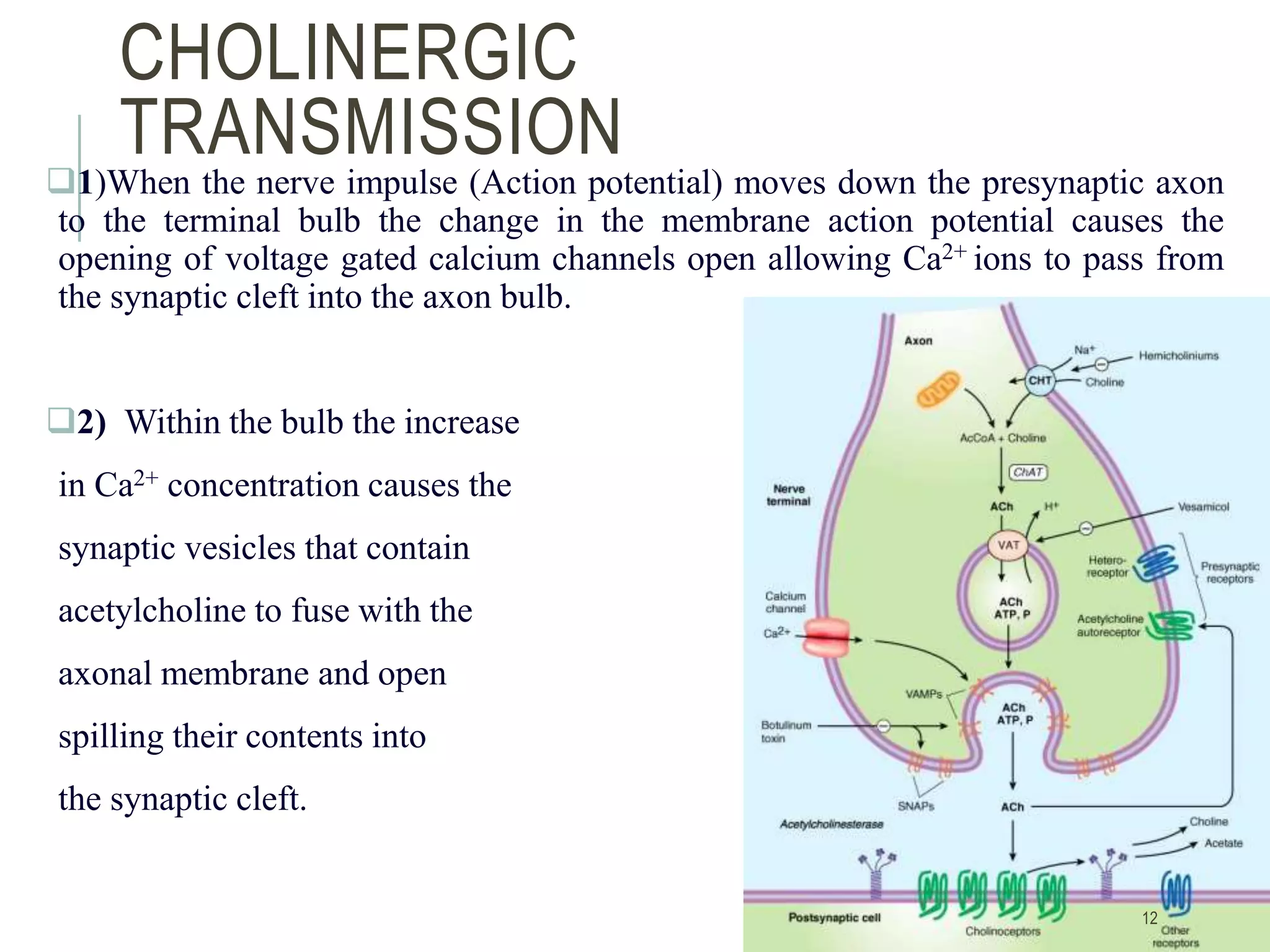
TRANSMISSIONThe postsynaptic membrane of the receptor dendrite has
specific cholinergic receptors toward which the
neurotransmitter diffuses. Binding of acetylcholine trigger the
opening of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane initiating
action potential that can pass in the next axon.
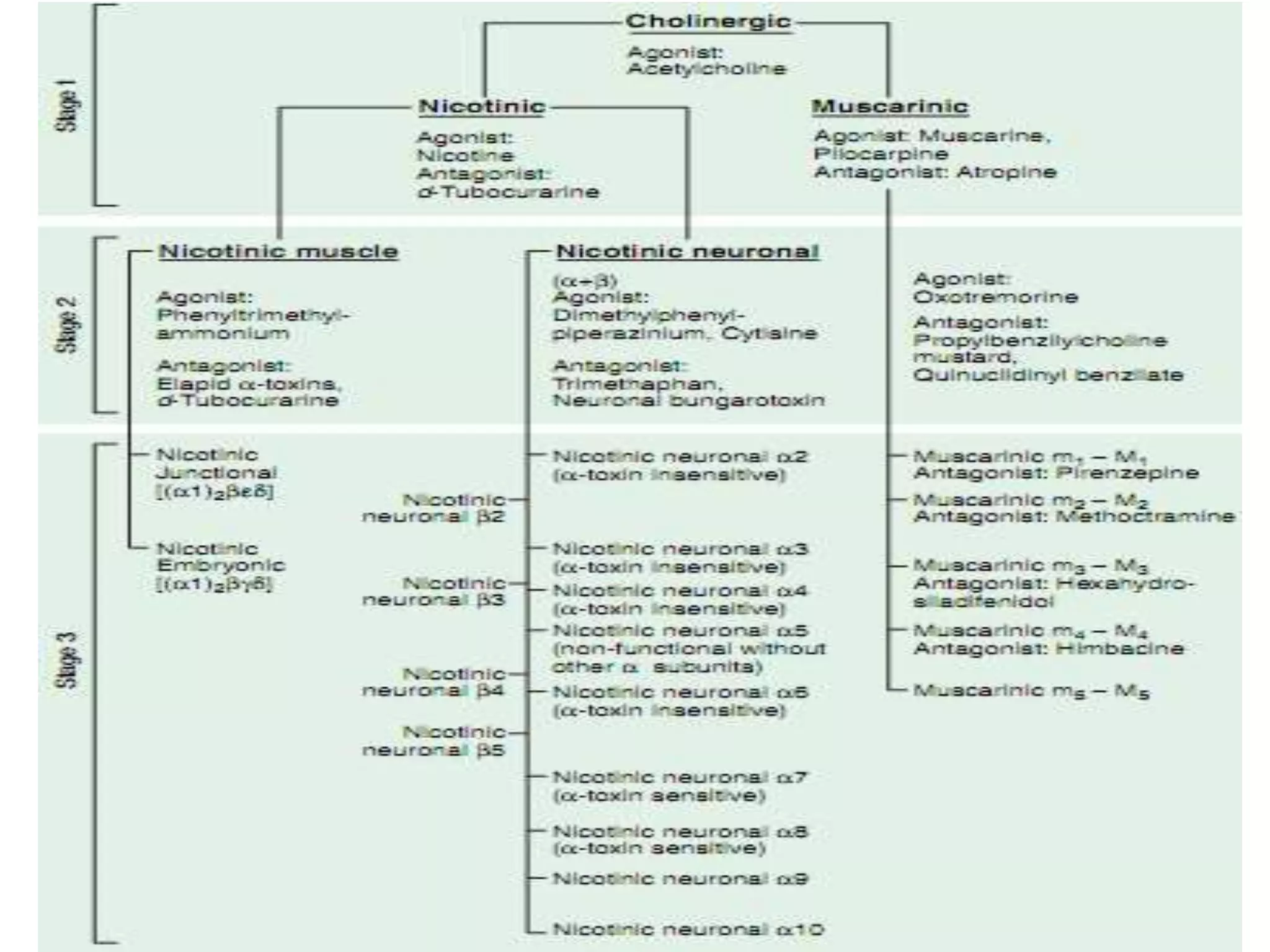
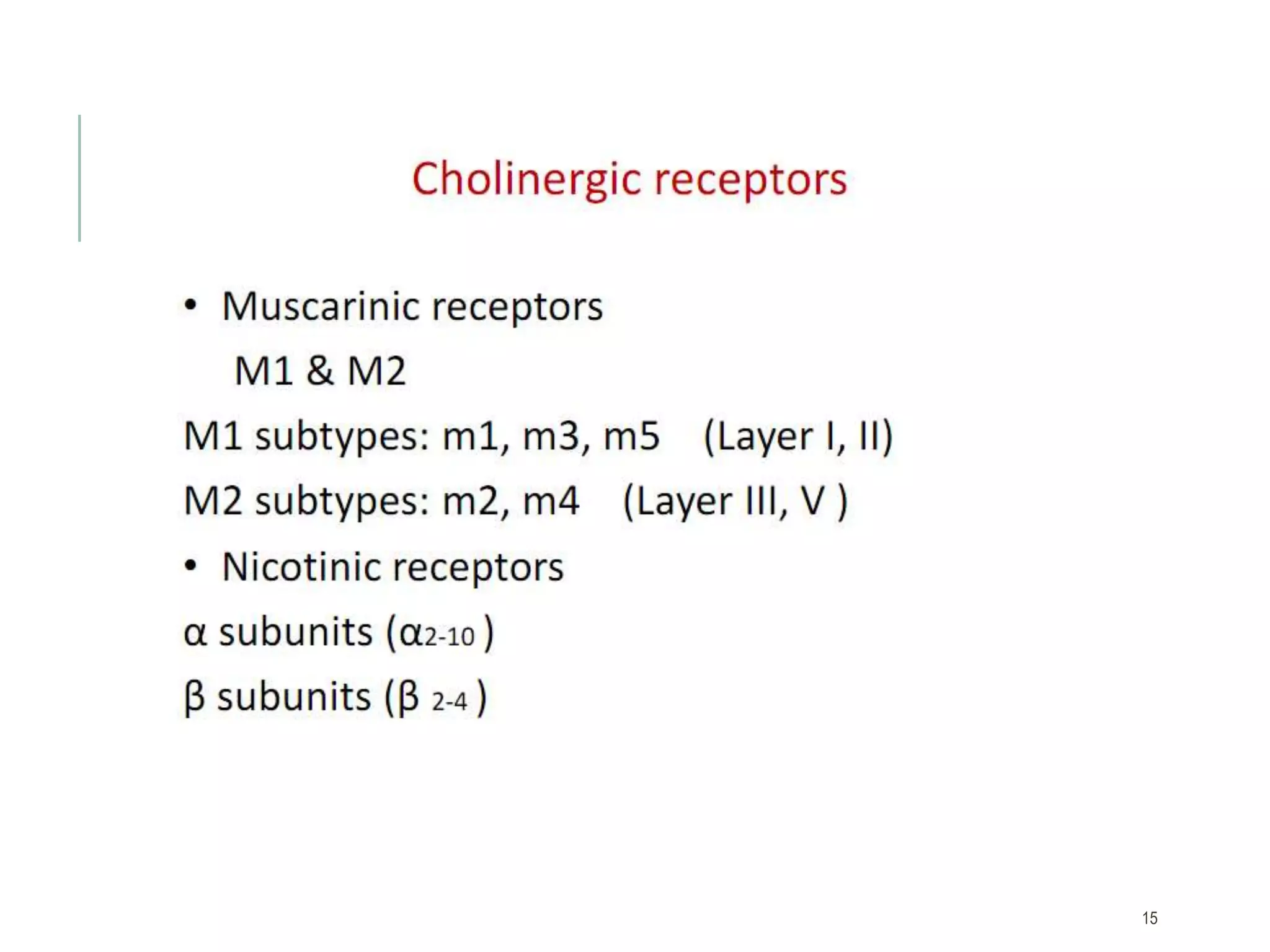
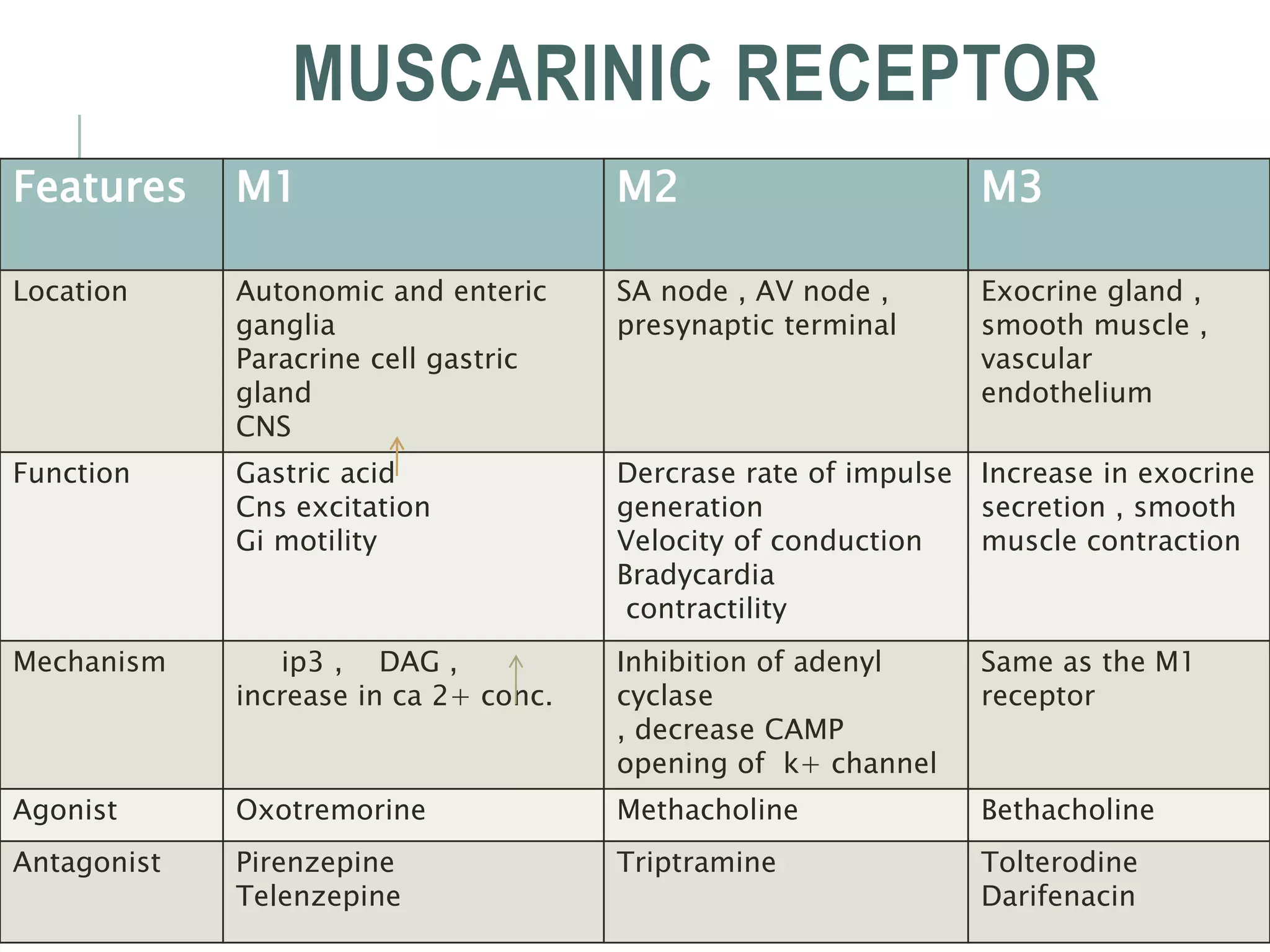
Acetylcholine receptors:
Acetylcholine receptors are ion channels receptors made of
many subunits arranged in the form [(α2)(β)(γ)(δ)].
When Acetylcholine is not bounded to the receptors, the bulky
hydrophobic leu side close the central channels preventing the
diffusion of any ions.
Binding of two acetylcholine molecules to the receptors will
rotate the subunits in which the smaller polar residues will line
the ion channel causing the influx of Na+ into the cell and
efflux of K+ resulting in a depolarization of the postsynaptic
neuron and the initiation of new action potential.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/96718b5a-85f0-4083-873b-40e7d867d8fc-160904130143/75/BIOSYNTHESIS-OF-ACETYLCHOLINE-IN-CNS-AND-CHOLINERGIC-TRANSMISSION-13-2048.jpg)