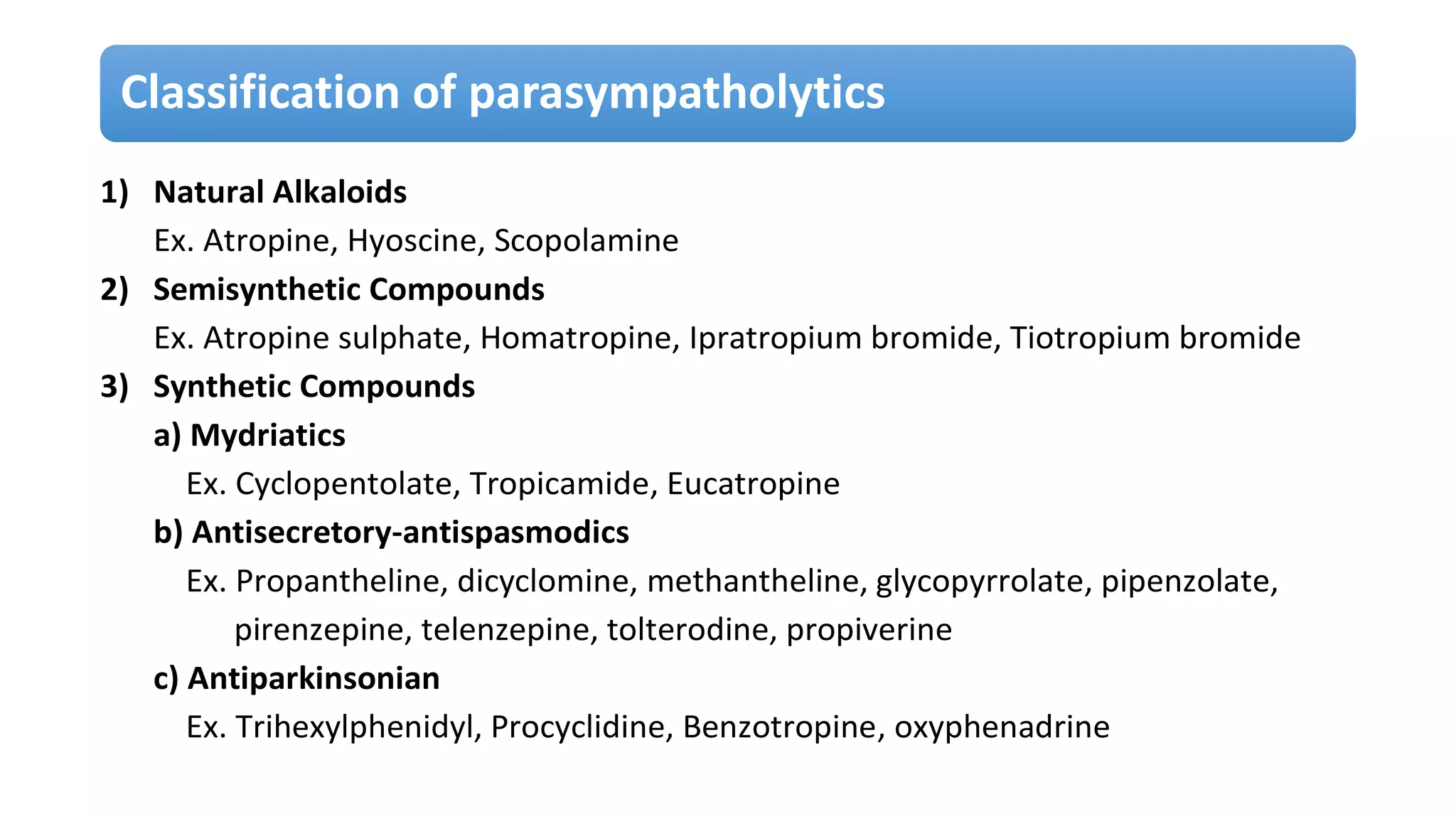
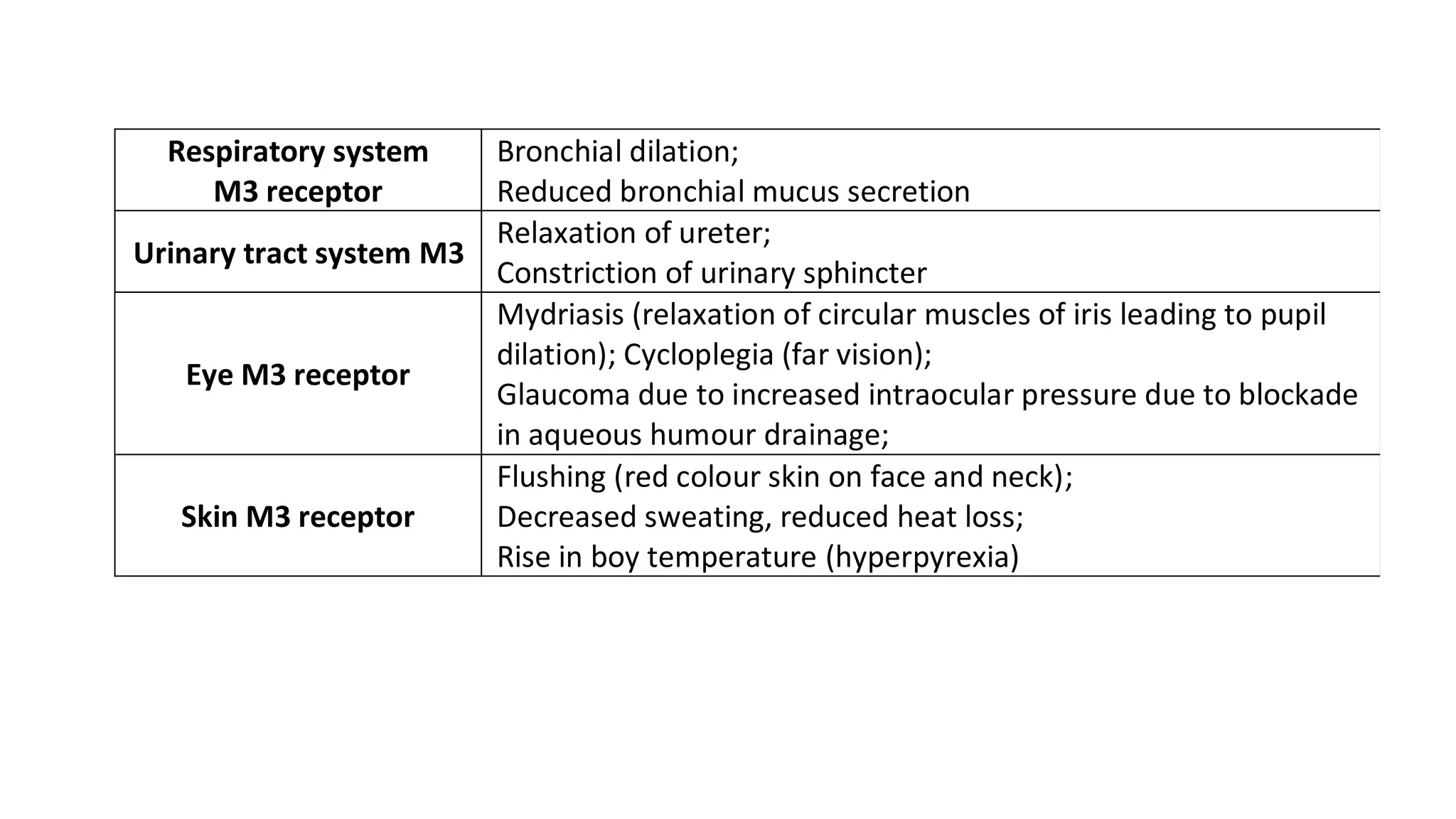
Parasympatholytics, also known as anticholinergics, are drugs that inhibit acetylcholine's actions at postganglionic nerve endings and cholinergic receptors, with atropine being the prototype. These drugs are classified into natural alkaloids, semisynthetic, and synthetic compounds, and have various therapeutic uses including treatment for CNS disorders, antispasmodics, antisecretory agents, and ophthalmic applications. Adverse effects may include dry mouth, increased body temperature, and urinary retention, with contraindications for patients with certain medical conditions.