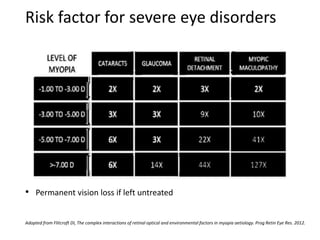
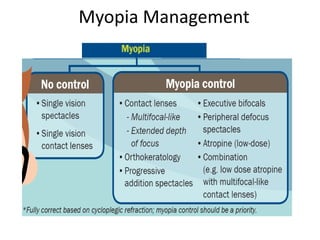
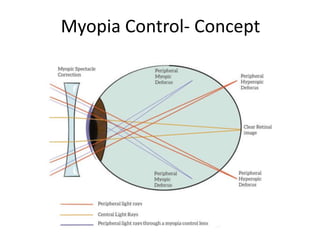
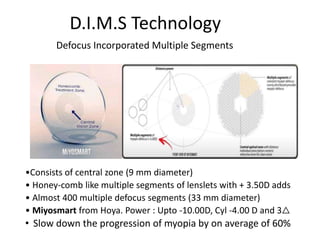
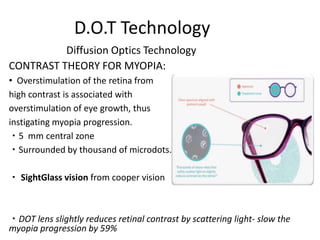
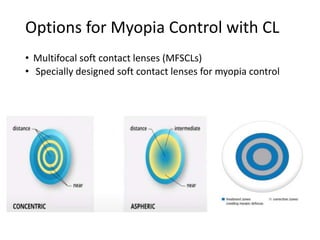
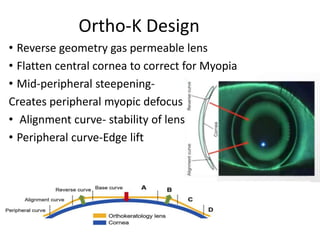
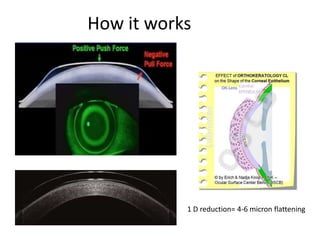
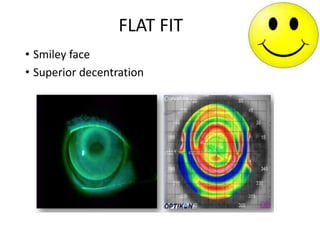
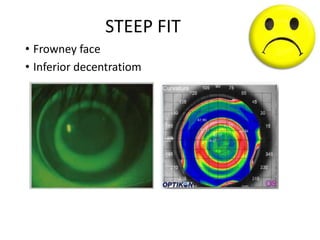
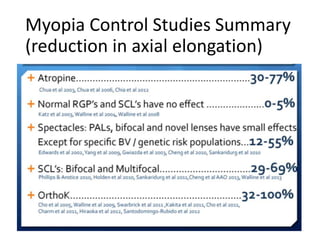
The document outlines various strategies for myopia control, a corrective approach for nearsightedness that is increasingly prevalent, especially among children. It discusses clinical guidelines for initiating myopia management, including optical technologies like traditional spectacles, next-generation spectacles, multifocal soft contact lenses, and orthokeratology. The document emphasizes the importance of early intervention and tailored solutions based on individual patient needs to slow down the progression of myopia.