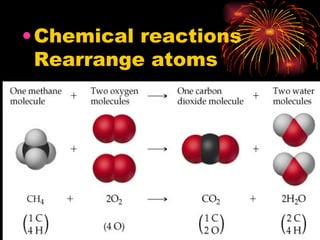
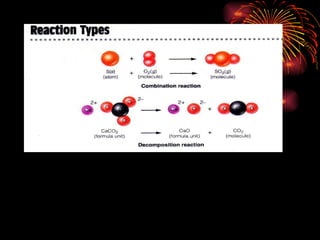
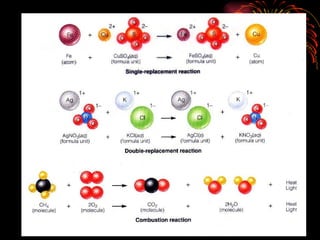
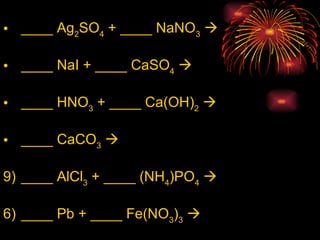
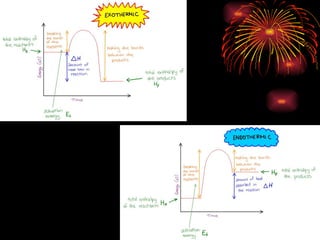
The document provides information about chemical reactions, including:
1) Chemical reactions use models and equations to represent and describe reactions involving rearrangement of atoms.
2) Reactions can be classified as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, combustion, or double replacement depending on how the reactants combine or break apart.
3) Factors like temperature, surface area, concentration, and catalysts can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.