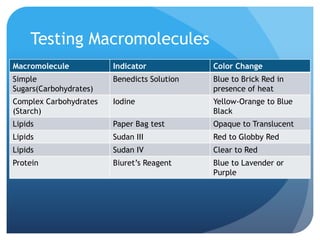
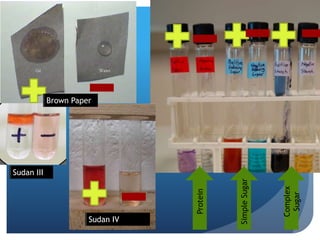
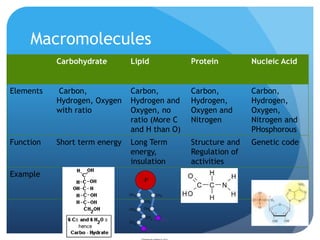
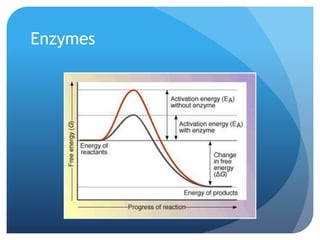
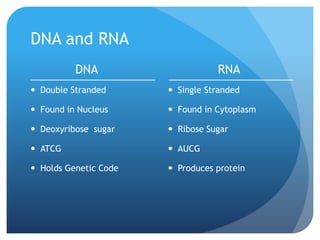
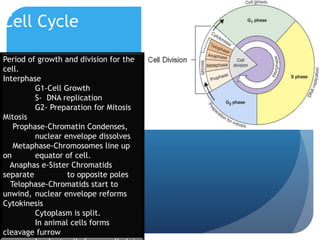
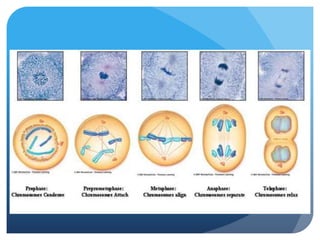
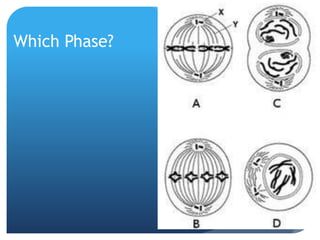
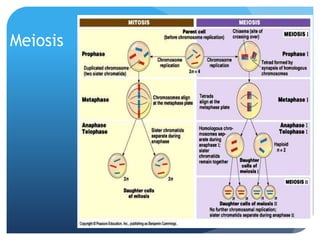
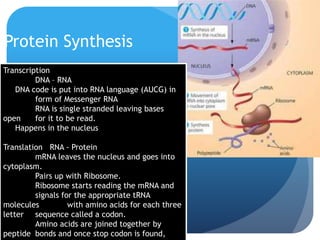
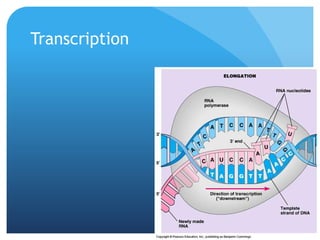
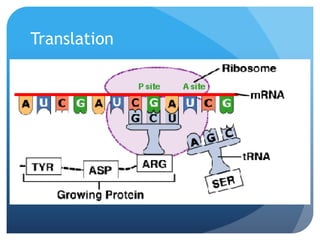
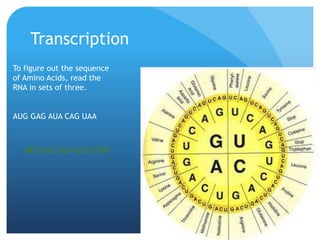
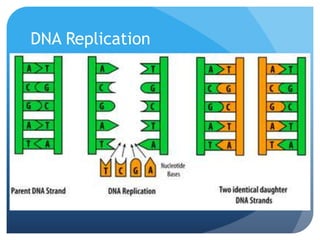
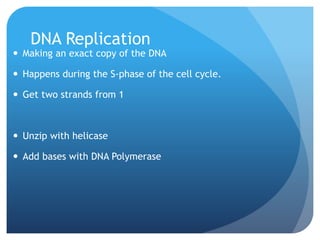
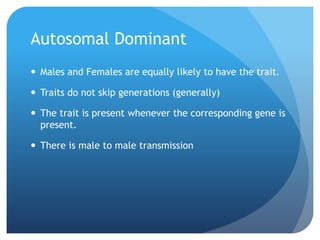
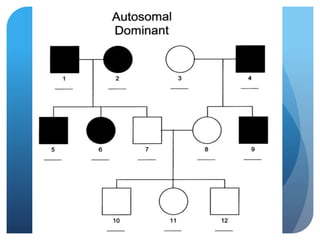
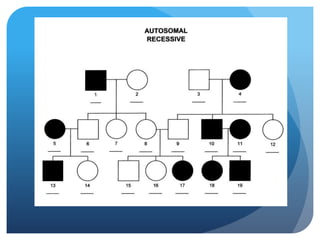
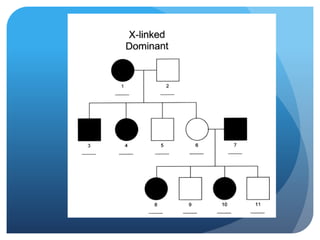
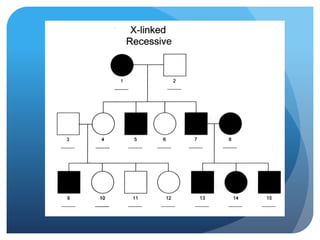
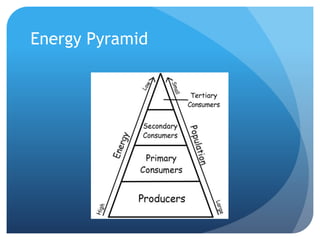
The document provides information about reviewing macromolecules and their testing indicators. It discusses carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and how they are tested using reagents like Benedict's solution, iodine, Sudan stains, and Biuret's reagent. It also provides a summary of enzymes, DNA and RNA, the cell cycle, meiosis, protein synthesis, and DNA replication.