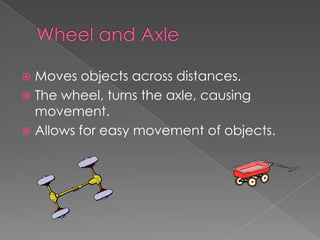
Without inclined planes, it would be much more difficult to overcome large resistances or move heavy objects using only a small amount of force. Inclined planes, such as ramps and wedges, allow us to apply a small force over a longer distance to lift or push objects. Other simple machines like screws, levers, pulleys, and wheels and axles also make work easier by either multiplying the force applied or changing the direction of force. All simple machines provide mechanical advantage to help humans perform tasks more easily.