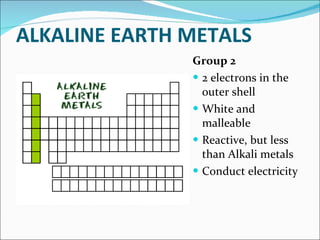
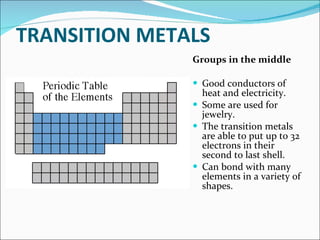
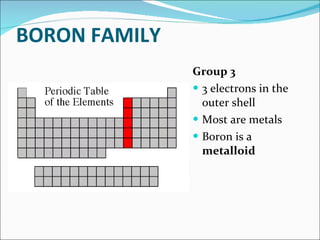
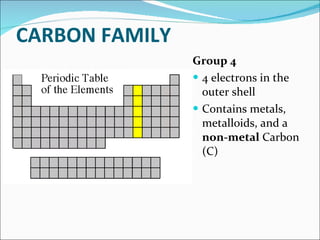
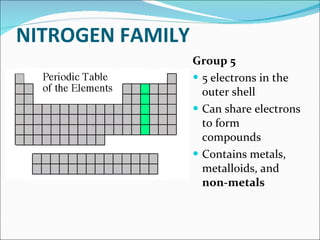
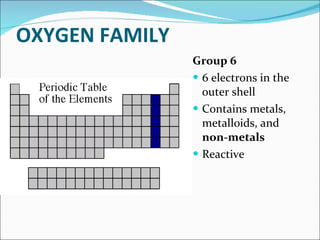
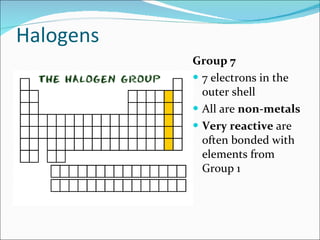
Most elements exist in the solid state of matter, while gases are least common. Mendeleev left spaces in his periodic table for elements like germanium that had not yet been discovered. The organization of the periodic table is most impacted by the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which determines the number of electrons. Elements are grouped based on their chemical properties, especially those of their valence electrons.