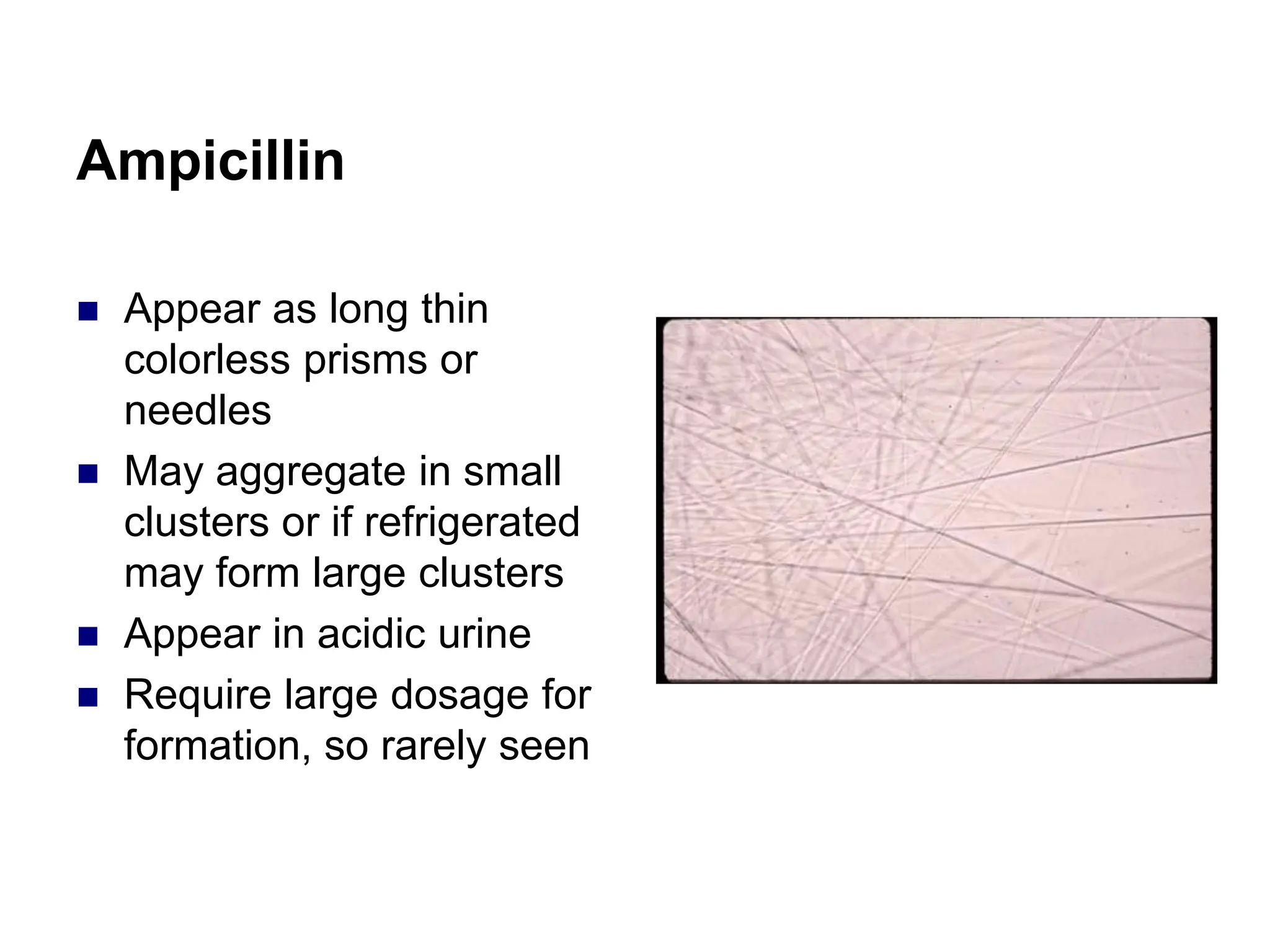
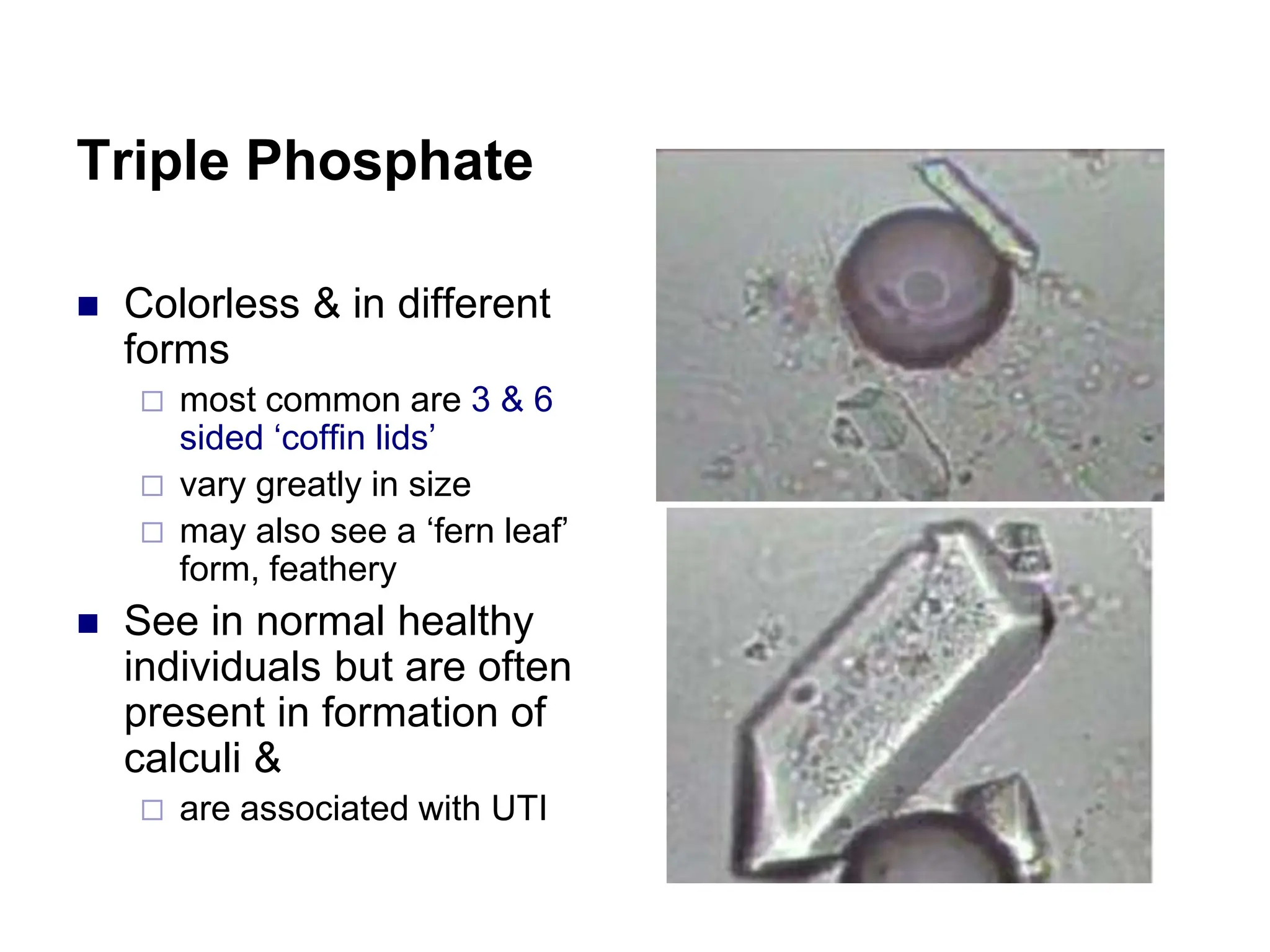
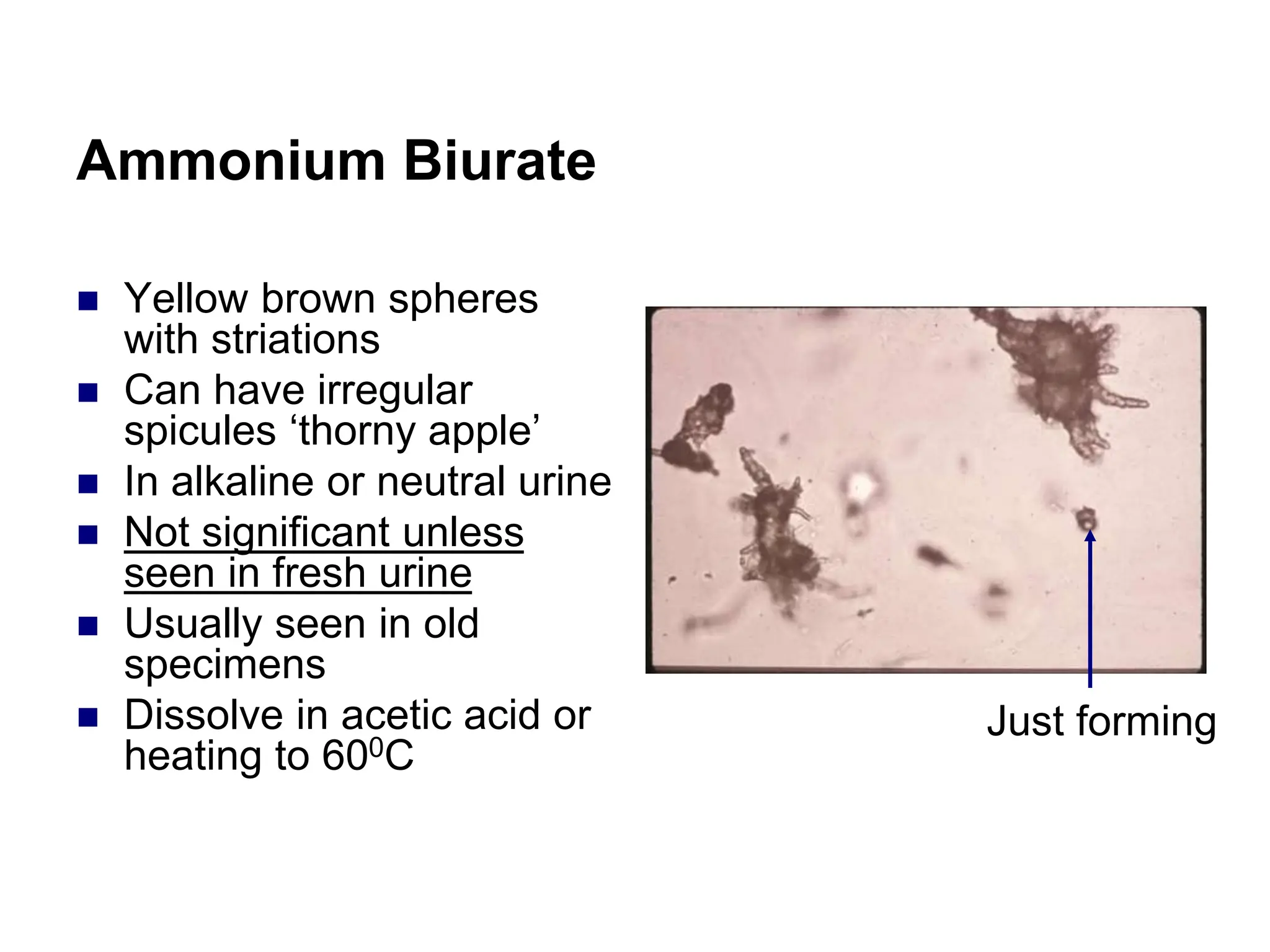
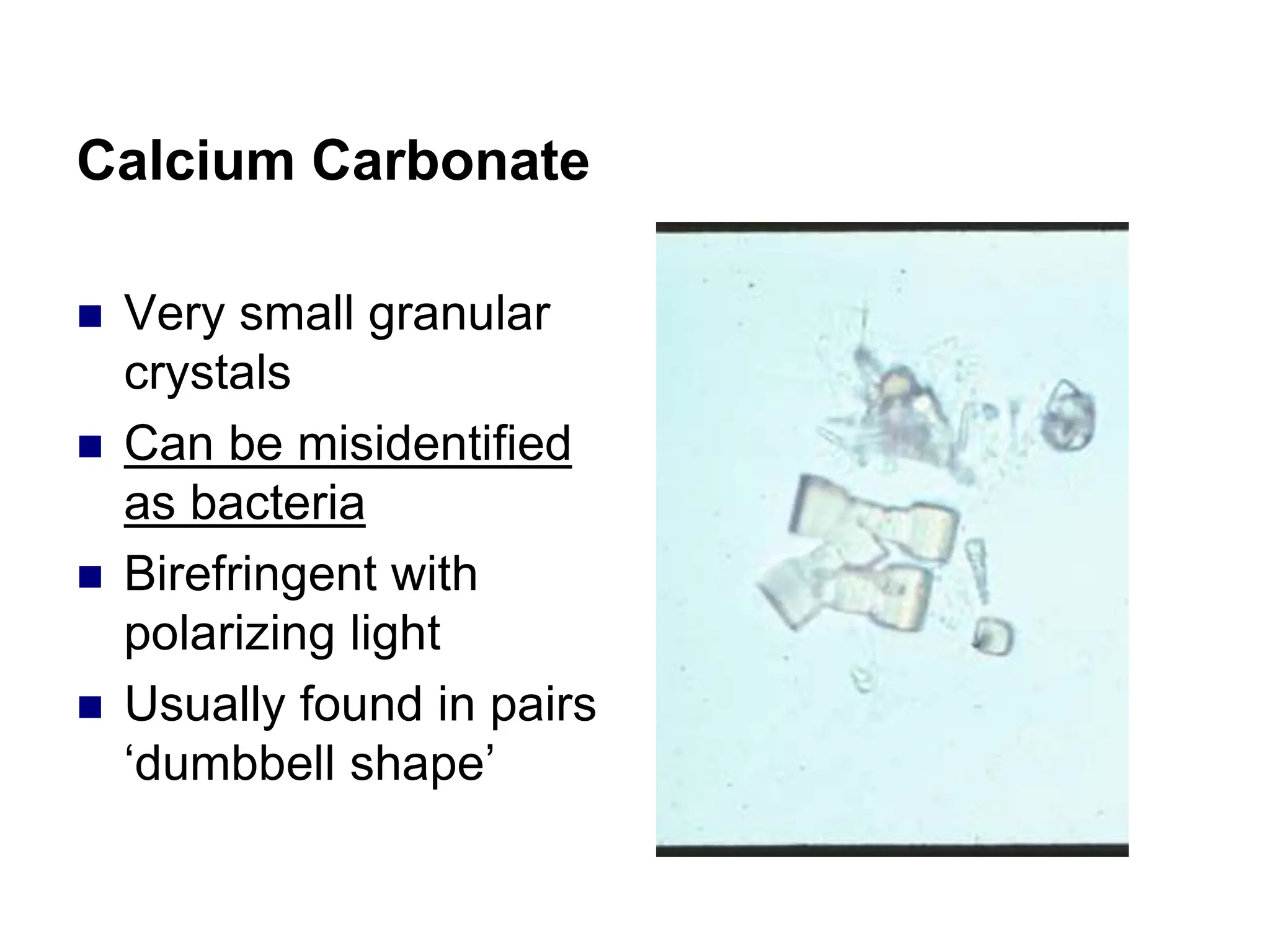
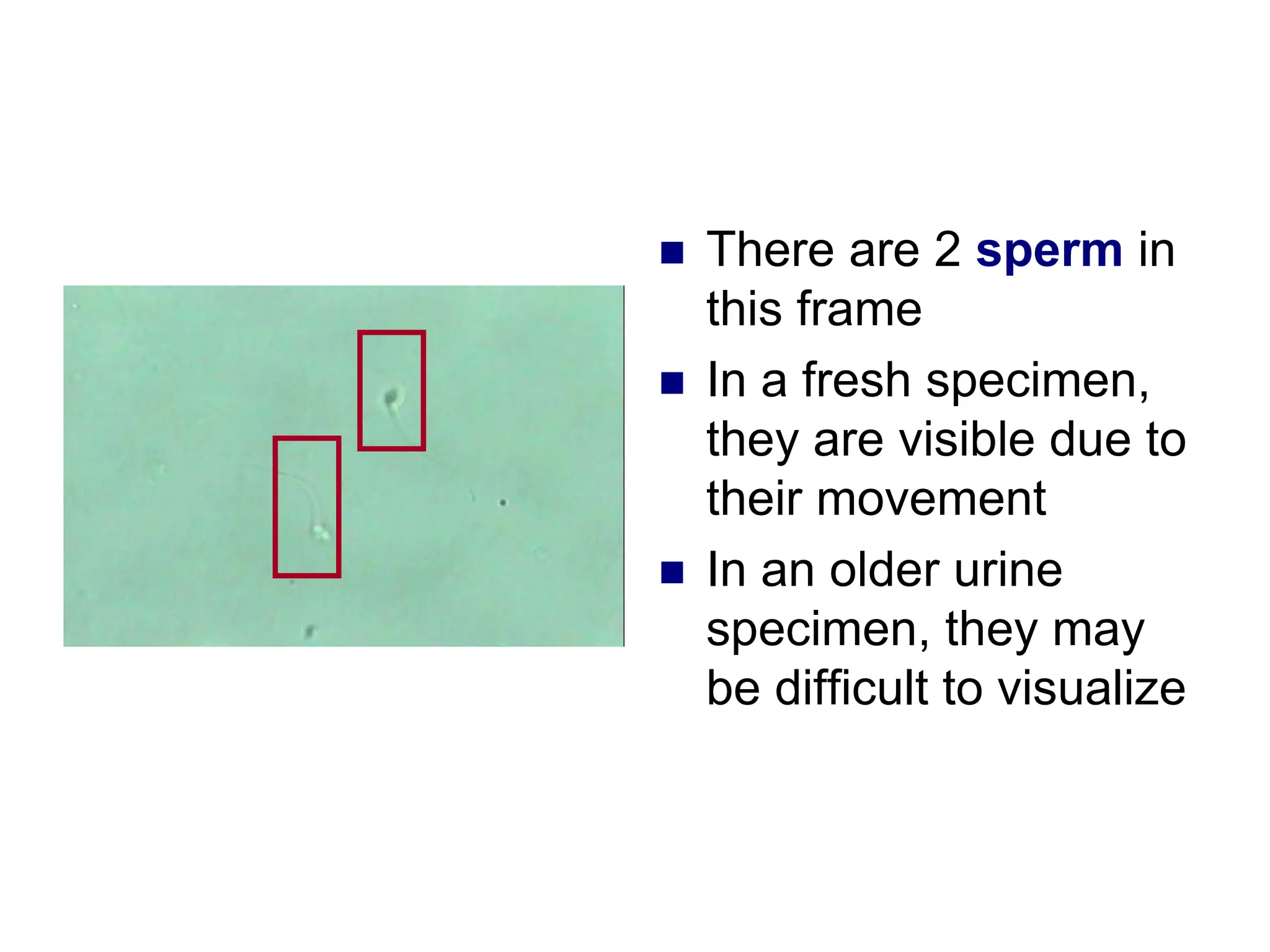
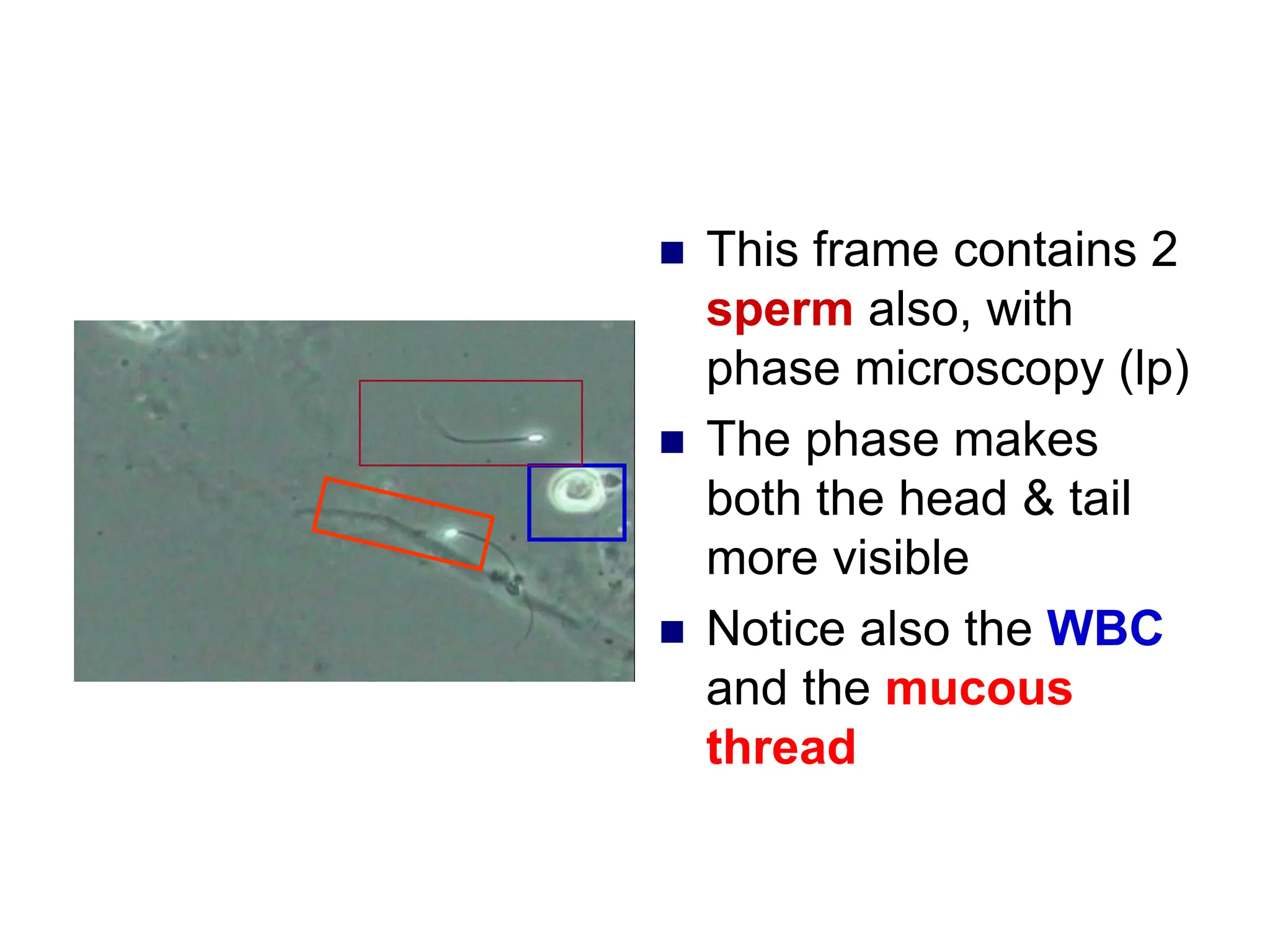
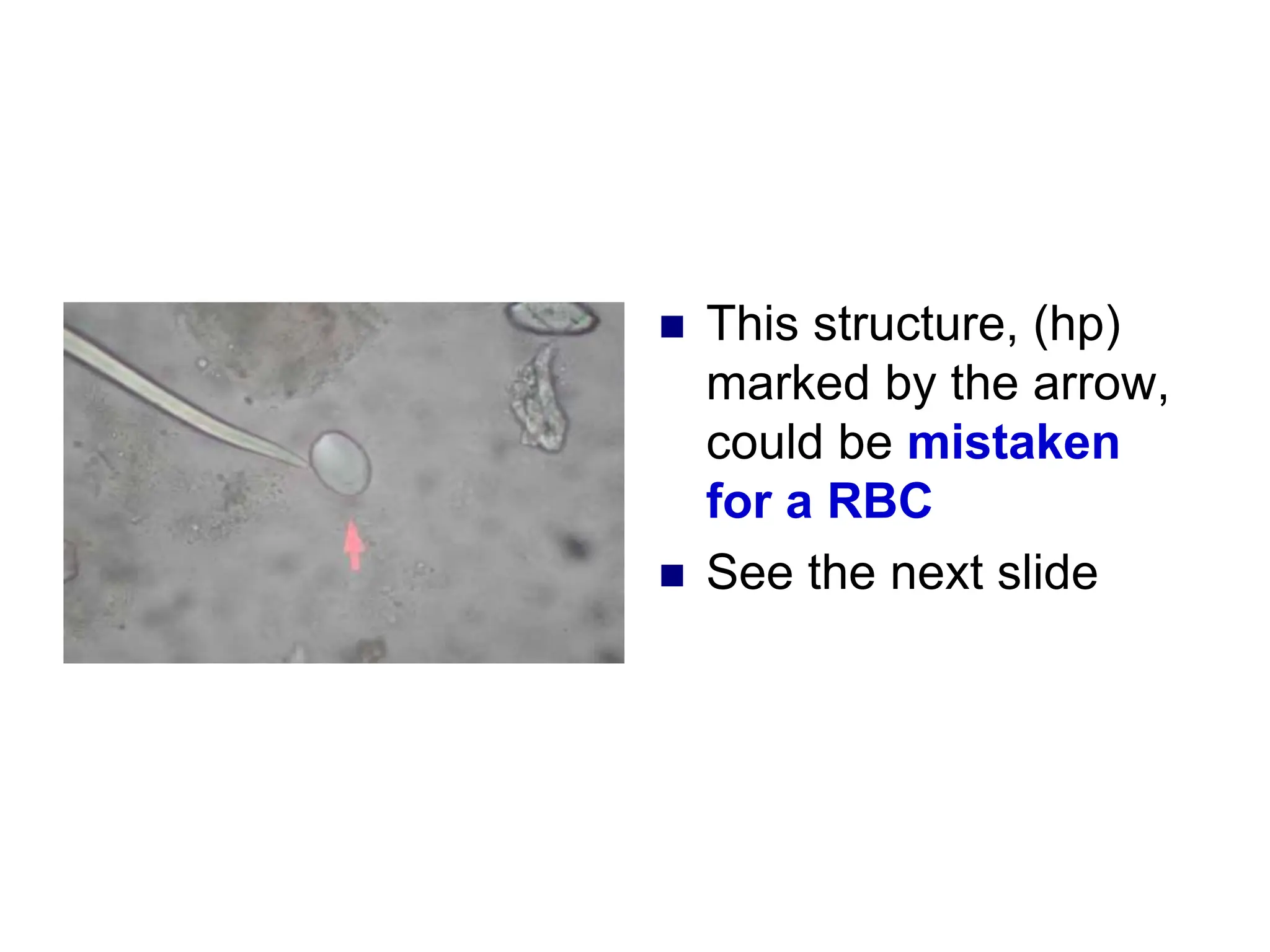
This chapter discusses microscopic examination of urine sediment. Key points include:
1) Microscopic examination provides valuable diagnostic information by identifying normal and abnormal urine sediments such as red blood cells, white blood cells, epithelial cells, casts, crystals, and bacteria.
2) The procedure for microscopic examination involves mixing and centrifuging a urine sample, examining the resuspended sediment under low and high power objectives, and reporting the results both quantitatively and qualitatively.
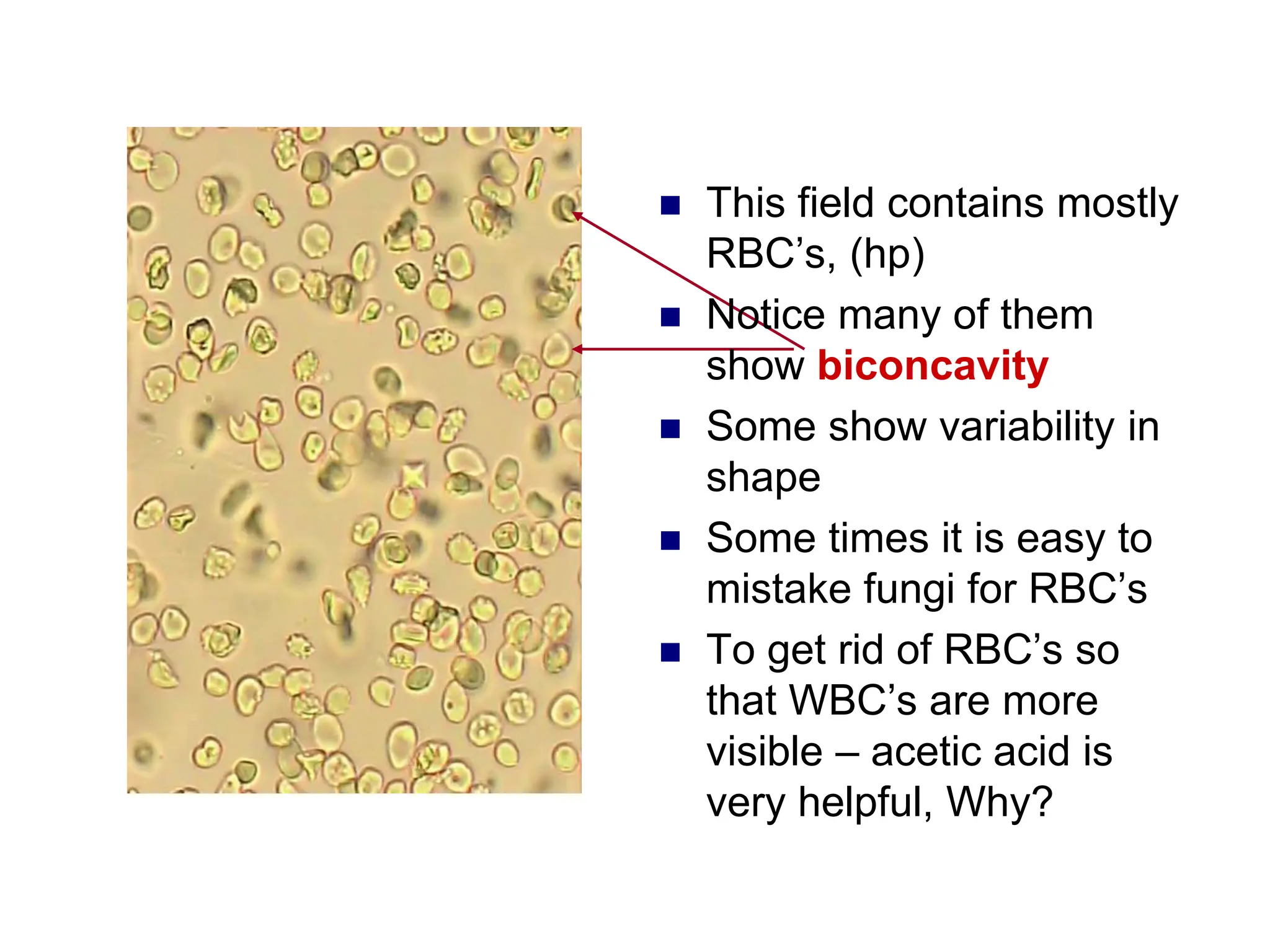
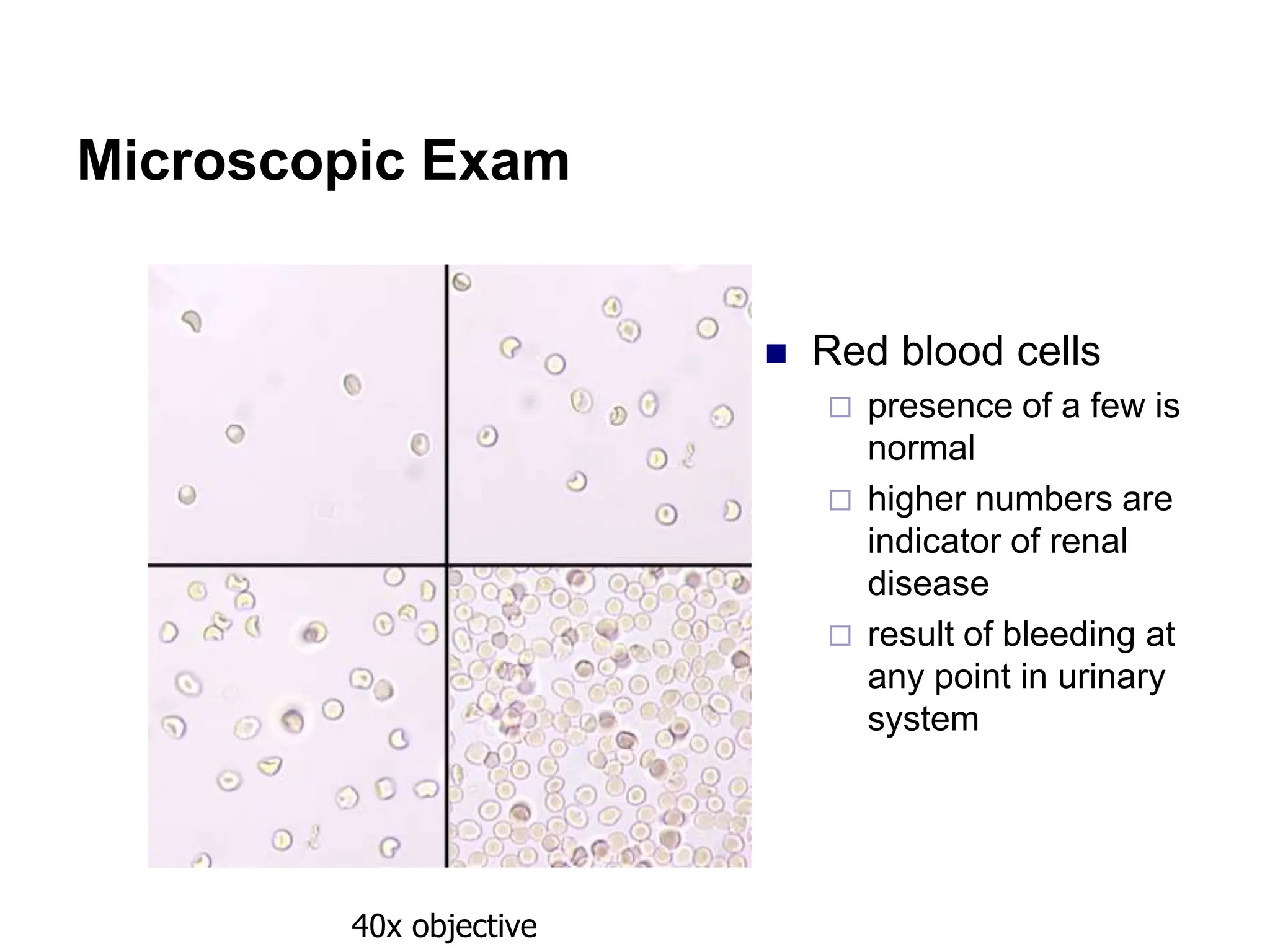
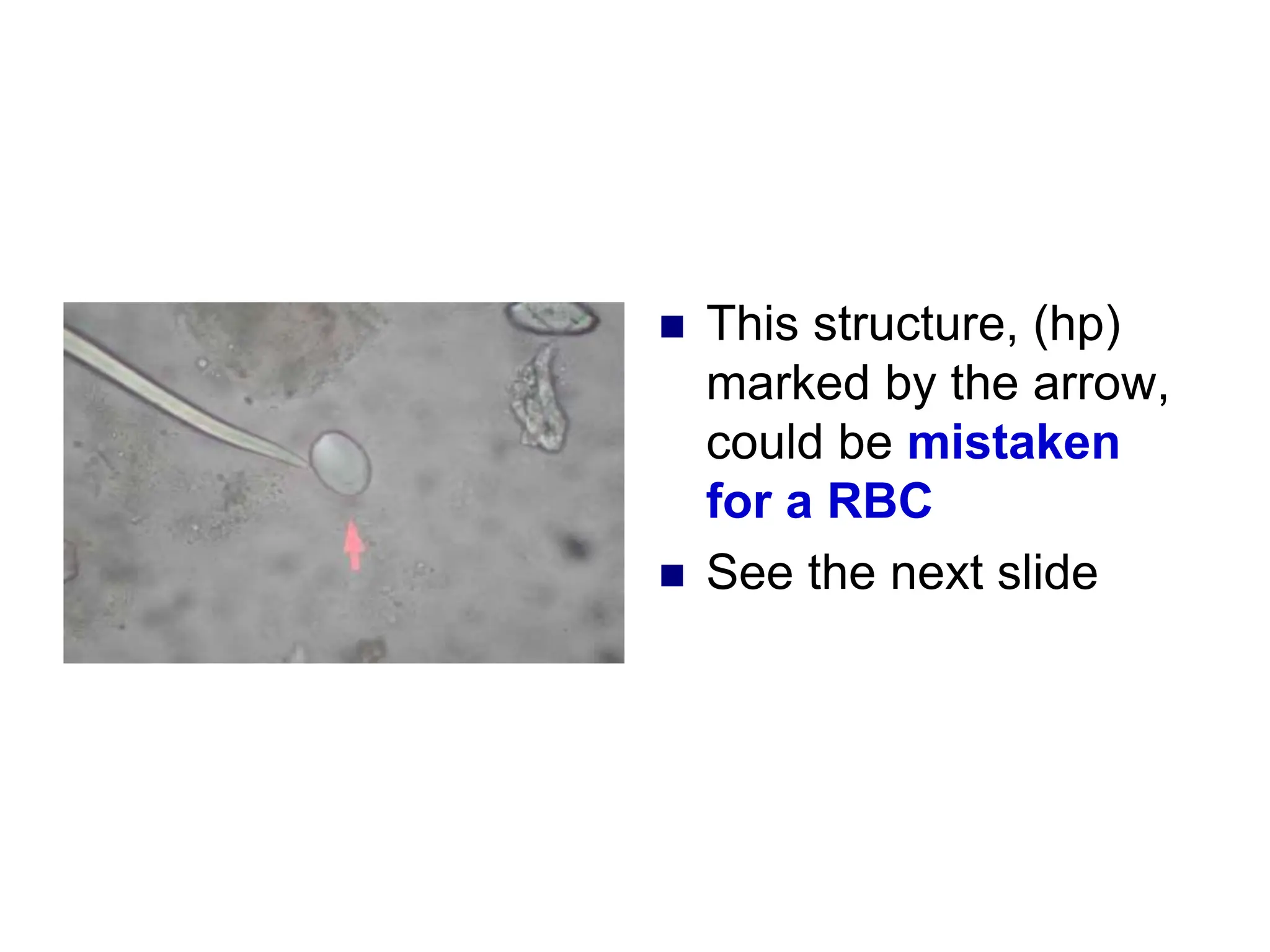
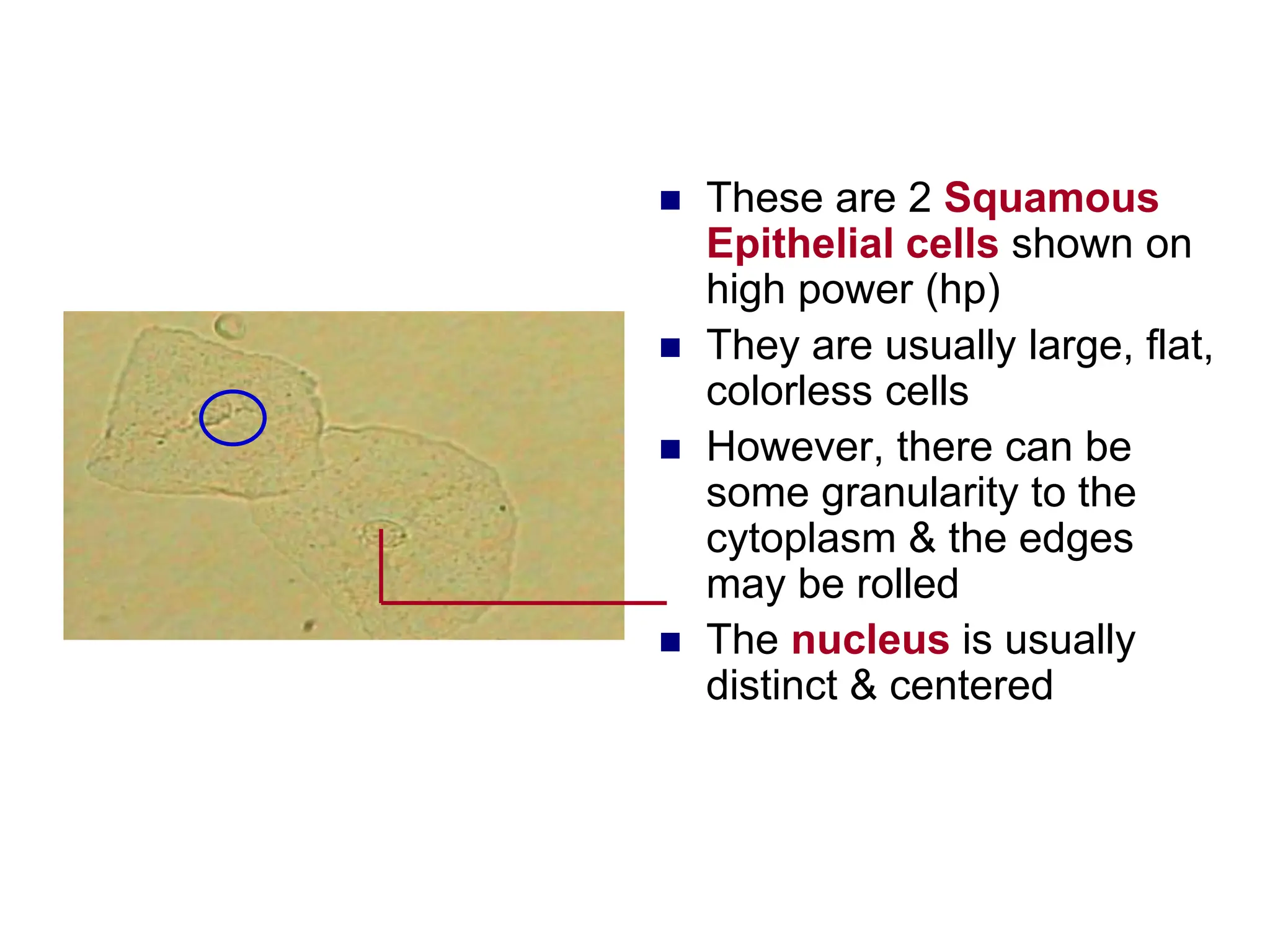
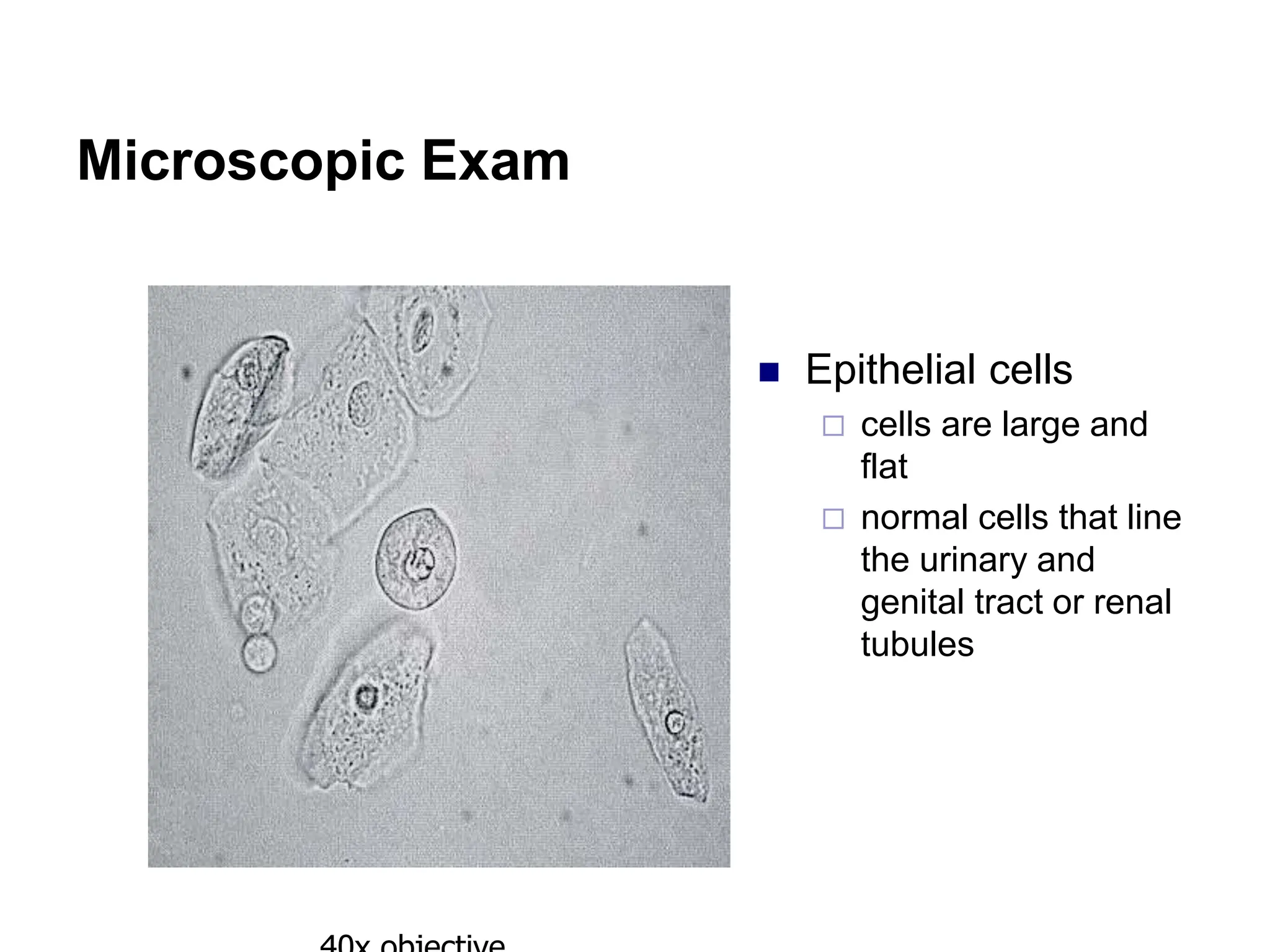
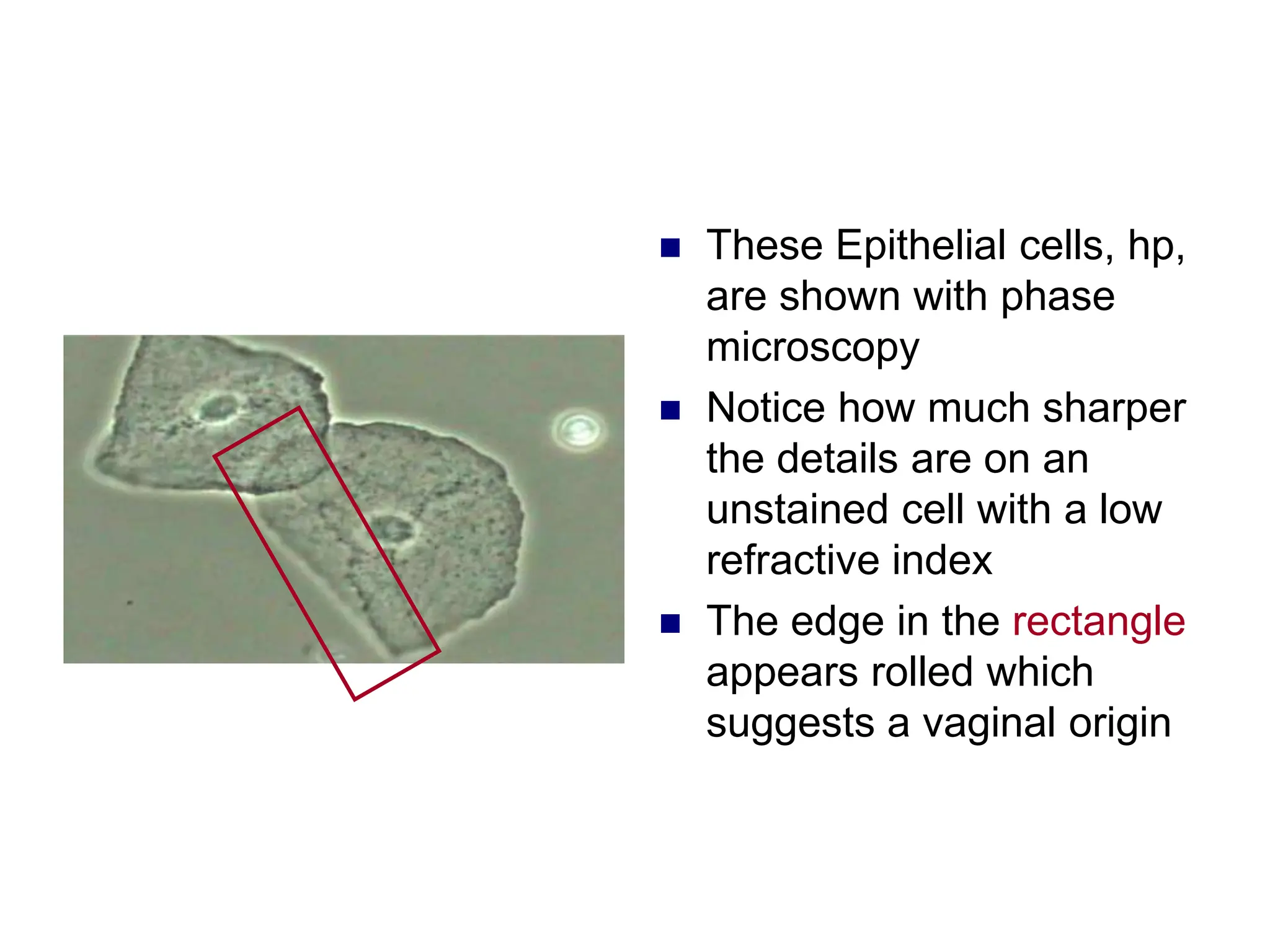
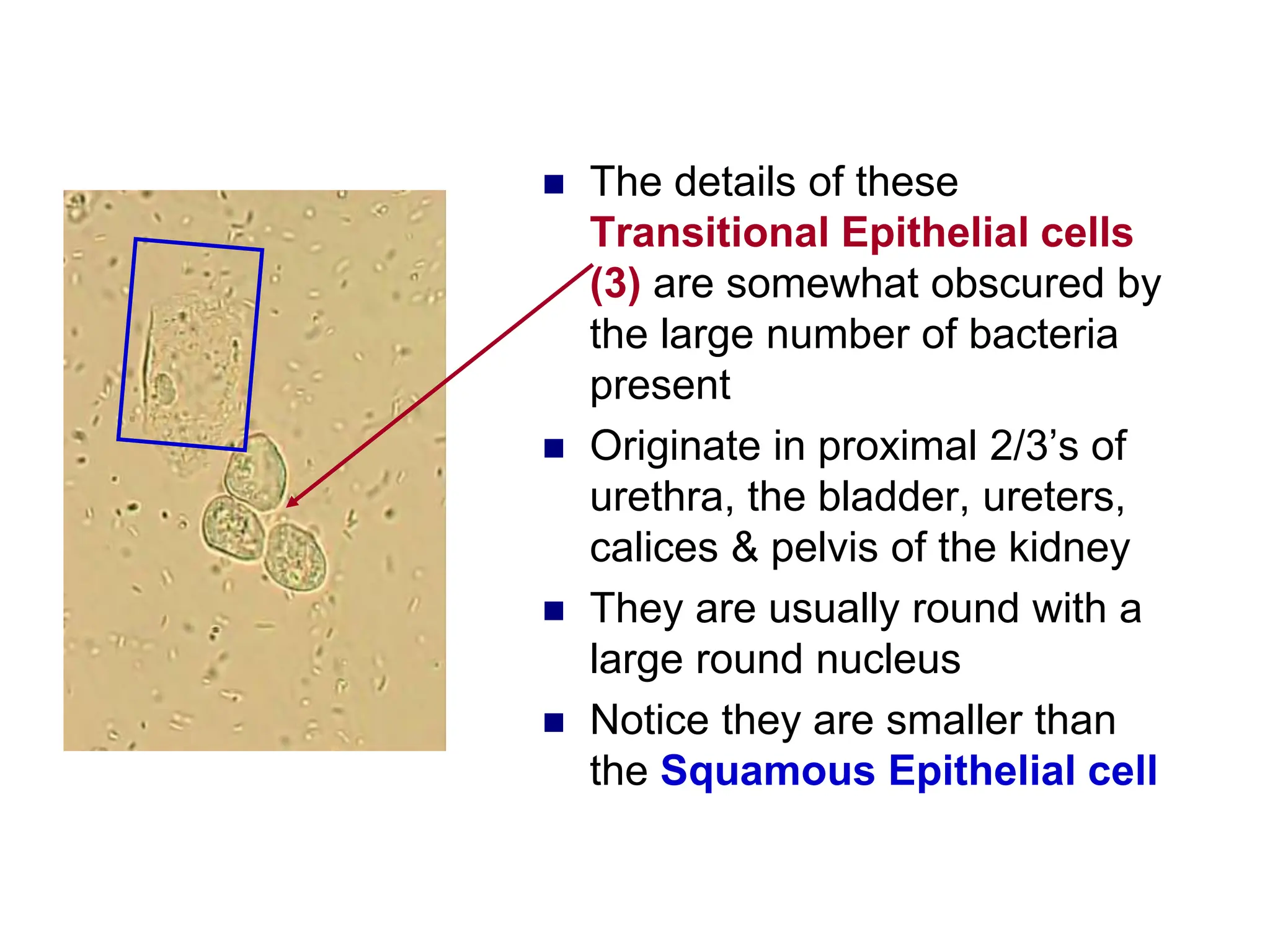
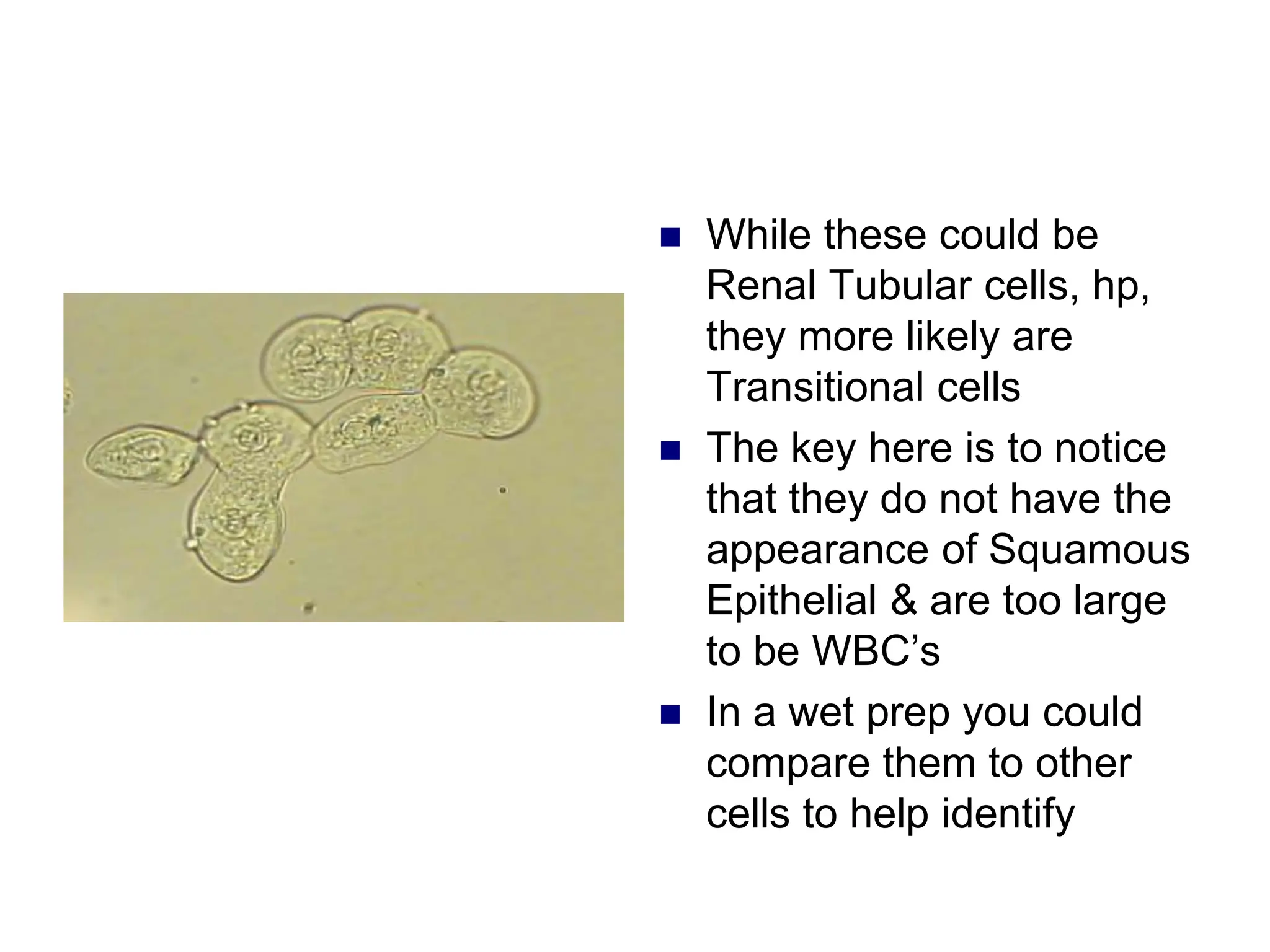
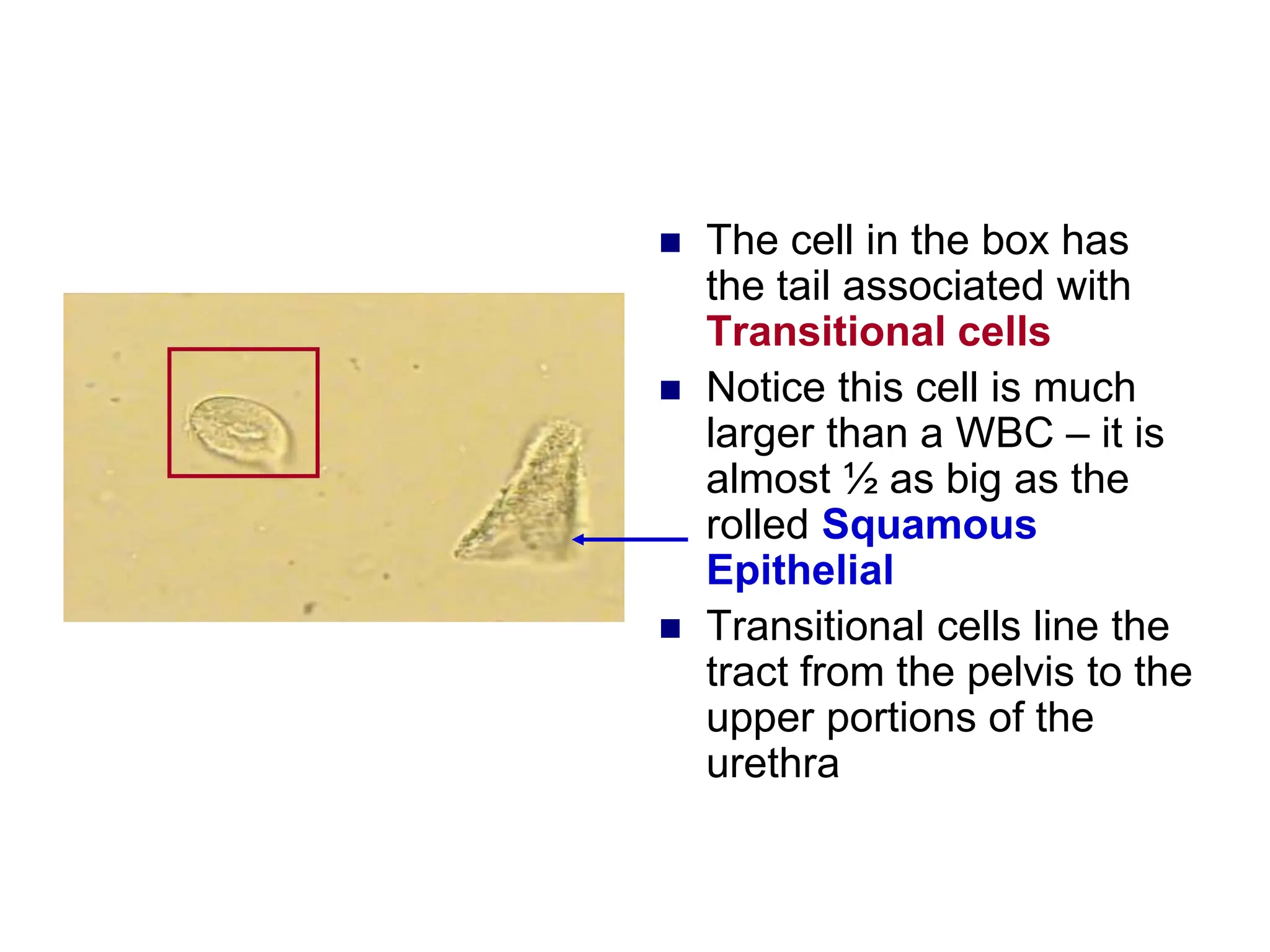
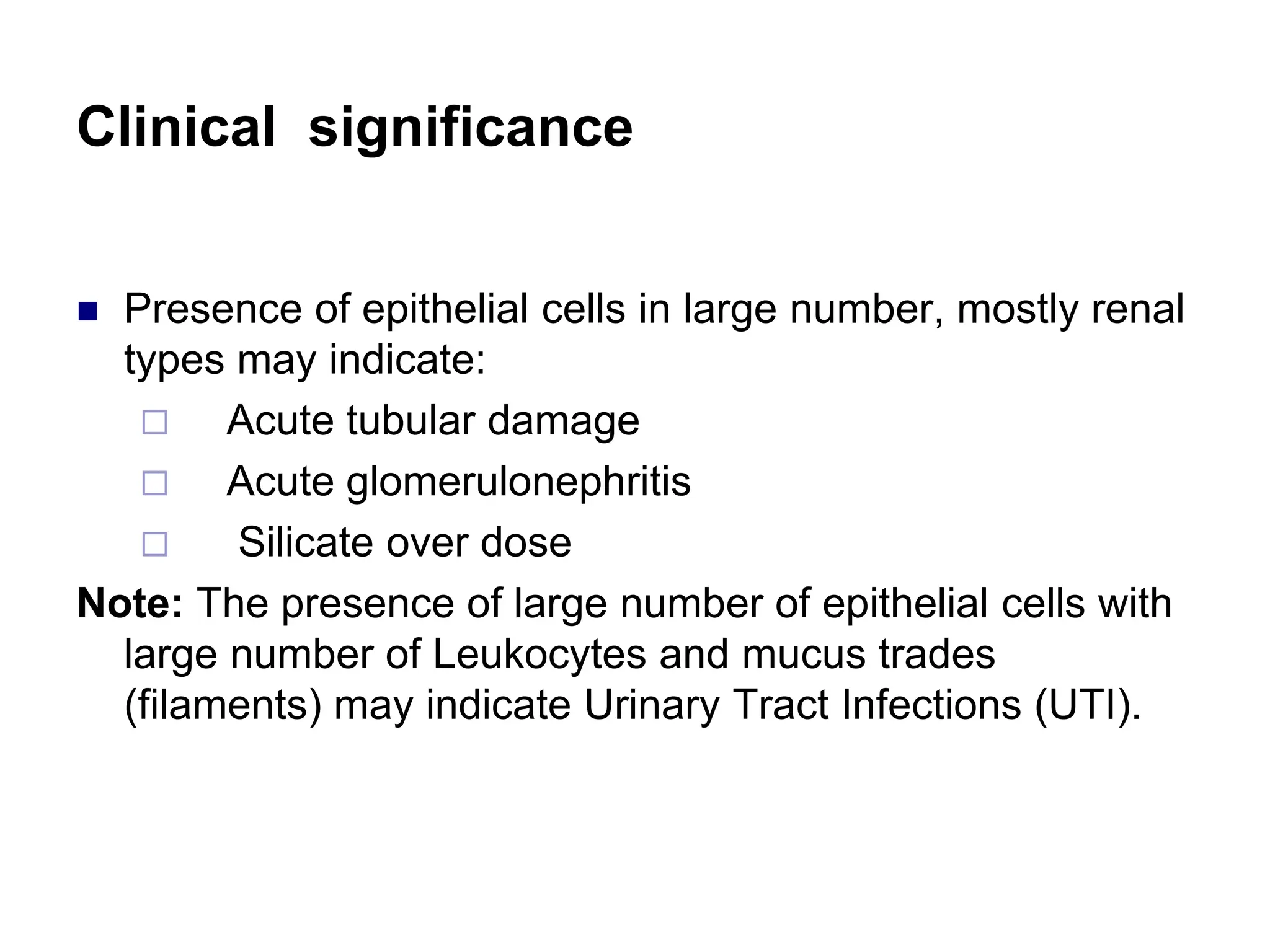
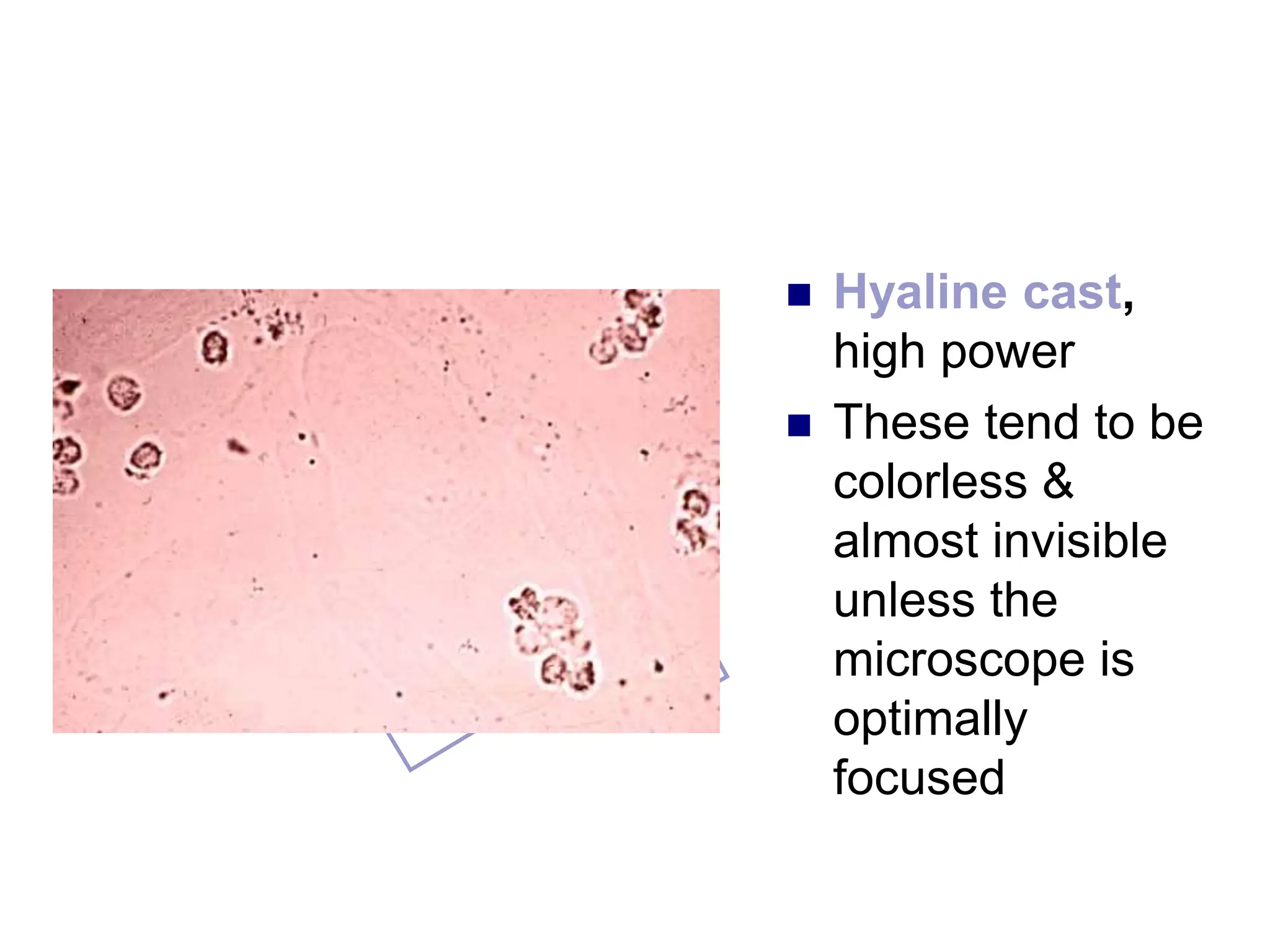
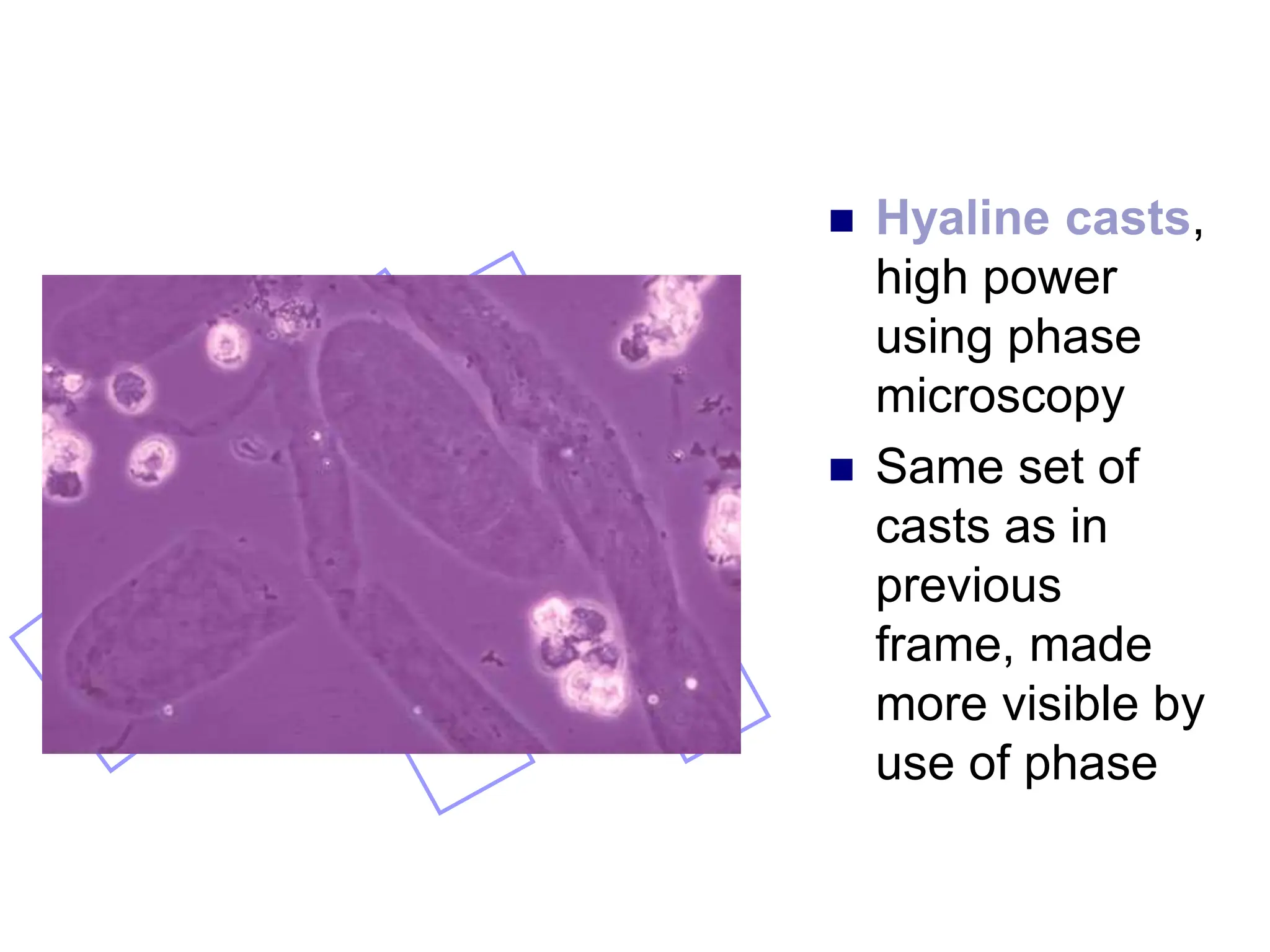
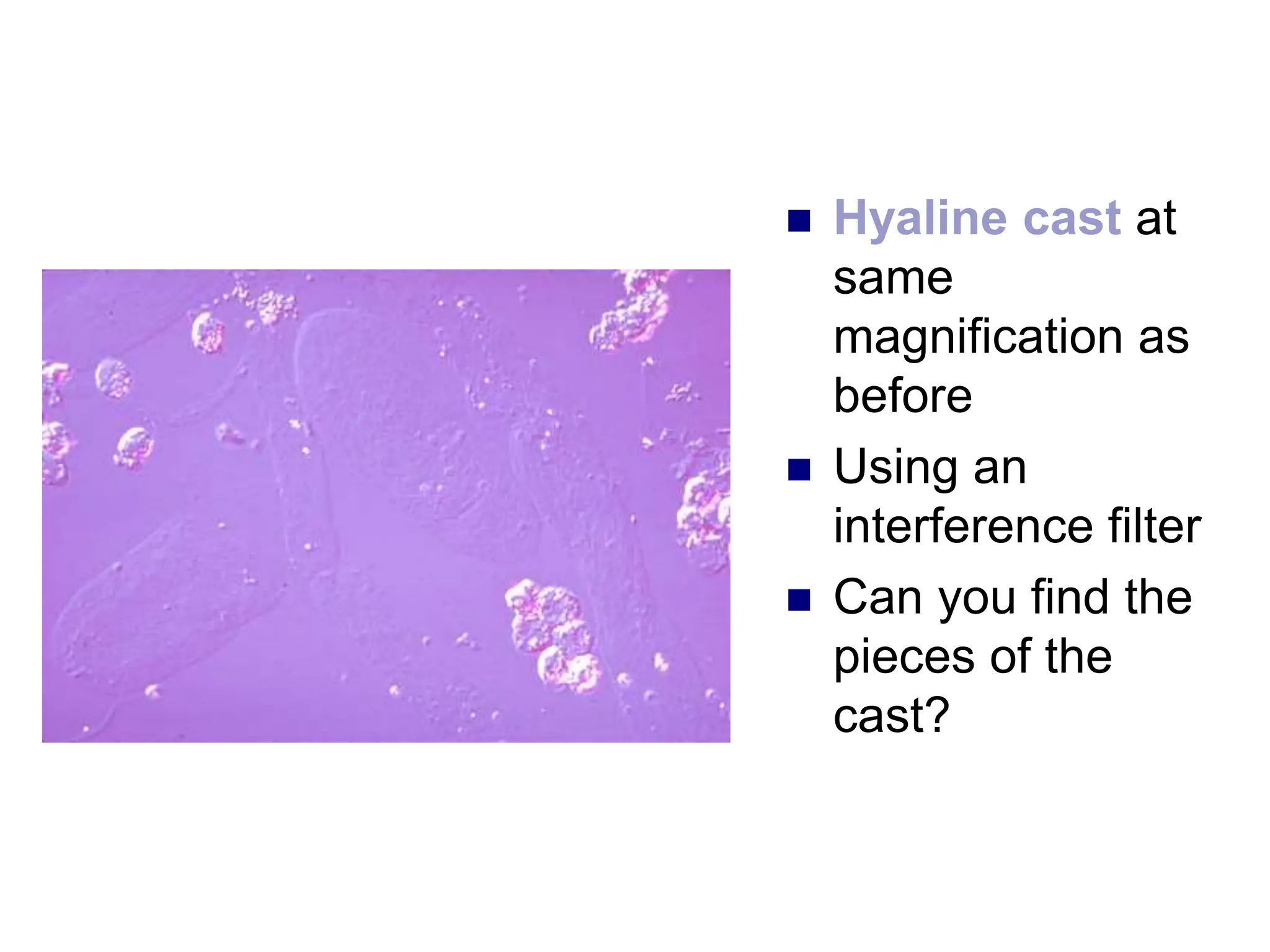
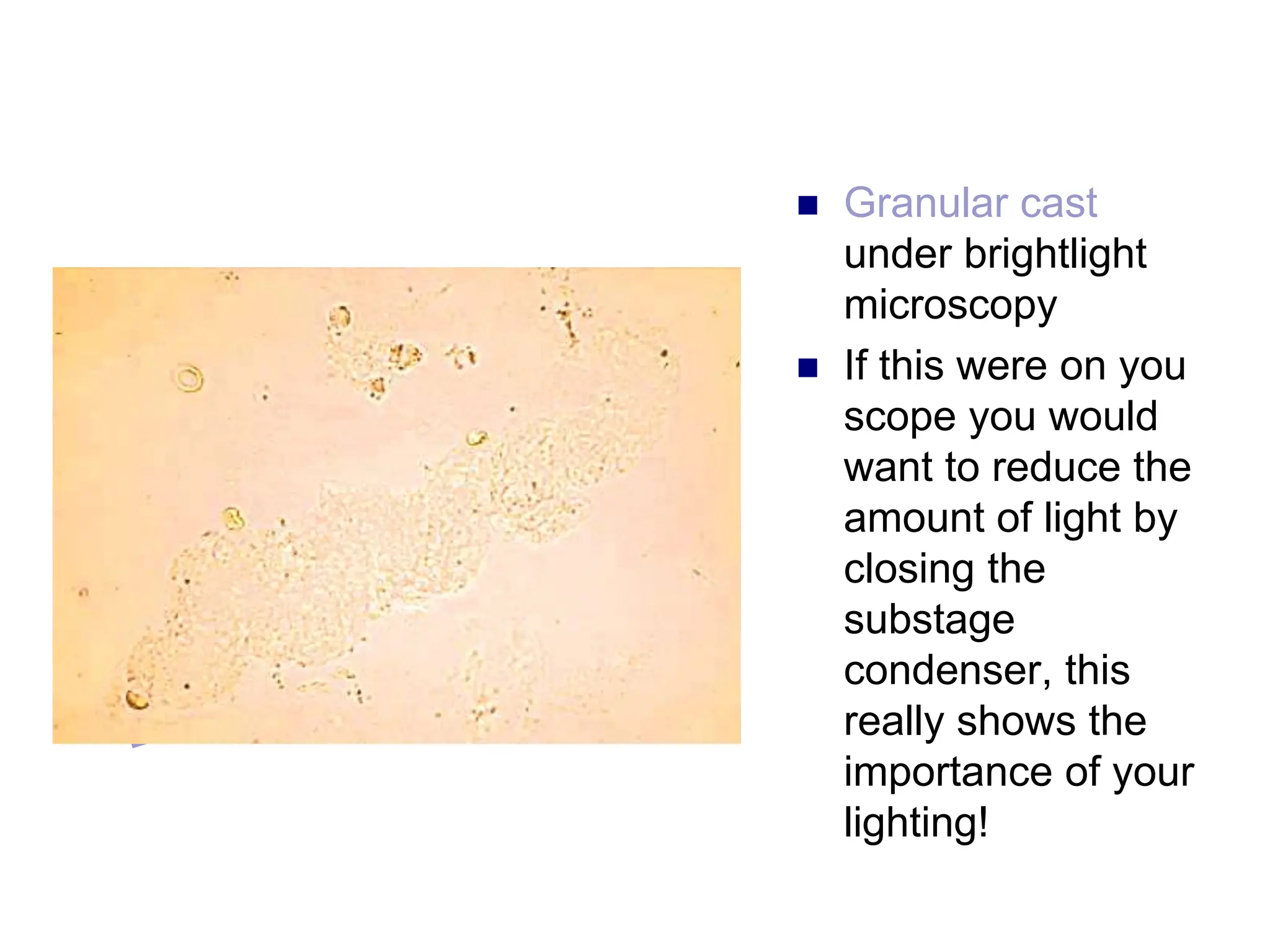
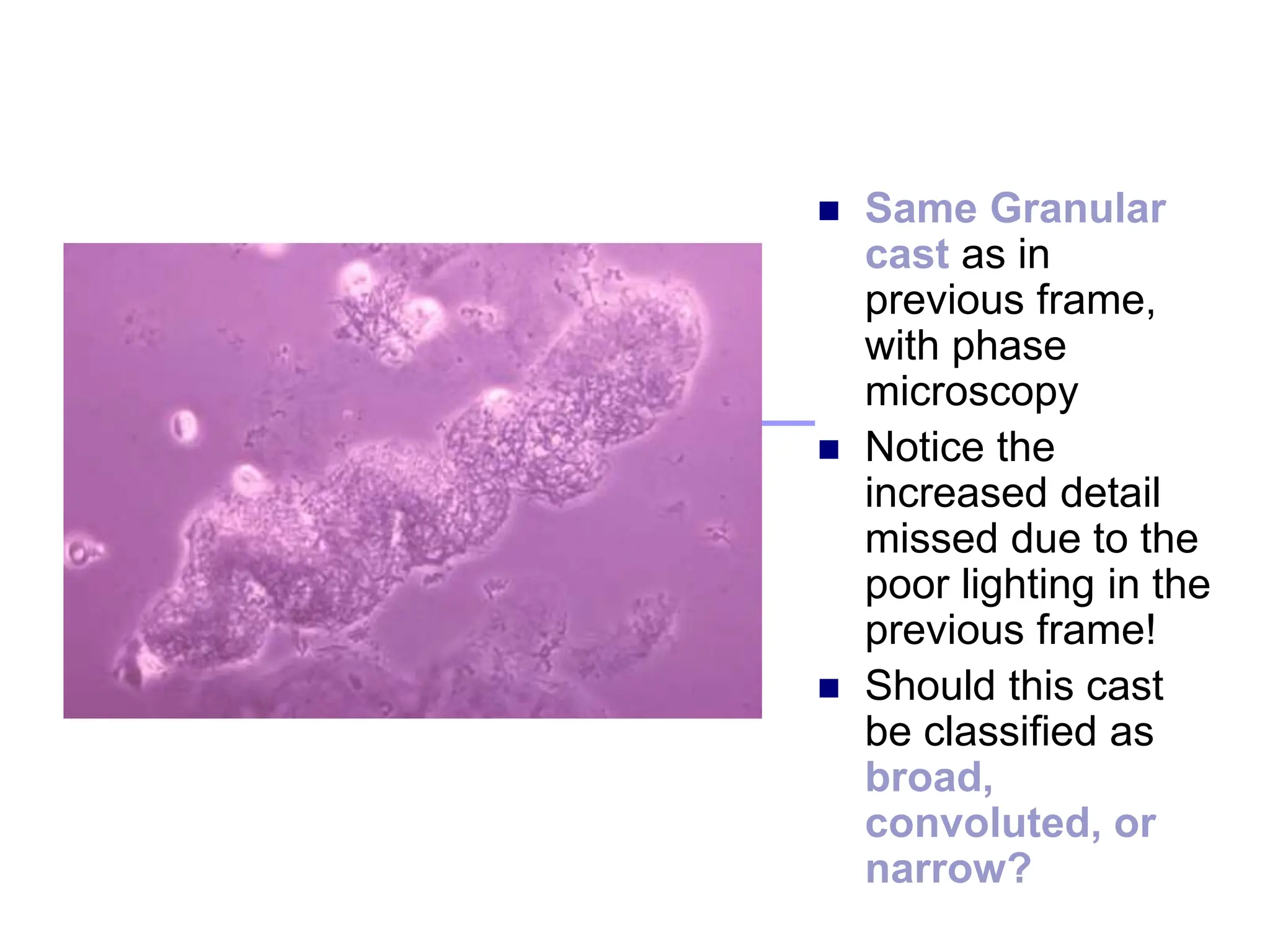
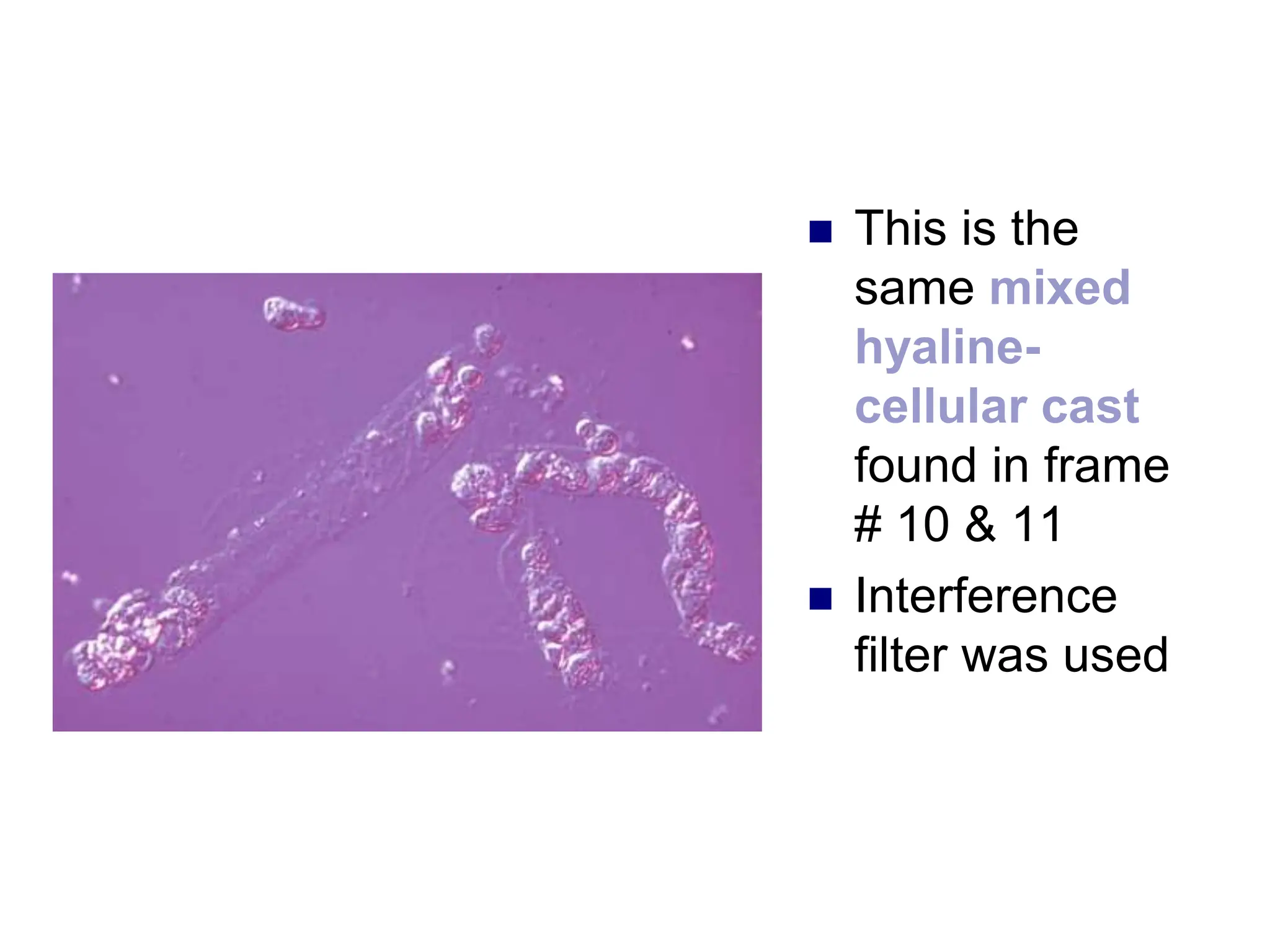
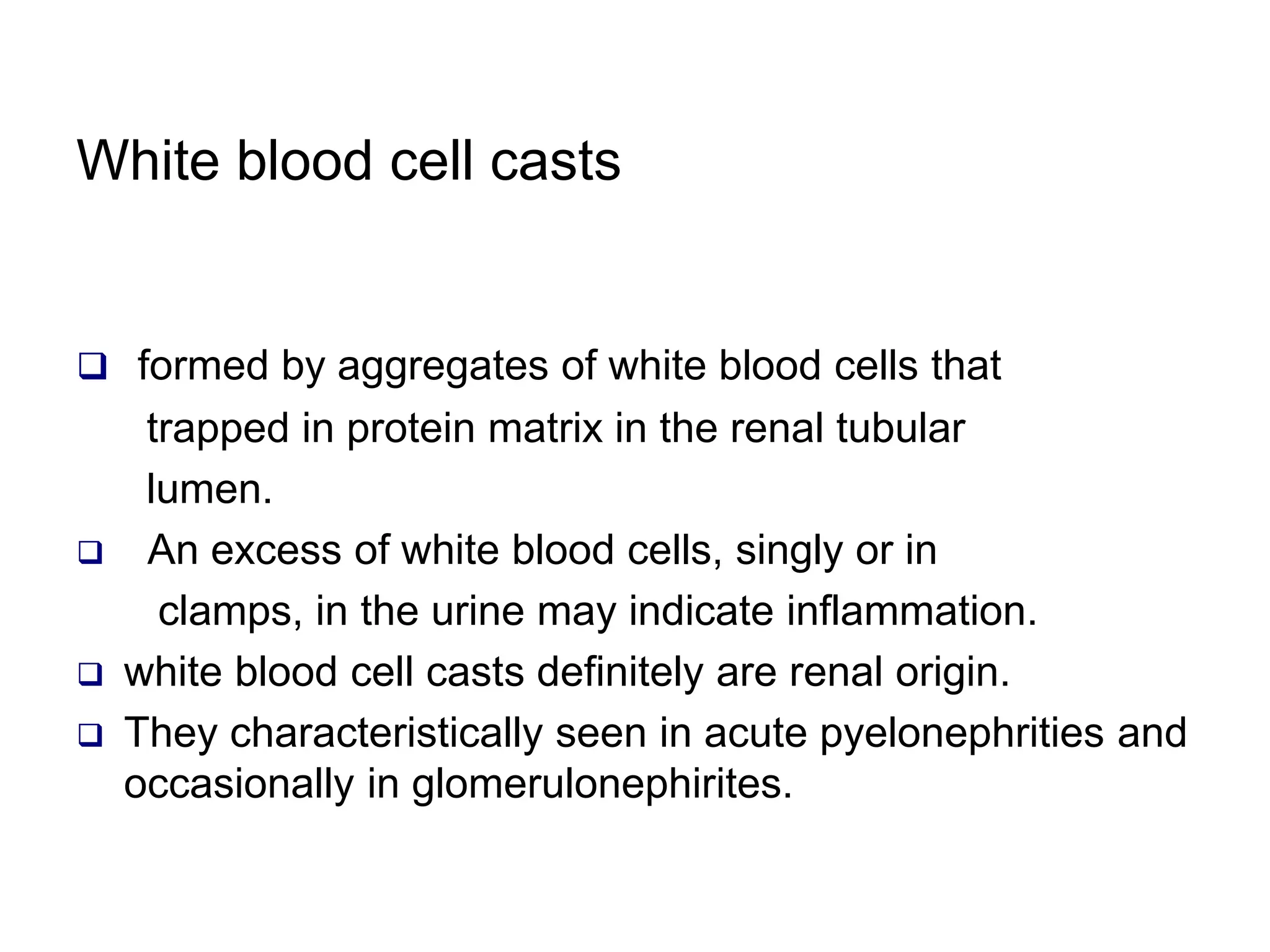
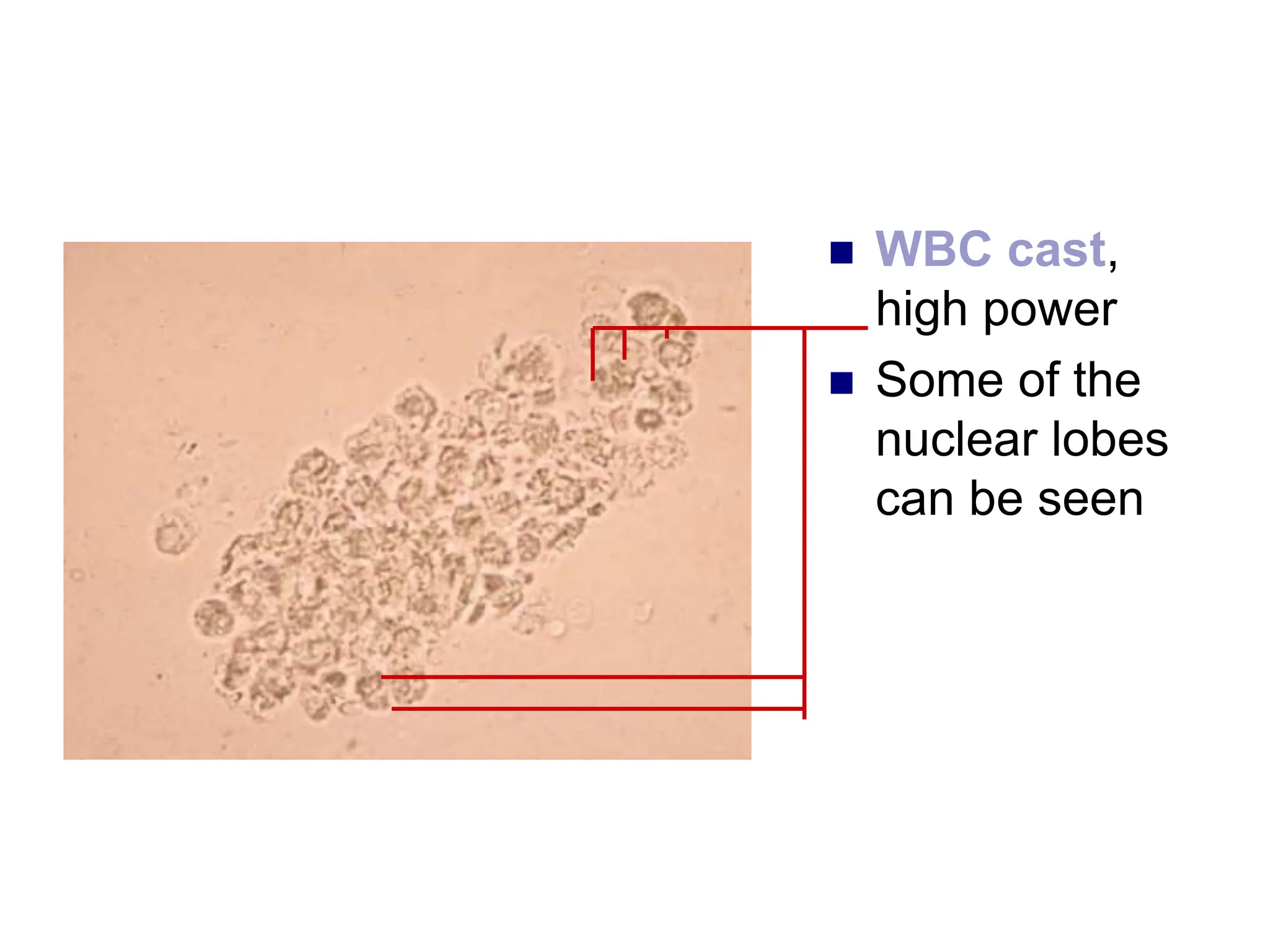
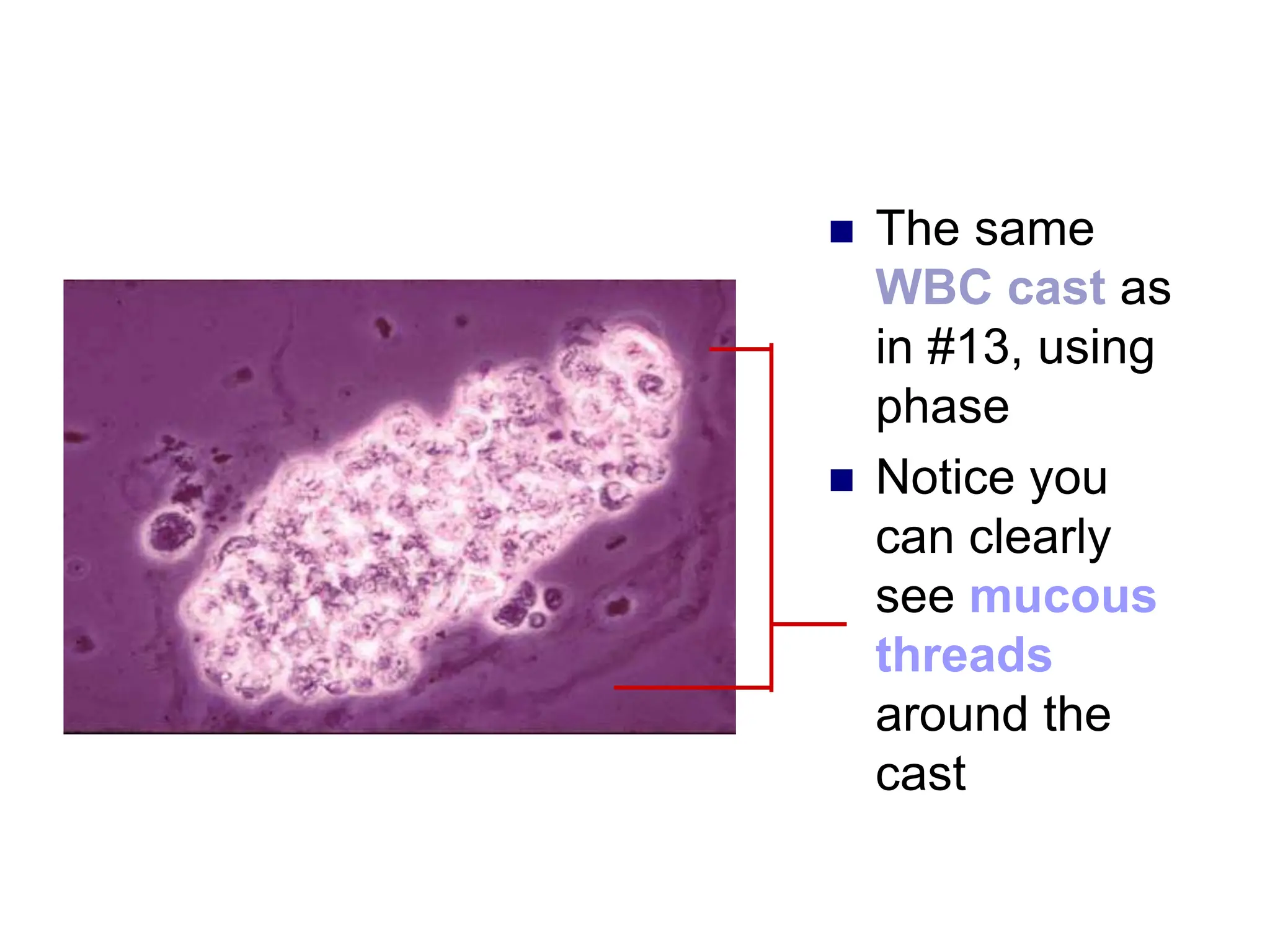
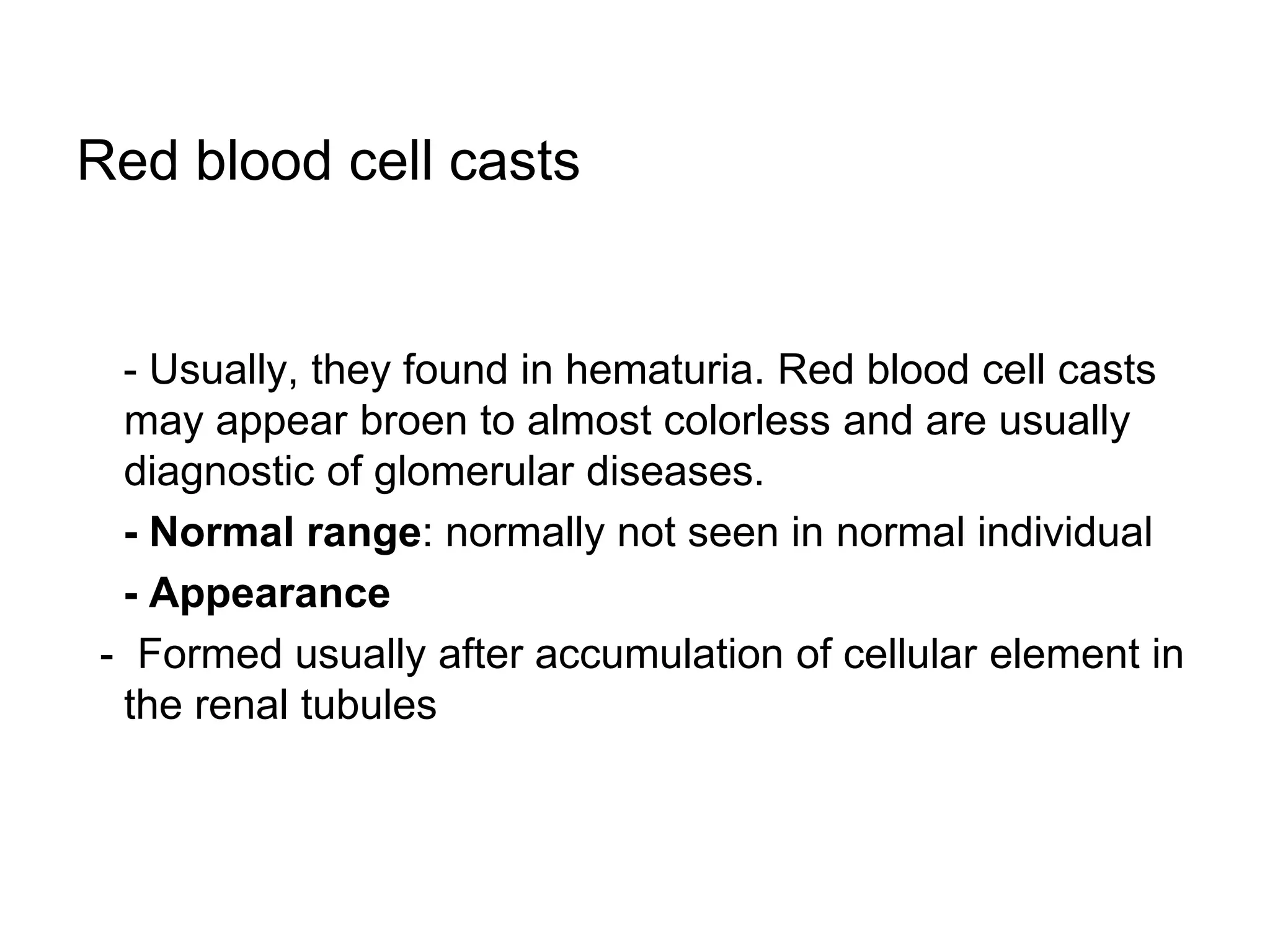
3) Common organized sediments include red and white blood cells, epithelial cells from the kidney, bladder, and urethra, and hyaline casts which indicate renal proteinuria. Abnormal quantities or types of sediments provide clues to urinary tract diseases.
















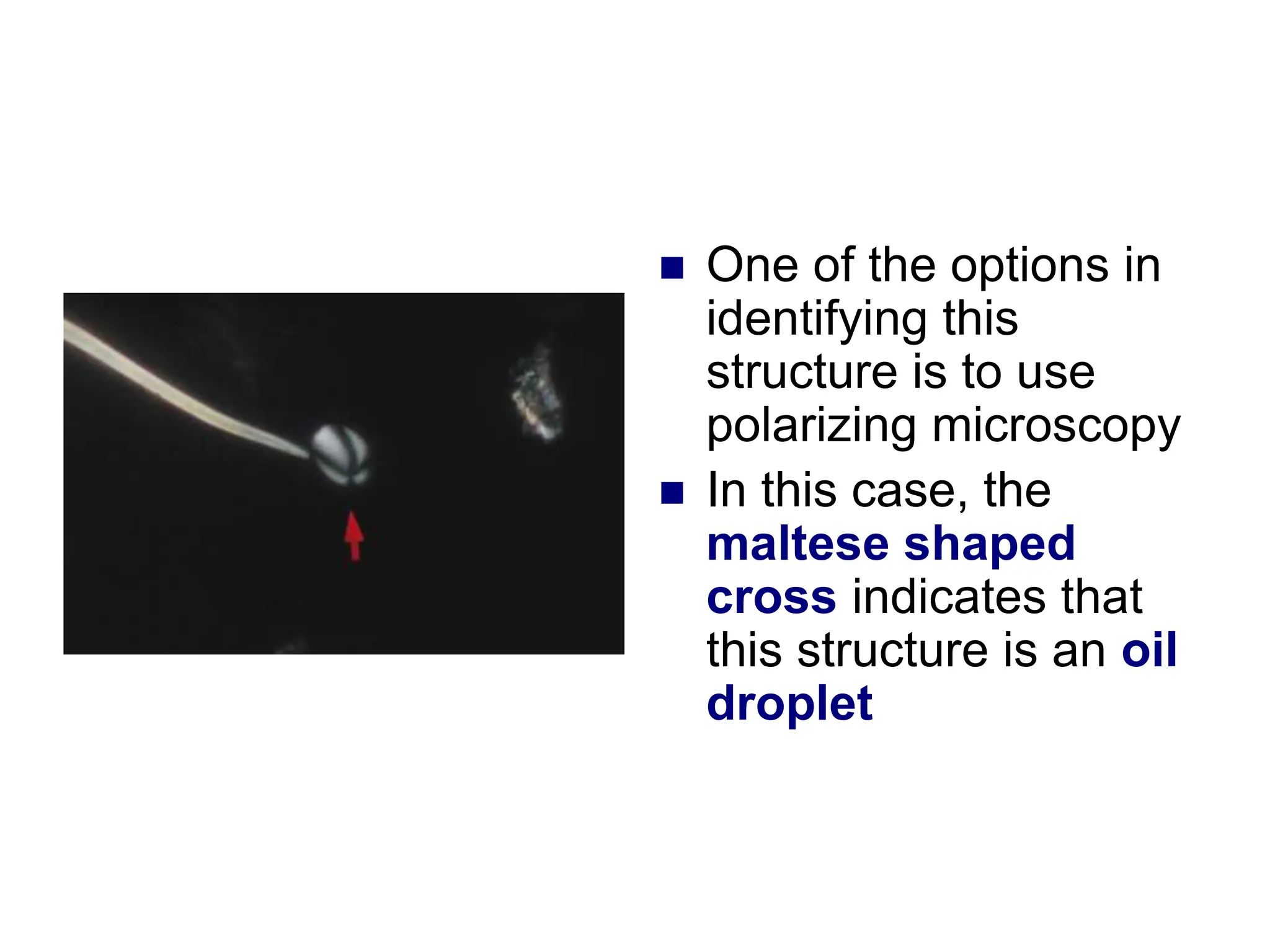















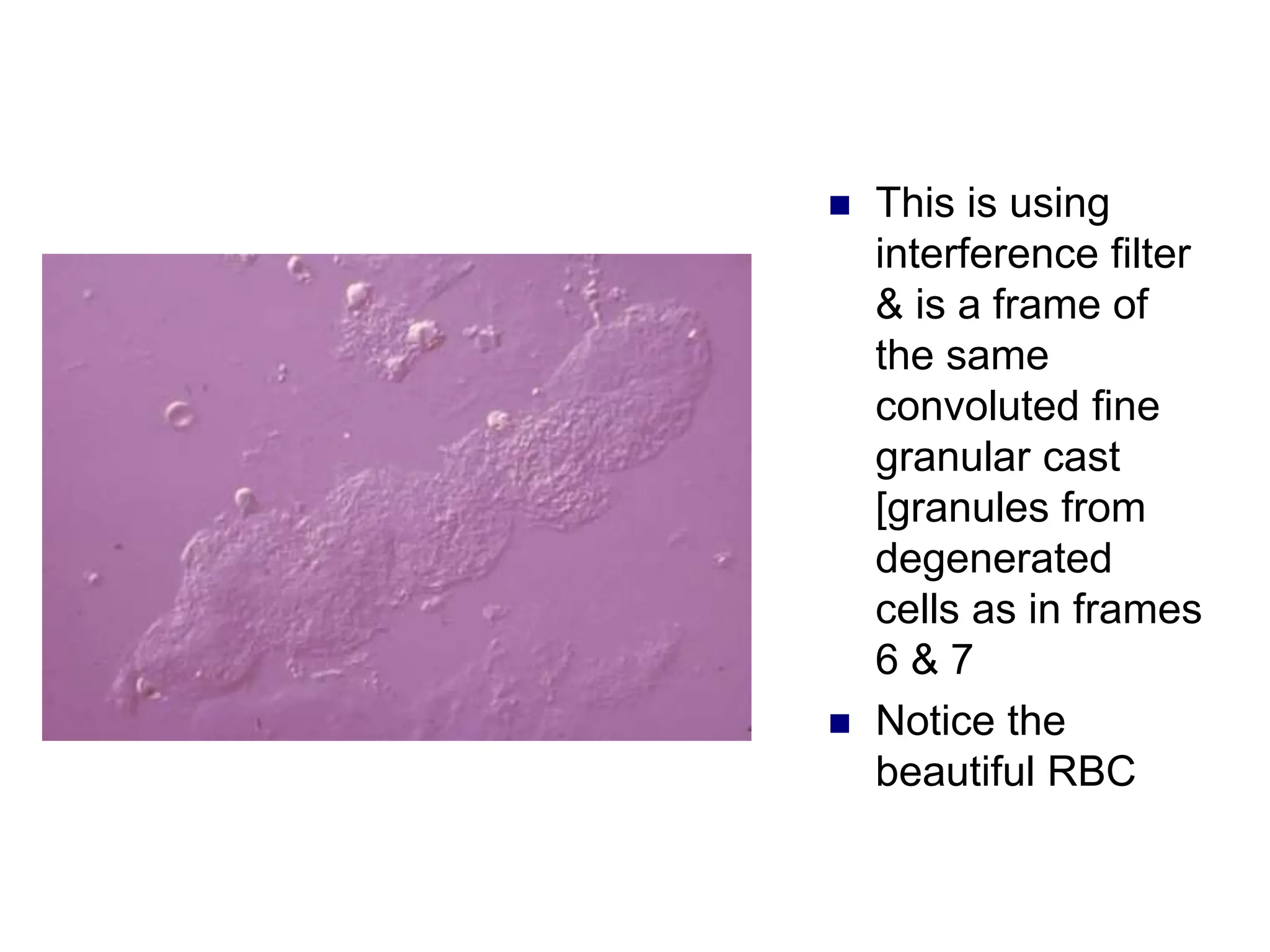
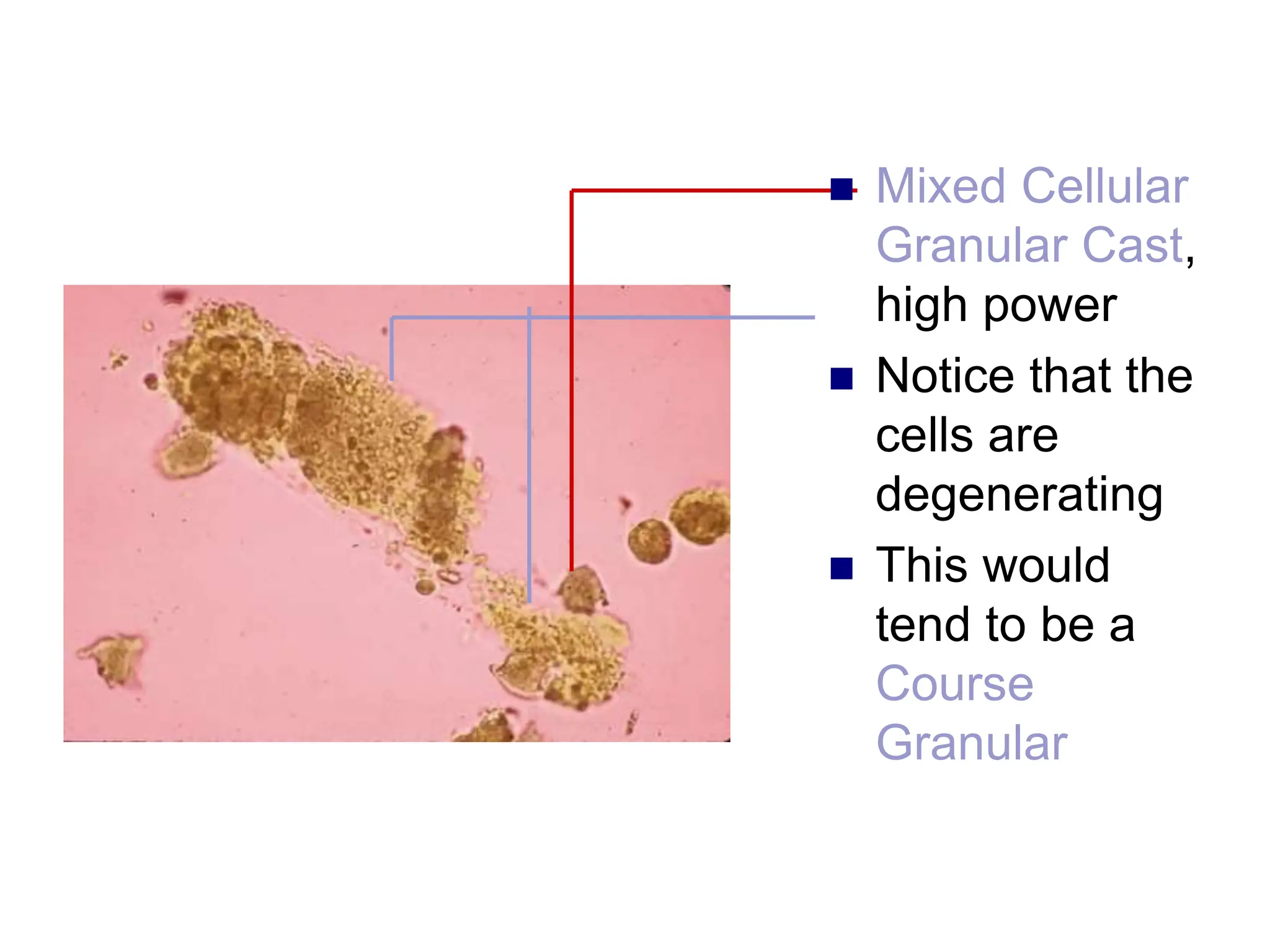
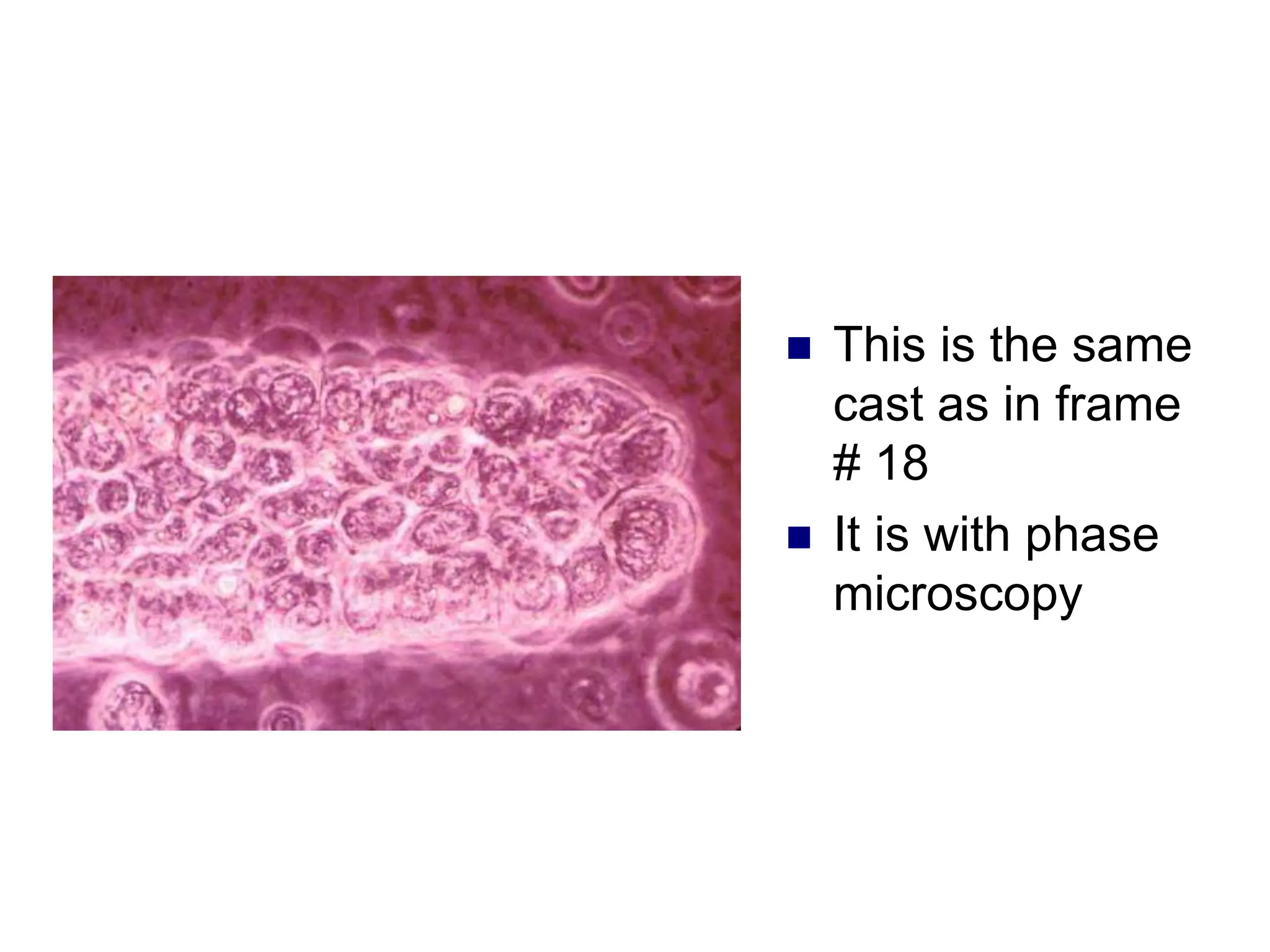
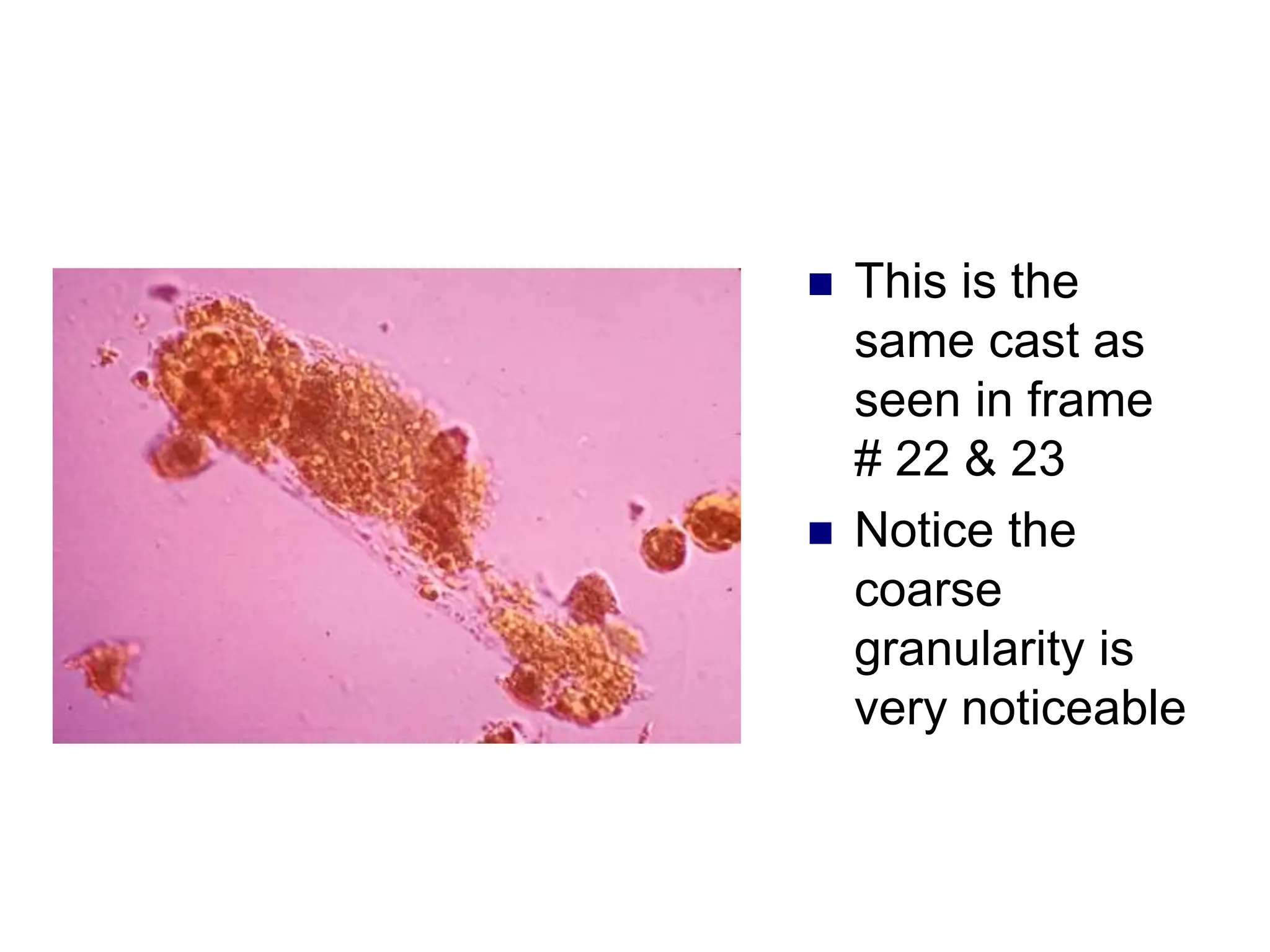



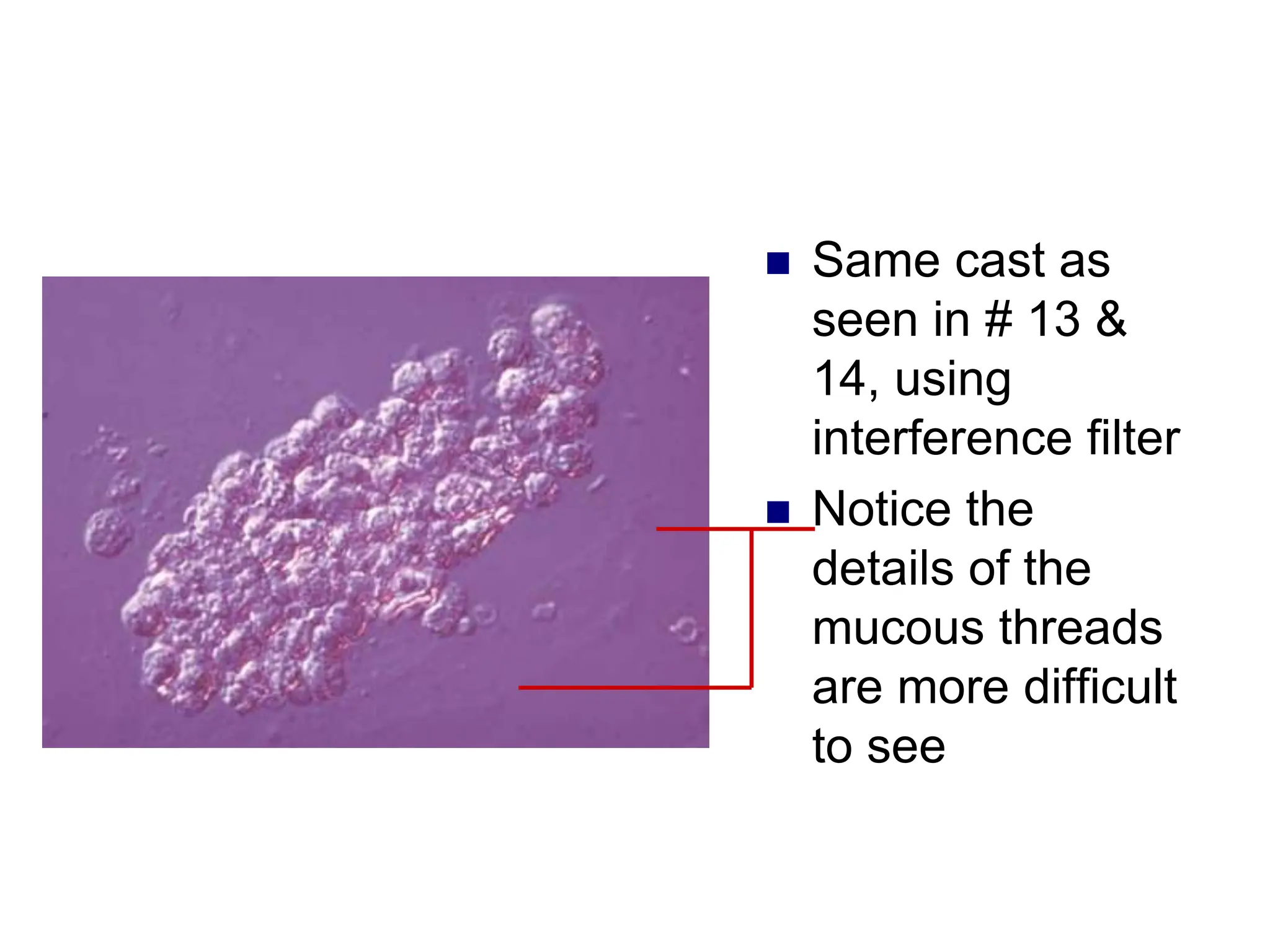
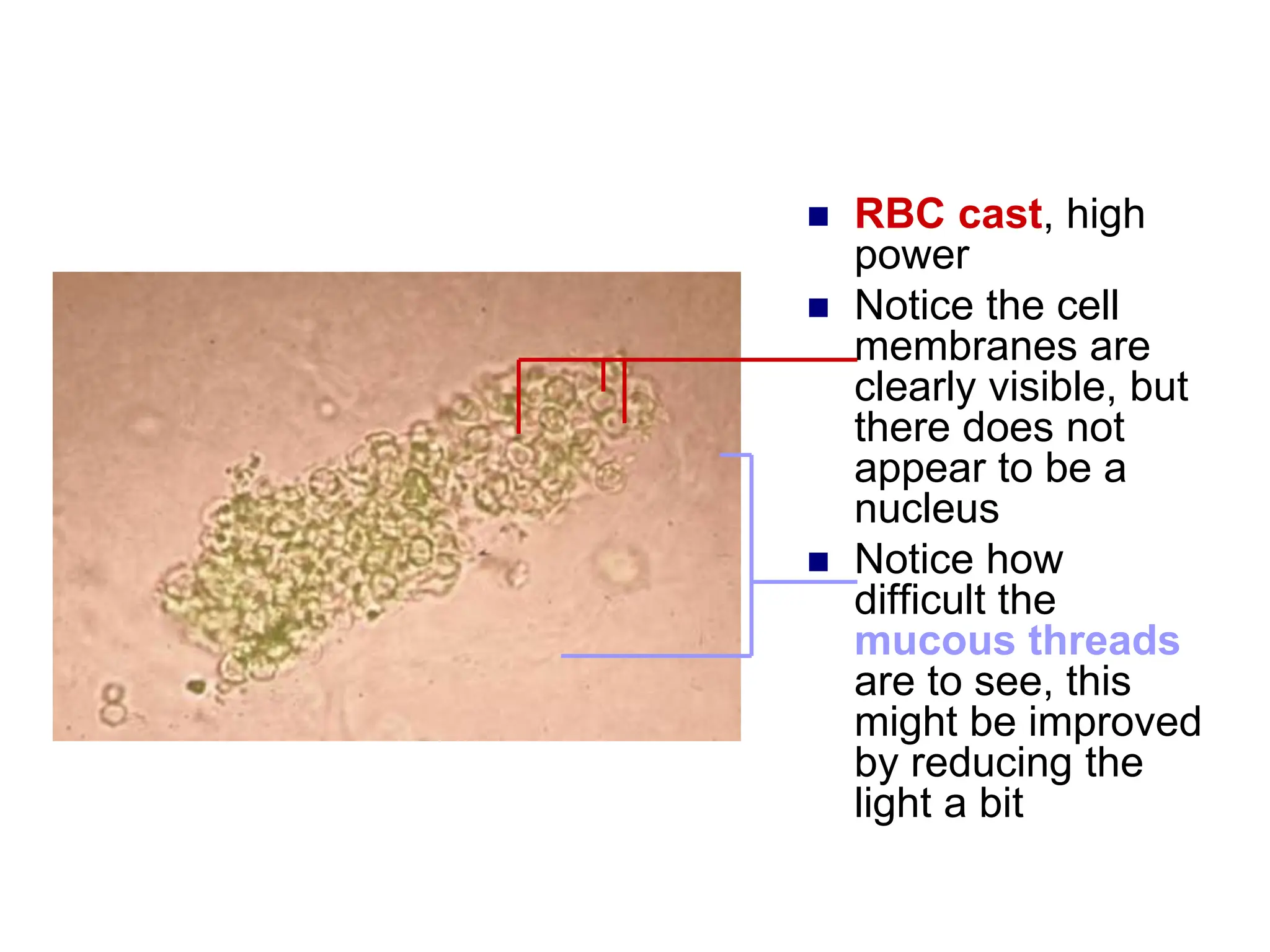
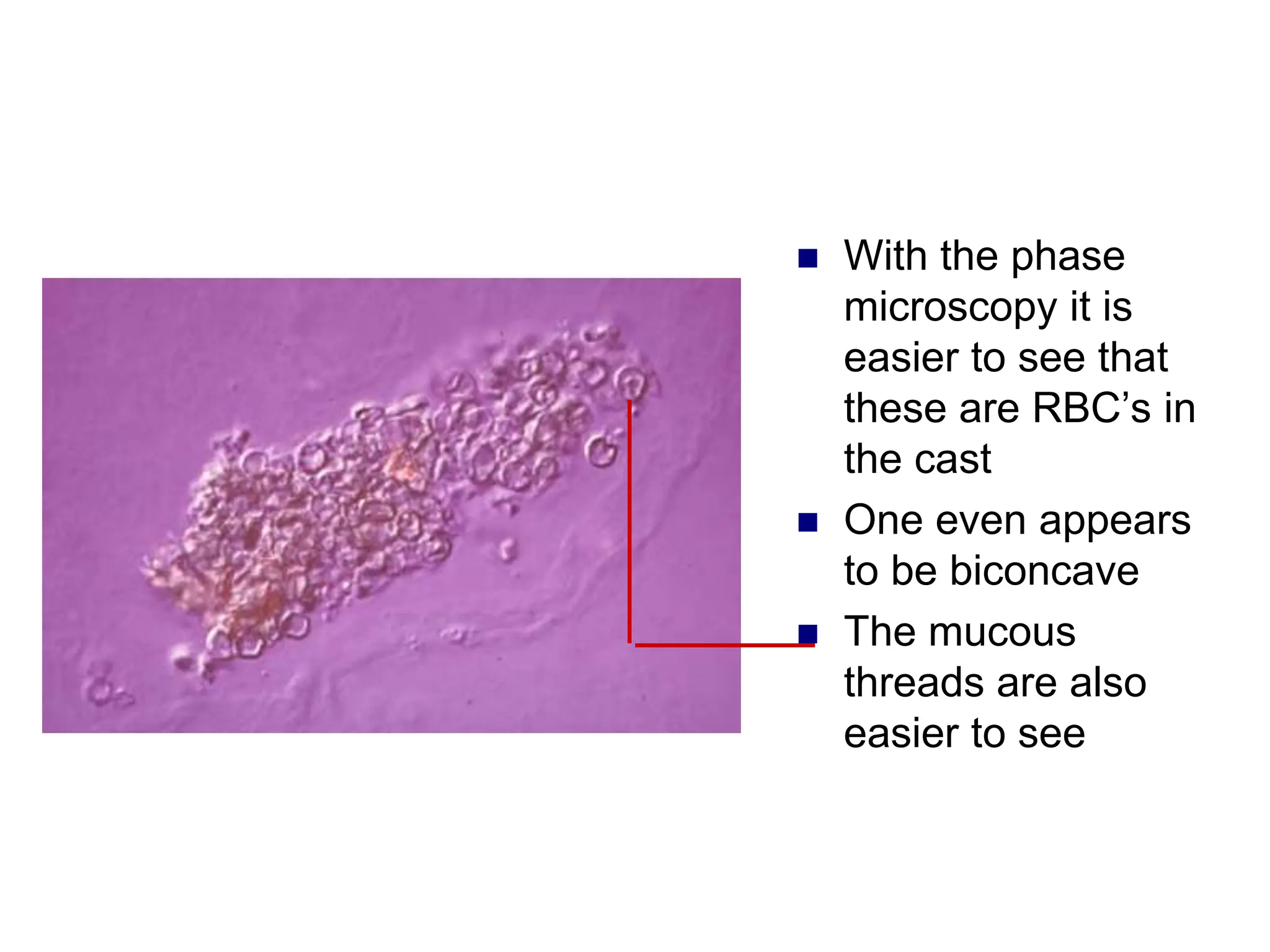



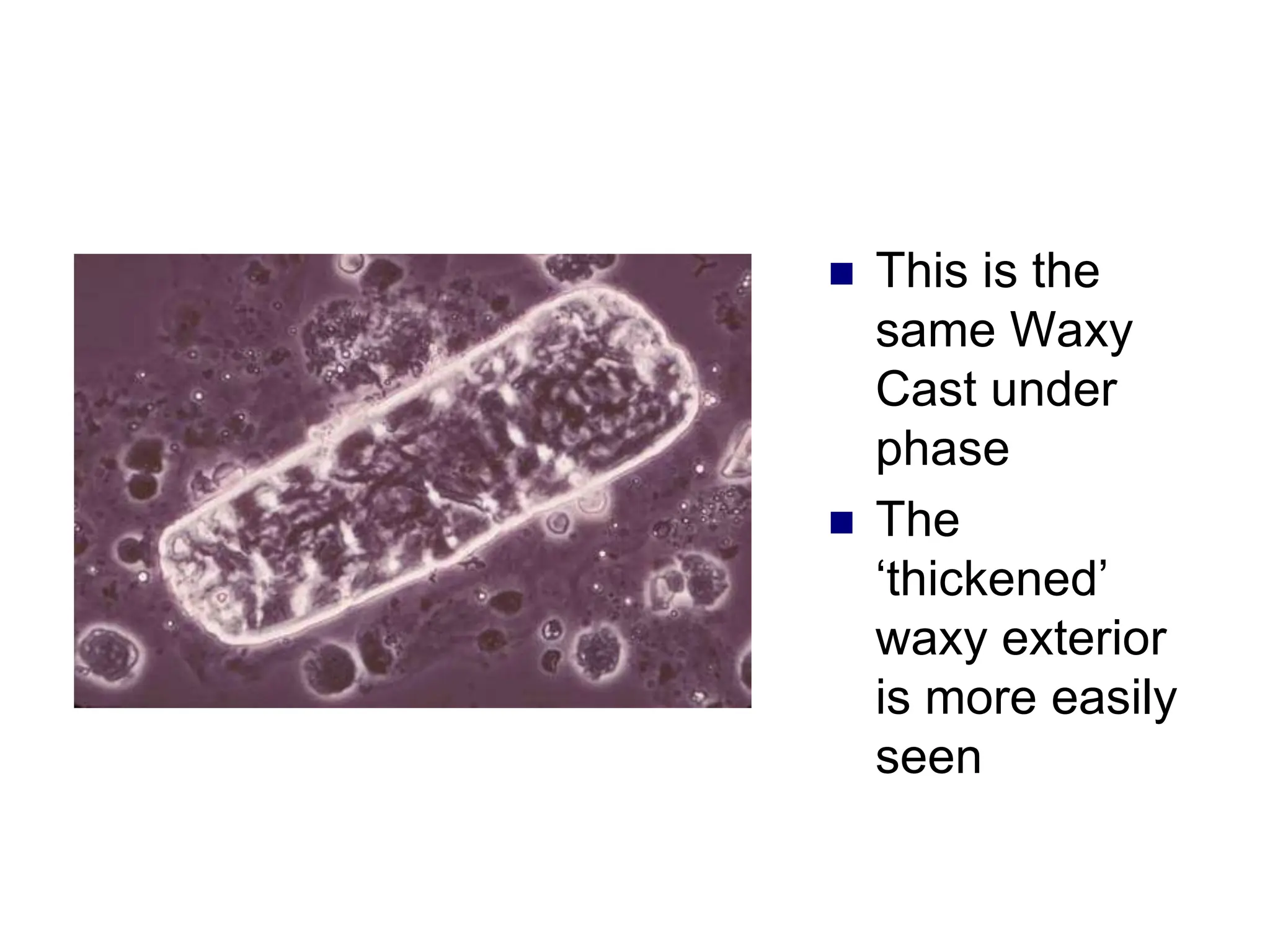
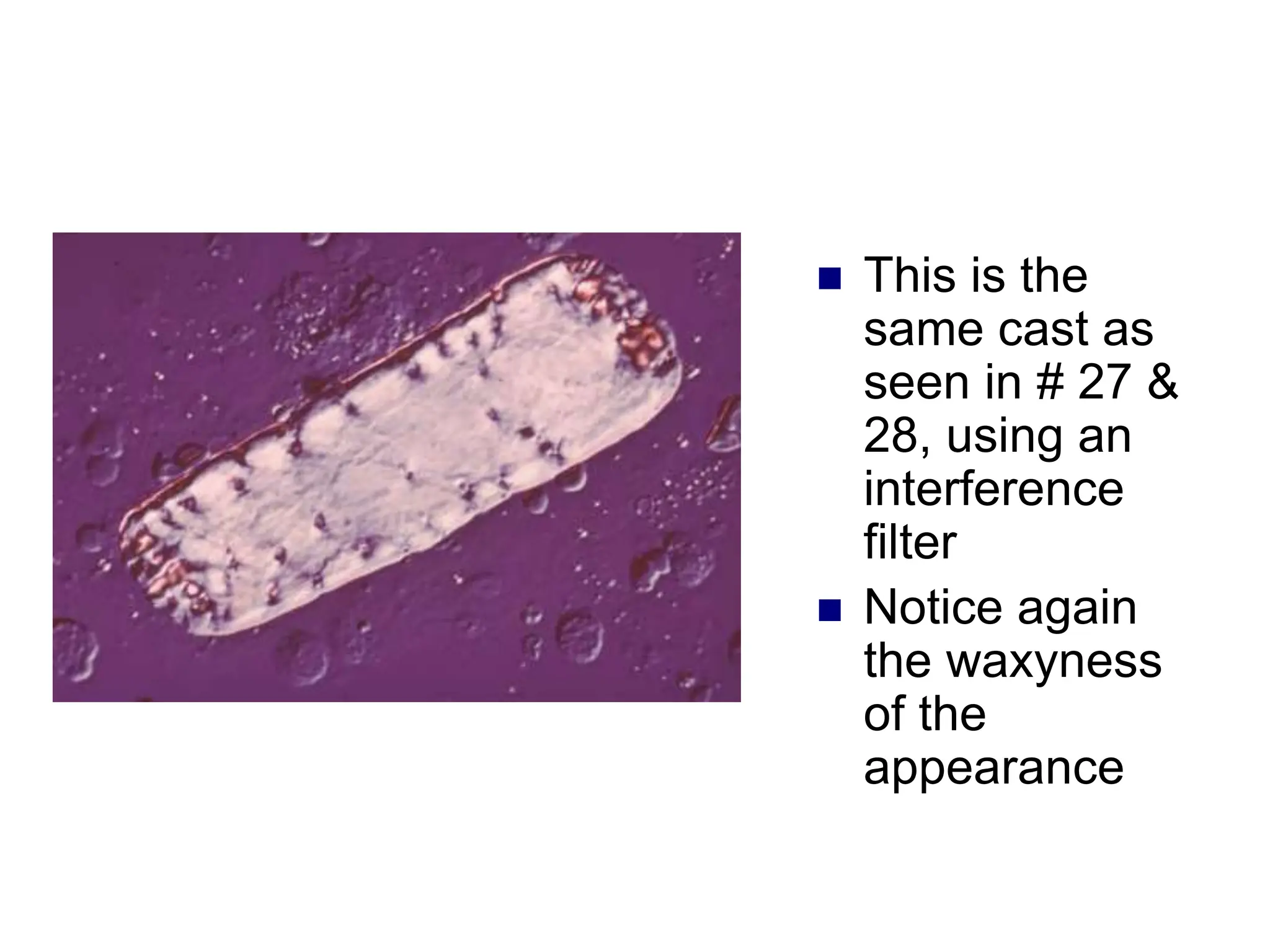


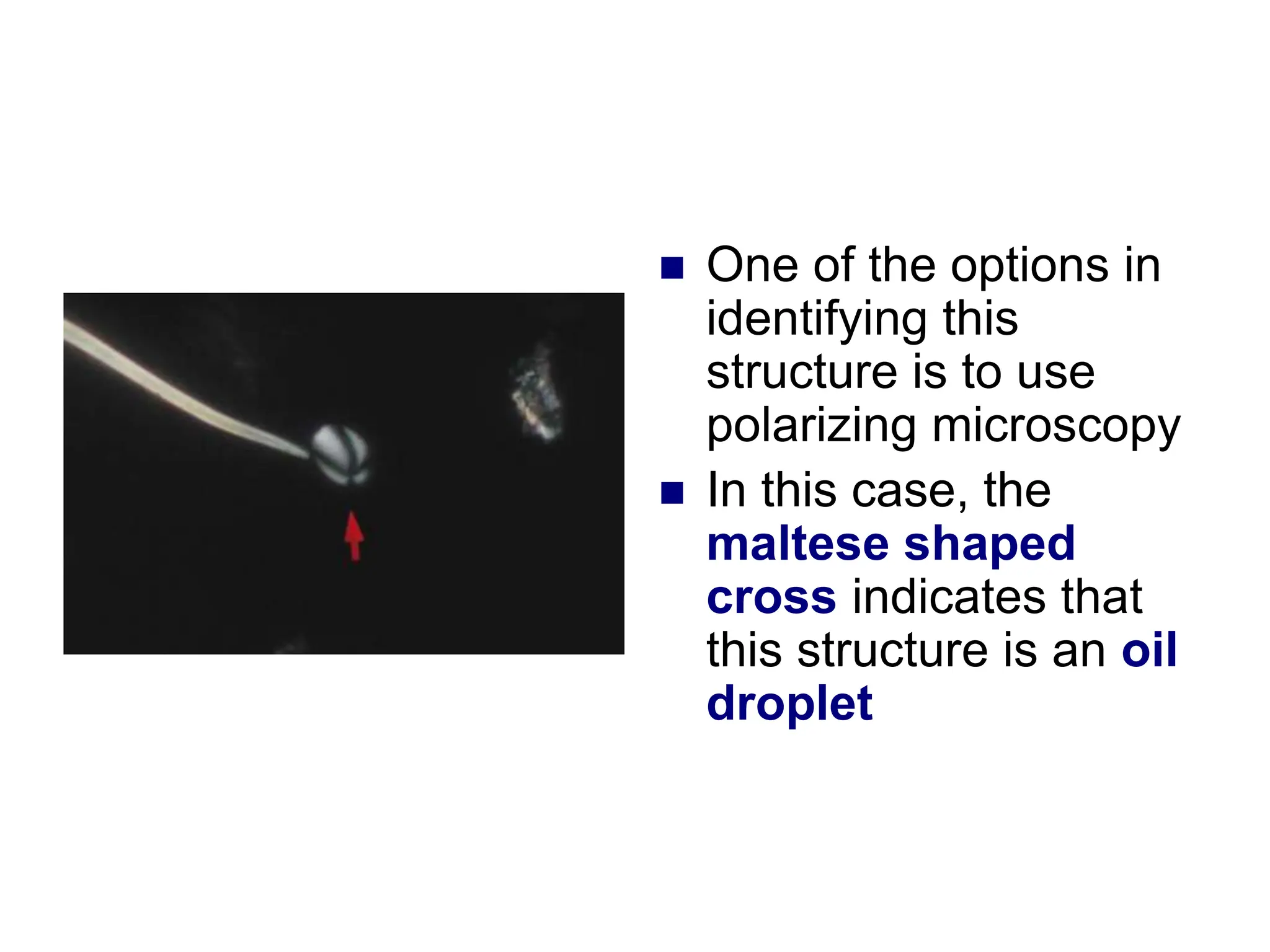
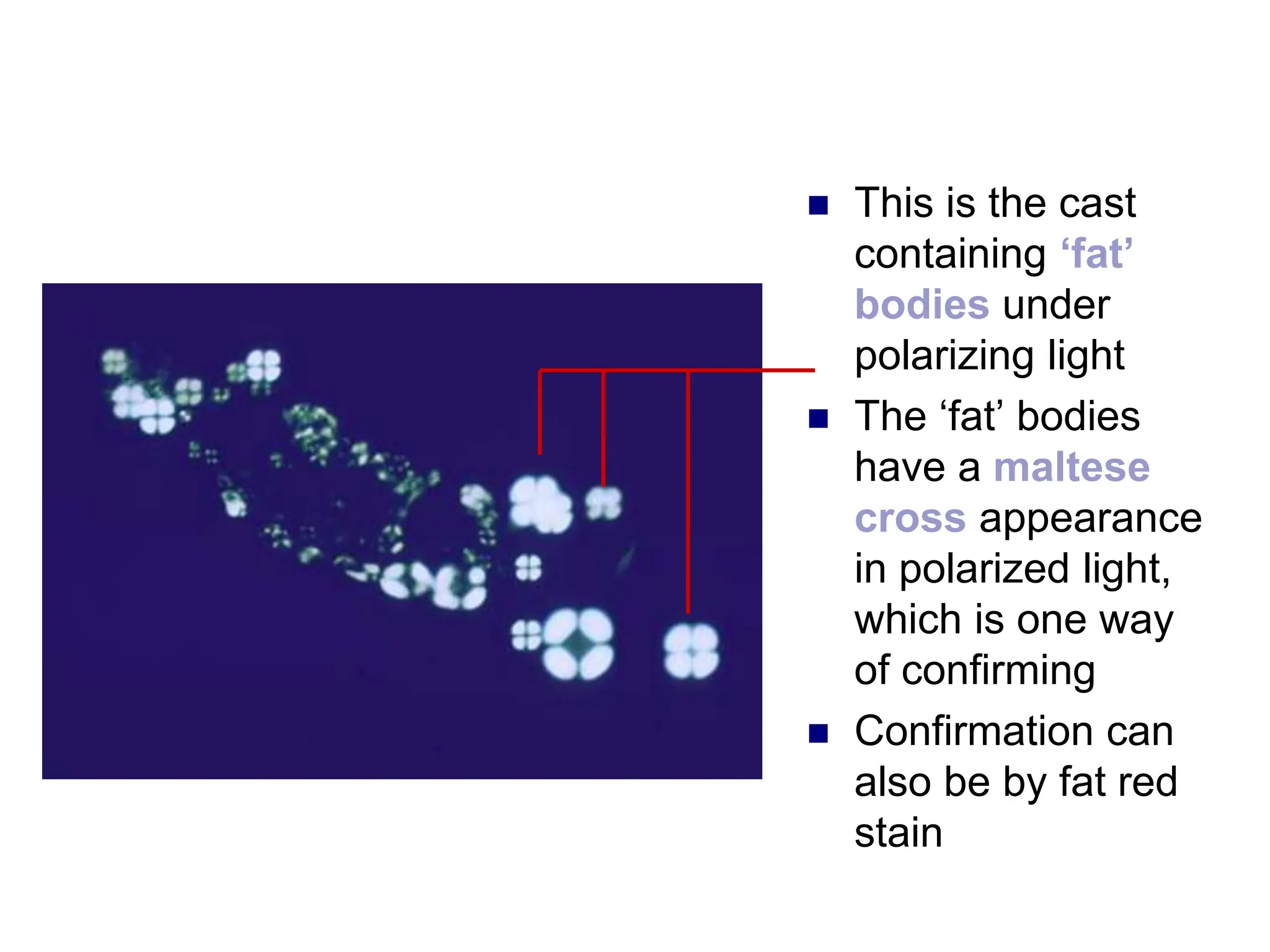
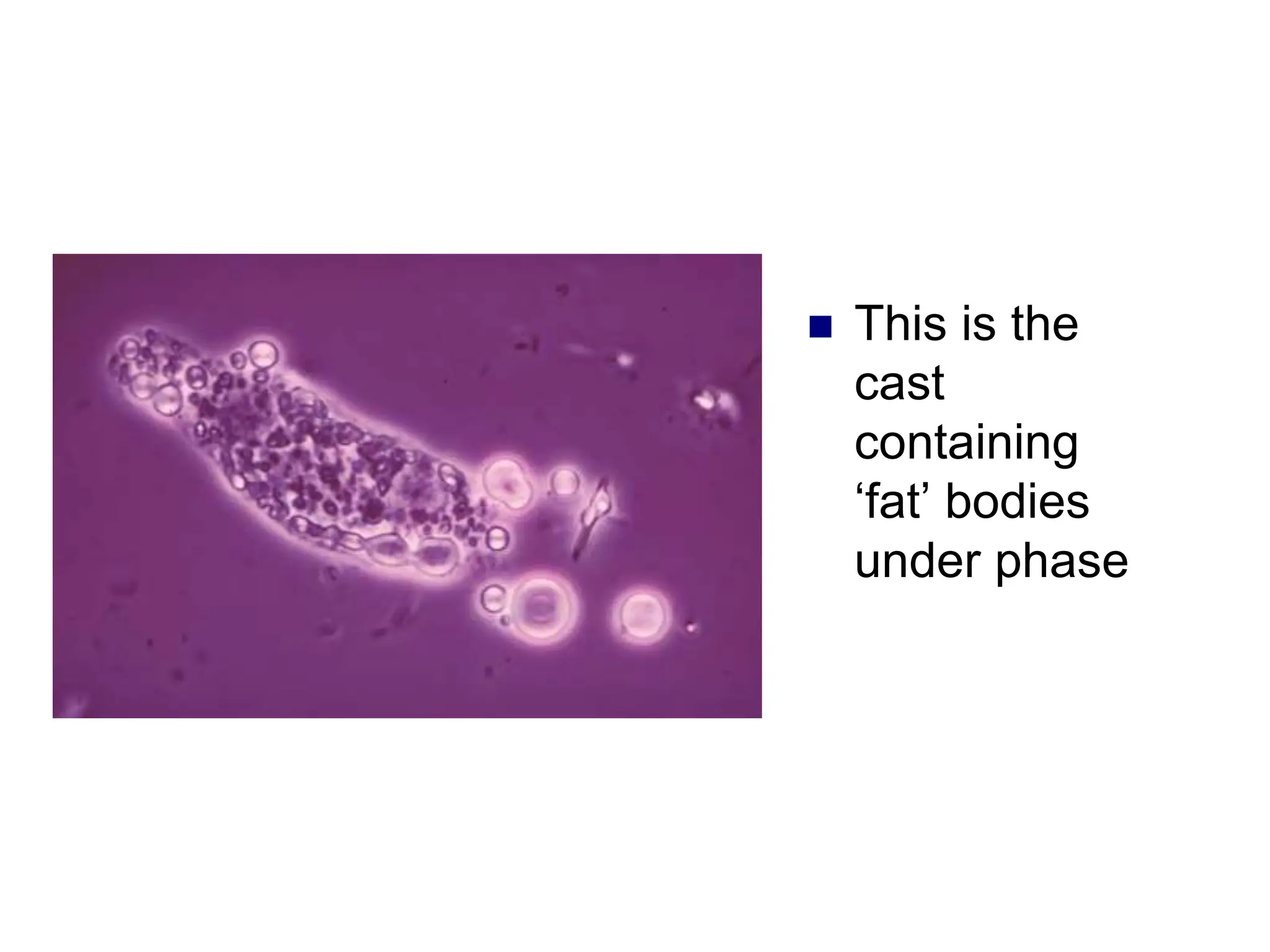
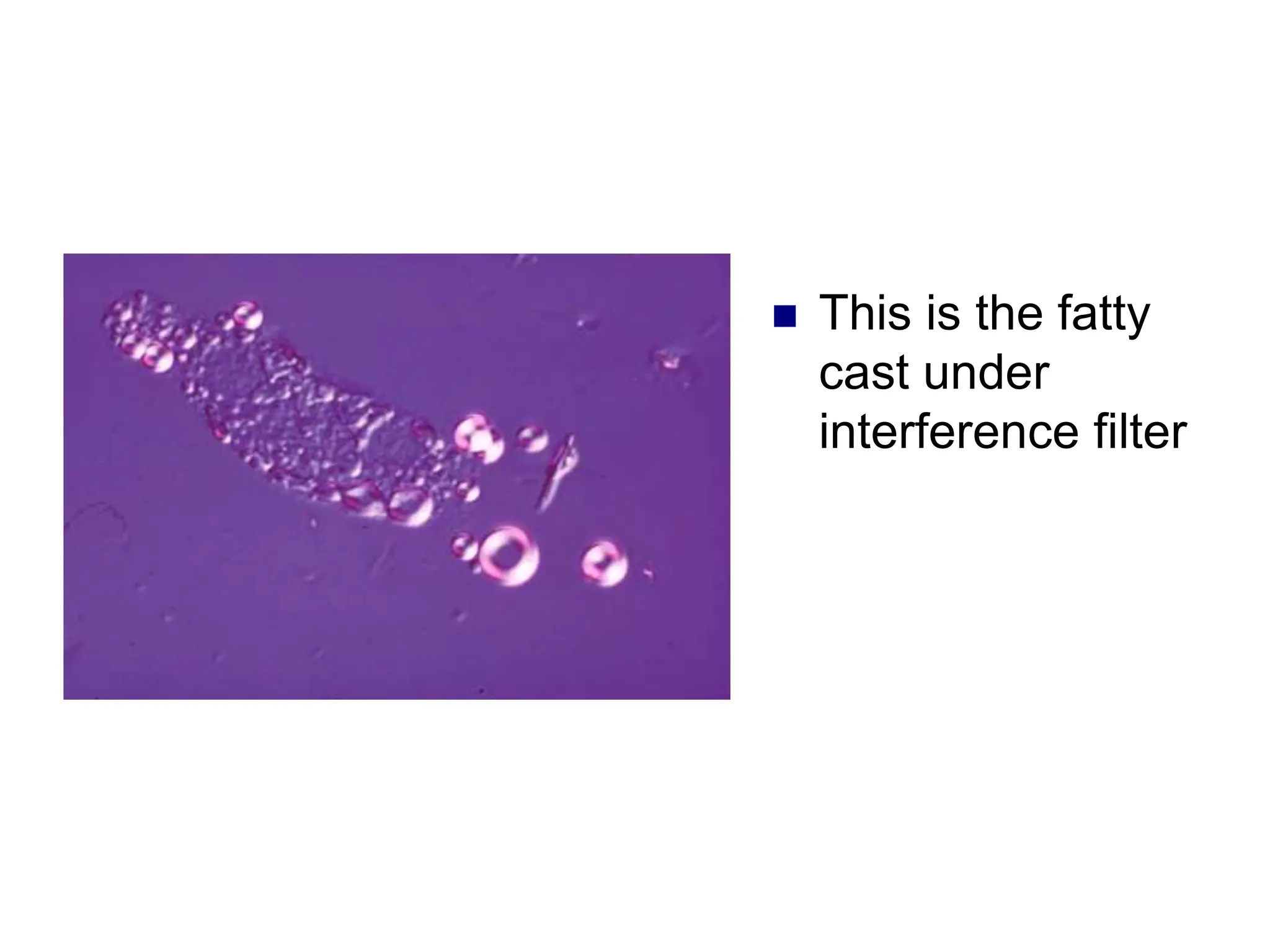
![ This is a cast
containing ‘fat’
bodies, high
power
On wet mount
the droplets are
highly refractile
[they bounce the
light back]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-240227071129-8fde615f/75/Chapter-5-Microscopic-examination-of-urine-ppt-77-2048.jpg)
























![Amino Acid Crystals
Tyrosine
fine, delicate needles,
colorless or yellow
frequently in clusters or
sheaves [as in stacks of
wheat]
see singly or in small groups
in acidic urine
less soluble than leucine, so
found more often](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-240227071129-8fde615f/75/Chapter-5-Microscopic-examination-of-urine-ppt-114-2048.jpg)
![Leucine
Highly refractile yellow to brown
spheres in acid urine.
Have concentric/radial
striations on their surface
Can be mistaken for fat
globules [or vice versa]
But will not stain with fat stains
or appear as maltese cross
under polarization
Can be seen in urine containing
tyrosine crystals if use alcohol
to ‘precipitate’
Bactrim has similar appearance
check patient history](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-240227071129-8fde615f/75/Chapter-5-Microscopic-examination-of-urine-ppt-115-2048.jpg)

![Confounding Conditions
Diatrizoate meglumine [radiopaque contrast medium]
can be mistaken for cholesterol
contrast medium will give abnormally high S.G. >1.040
not associated with proteinuria or lipiduria
cholesterol crystals found with normal S.G.
Medications
can be excreted in high concentrations, resulting in precipitation
these crystals are termed ‘iatrogenic’
proper identification of drug crystals important in alerting to
potential renal tubular damage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-240227071129-8fde615f/75/Chapter-5-Microscopic-examination-of-urine-ppt-118-2048.jpg)