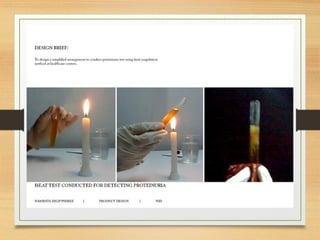
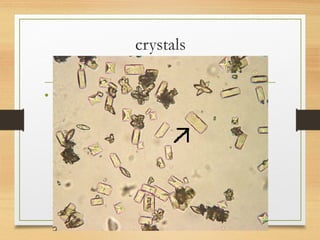
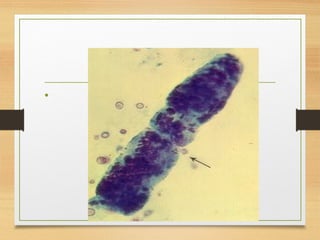
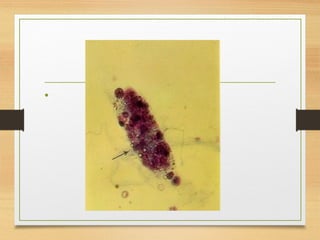
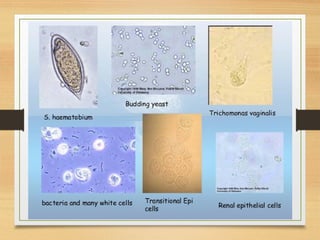
This document provides an overview of urine analysis including physical, chemical, and microscopic examination. Physical examination assesses volume, color, odor, pH, and specific gravity. Chemical examination tests for proteins, sugars, ketone bodies, bilirubin, and blood. Microscopic examination identifies epithelial cells, red blood cells, crystals, and casts which can indicate various conditions. Urine dipsticks provide a convenient qualitative analysis of various urine components. A comprehensive urine analysis evaluates kidney and bladder function and detects underlying diseases.