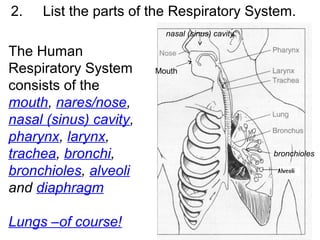
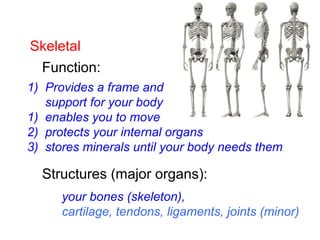
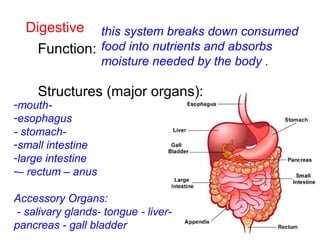
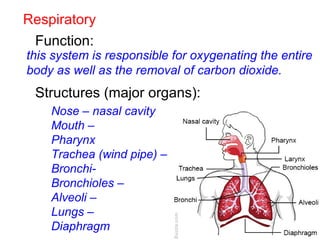
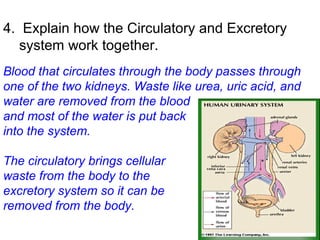
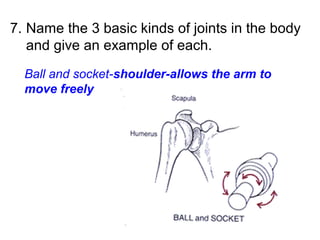
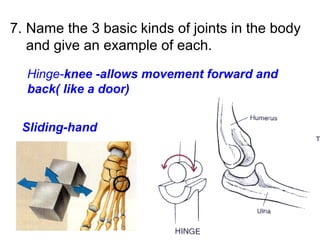
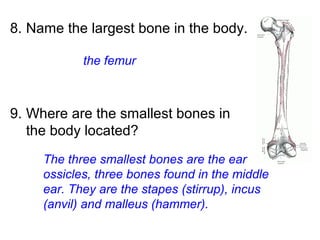
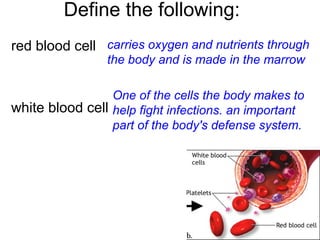
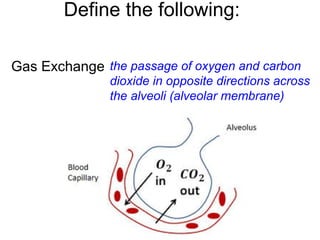
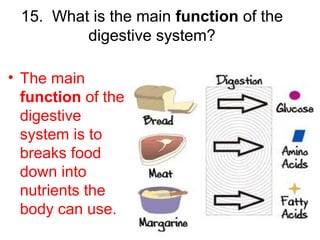
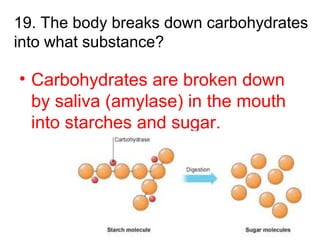
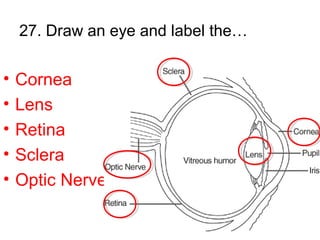
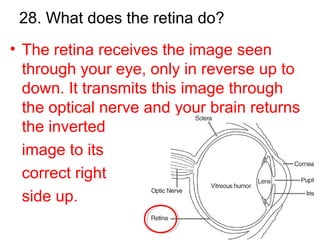
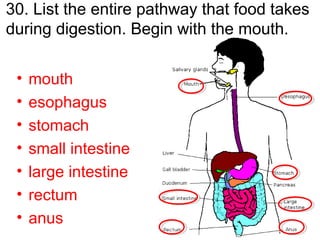
This document provides a review of various human body systems, including the integumentary, respiratory, circulatory, muscular, skeletal, digestive, endocrine, nervous, and excretory systems. It lists the key parts and functions of each system and explains how some systems work together, such as the respiratory and circulatory systems in gas exchange and the circulatory and excretory systems in waste removal. Key terms related to anatomy and physiology are also defined.