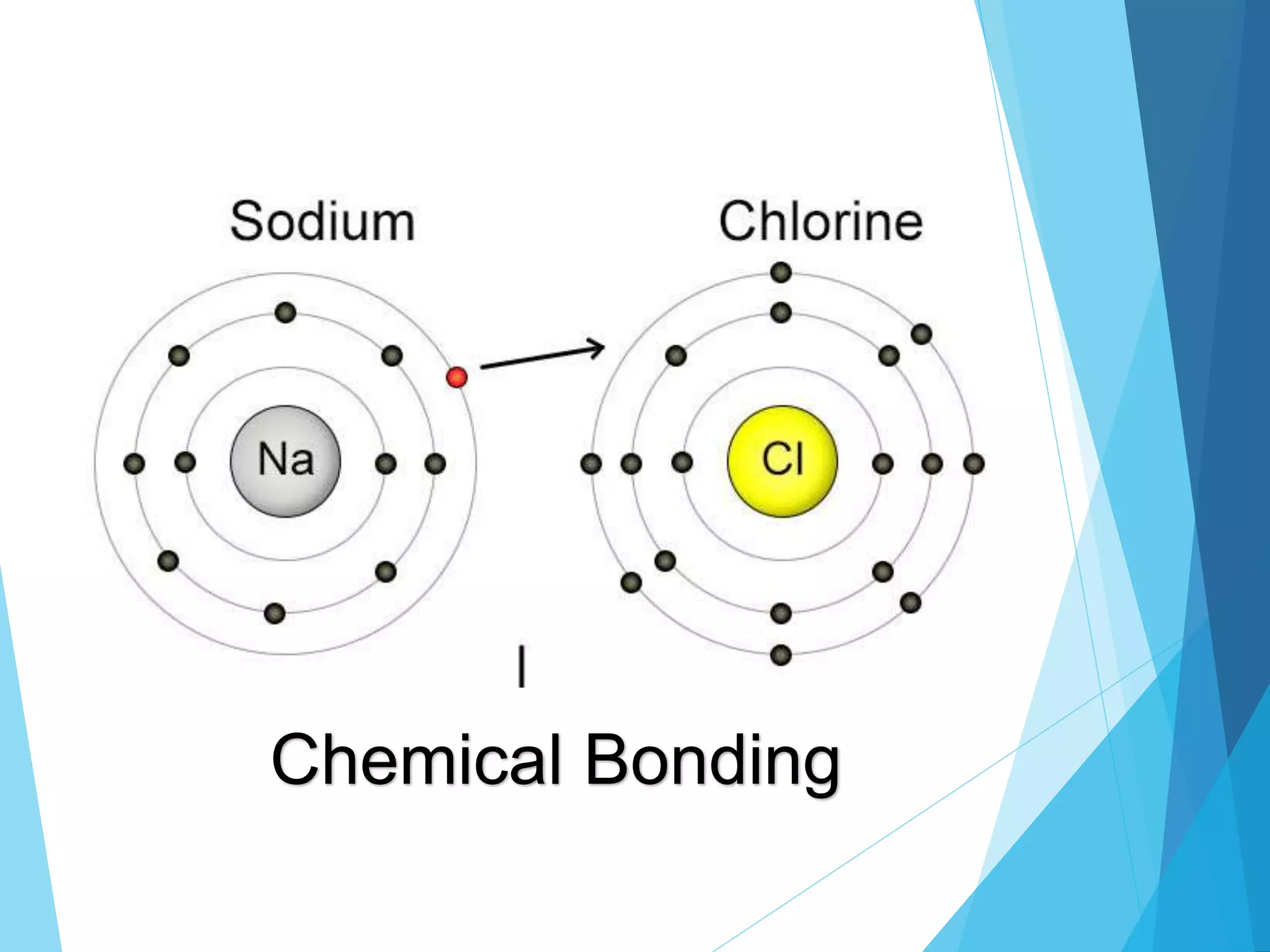
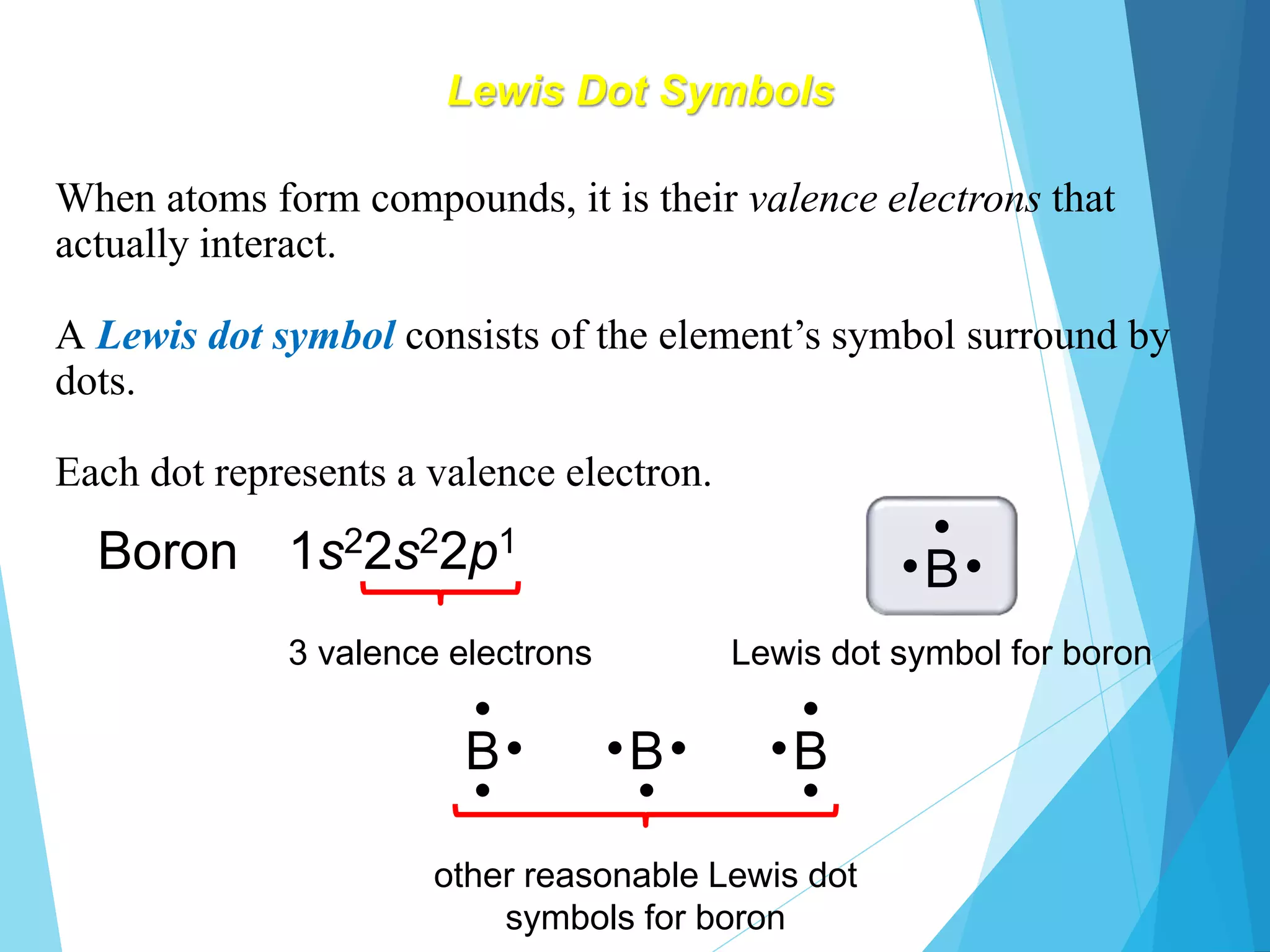
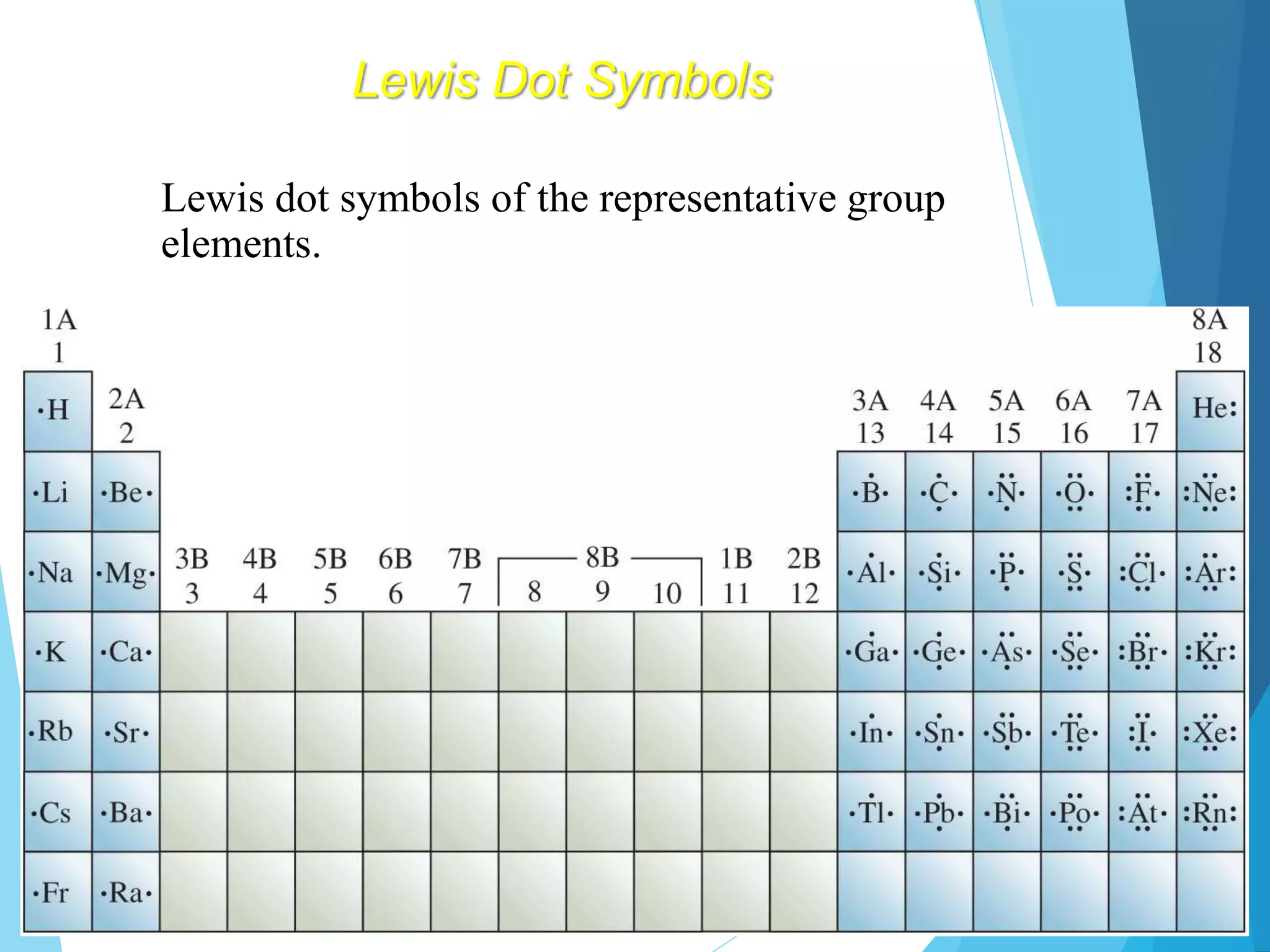
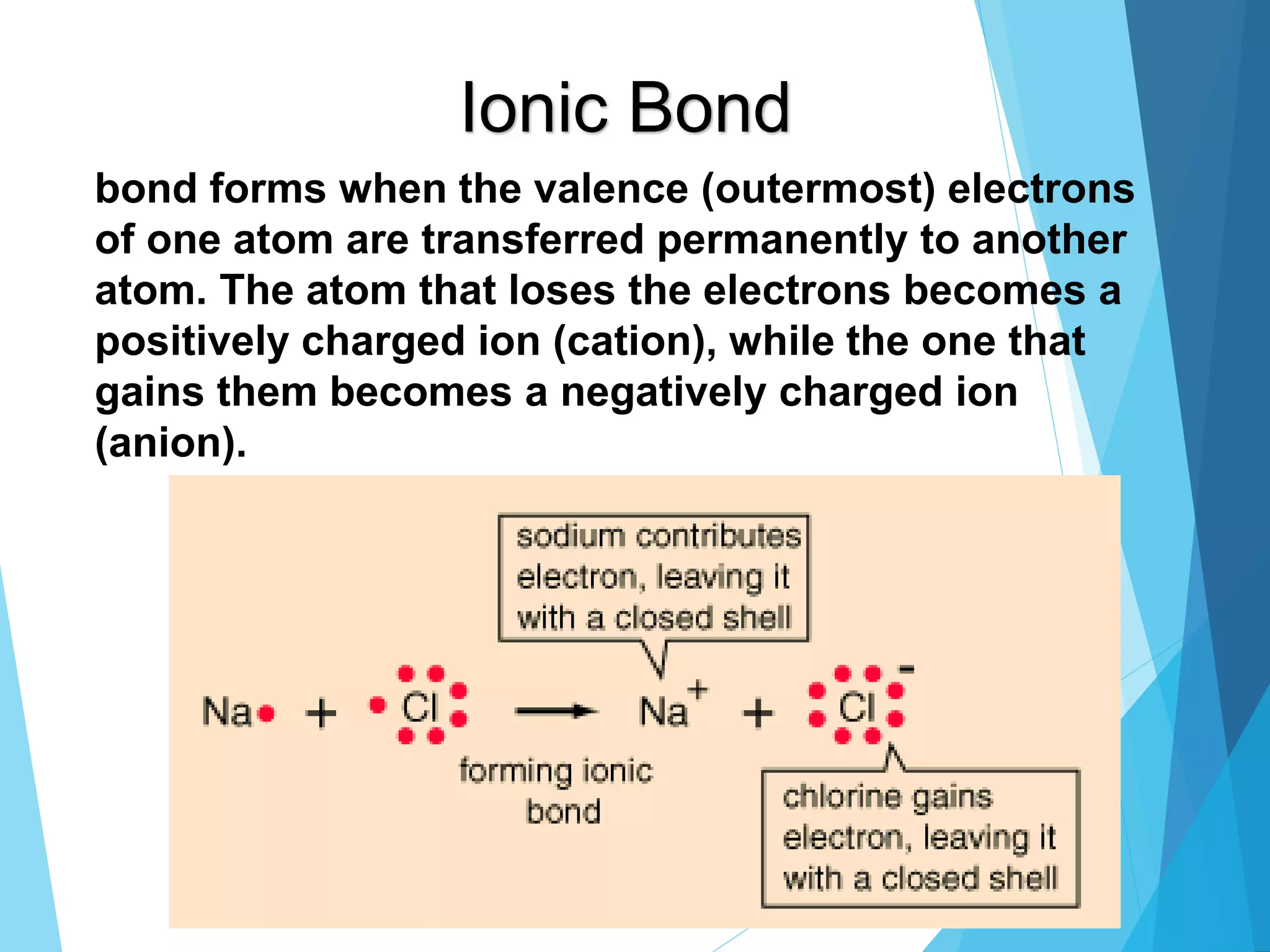
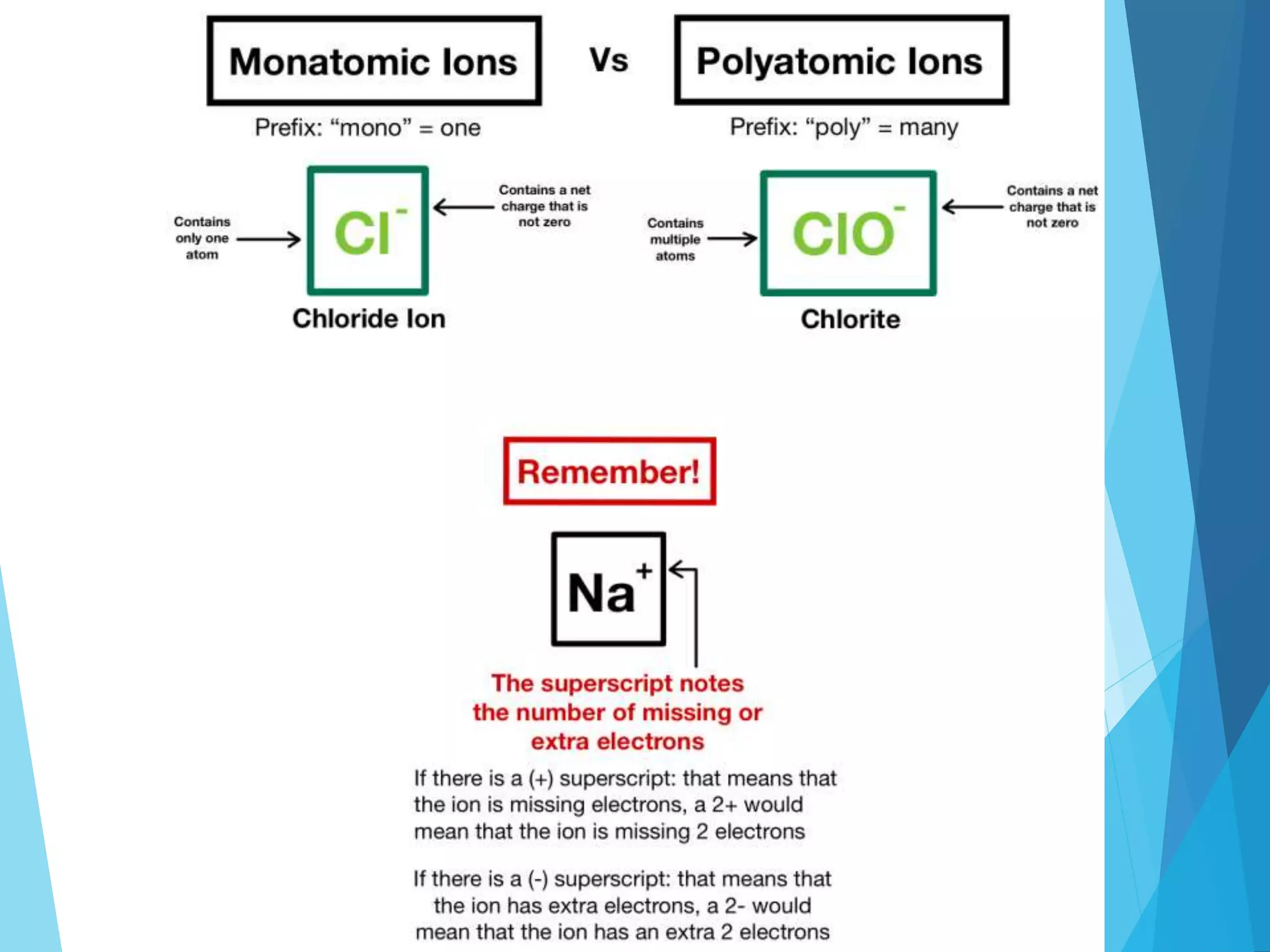
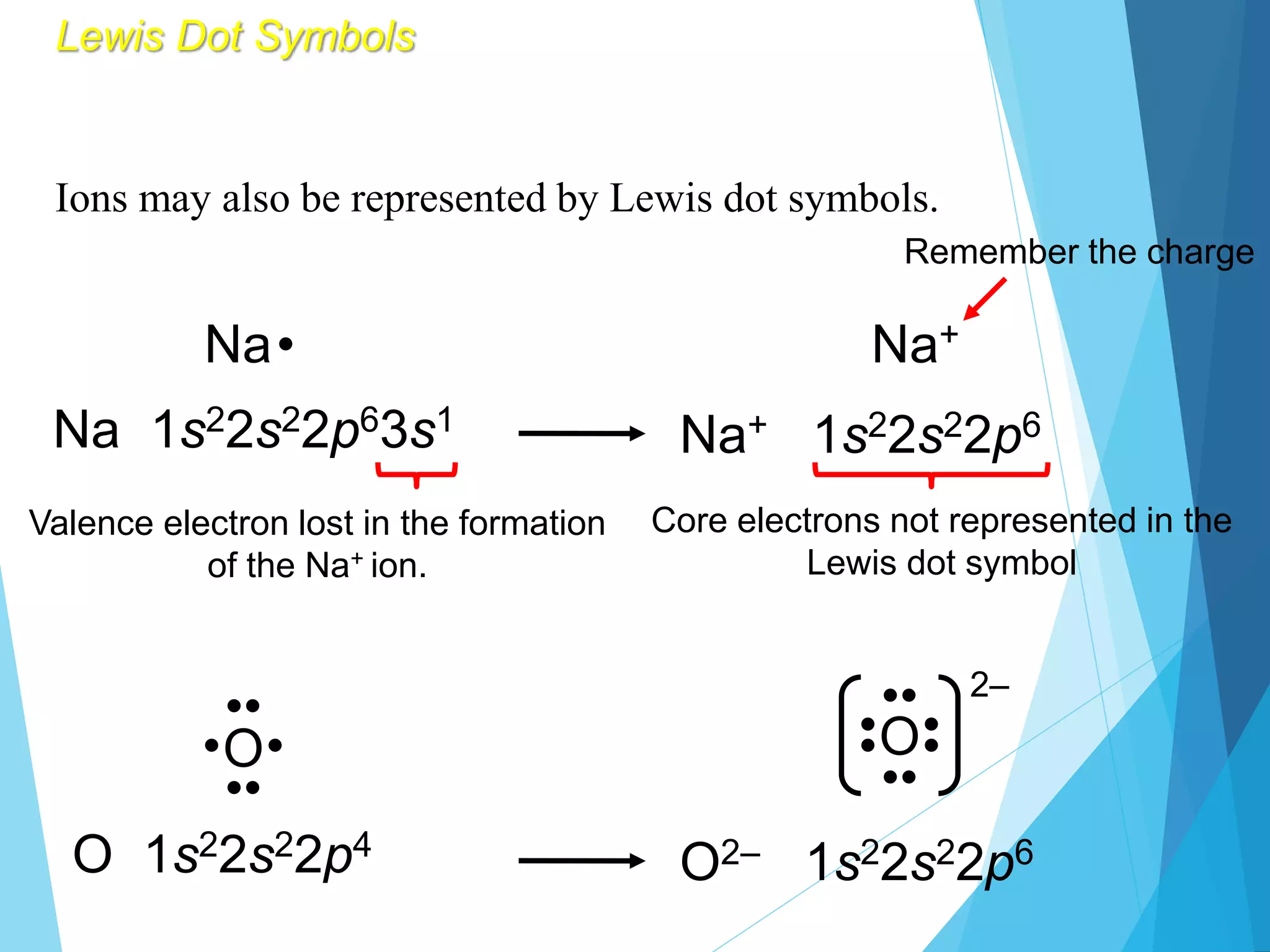
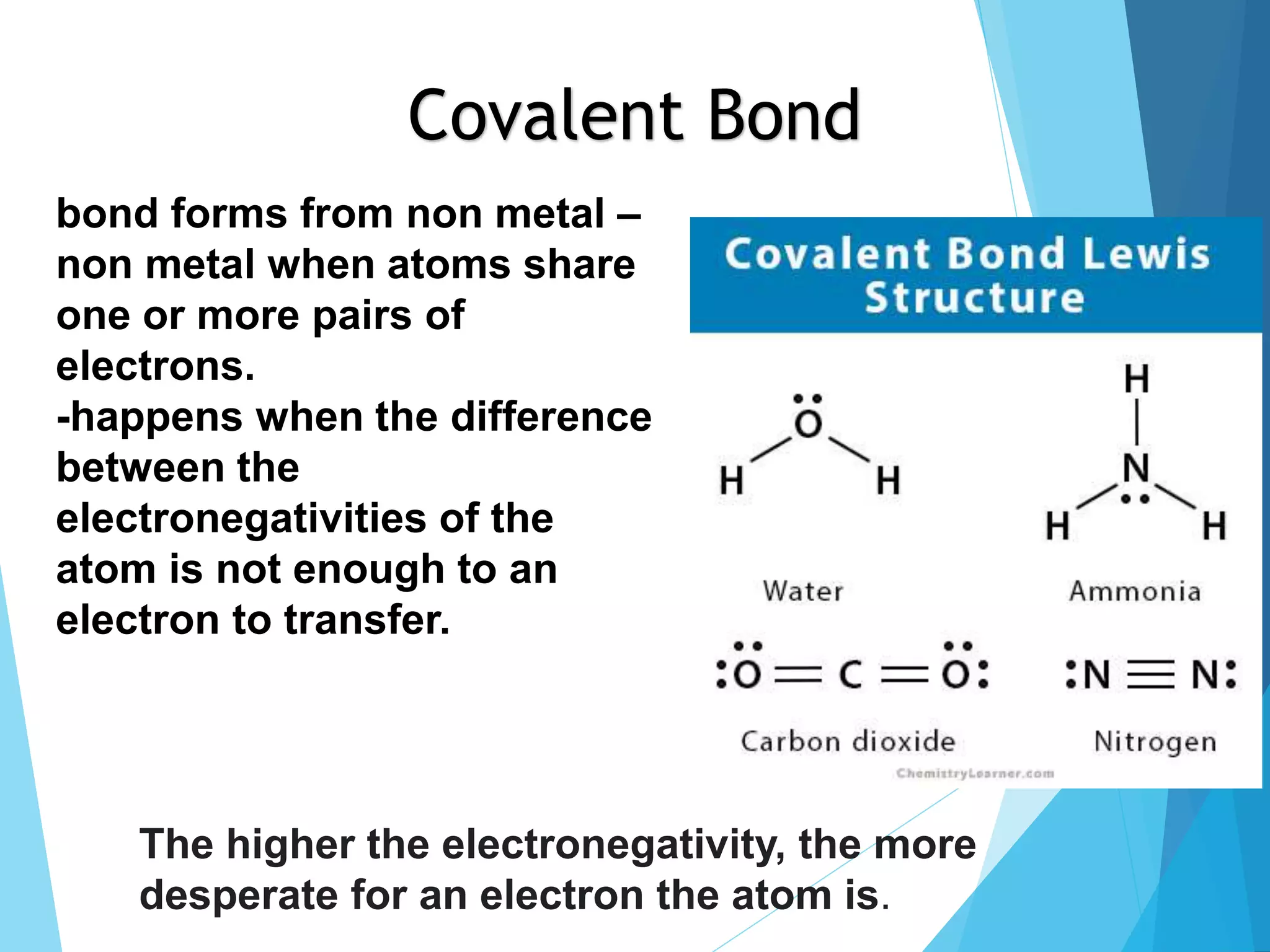
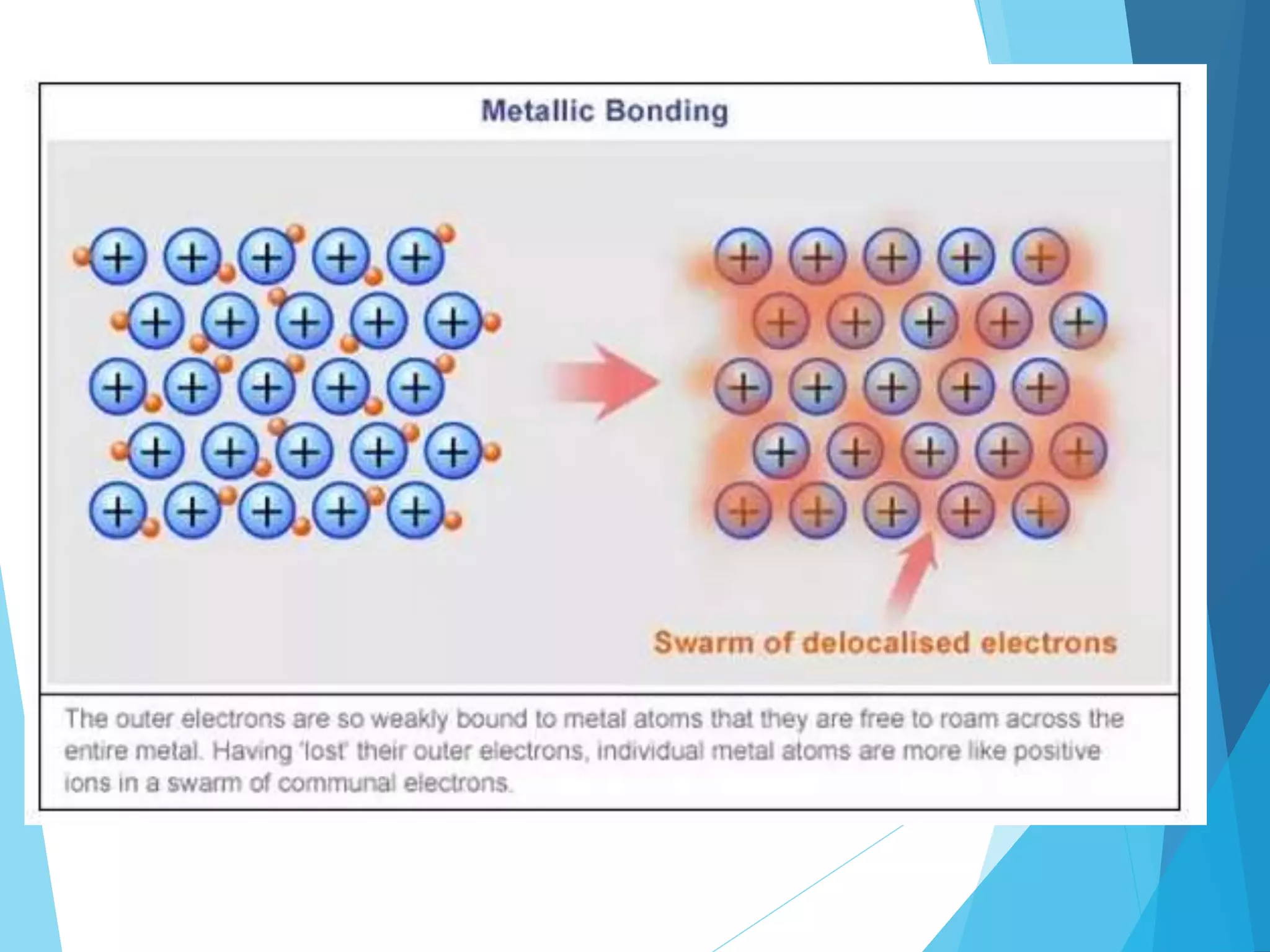
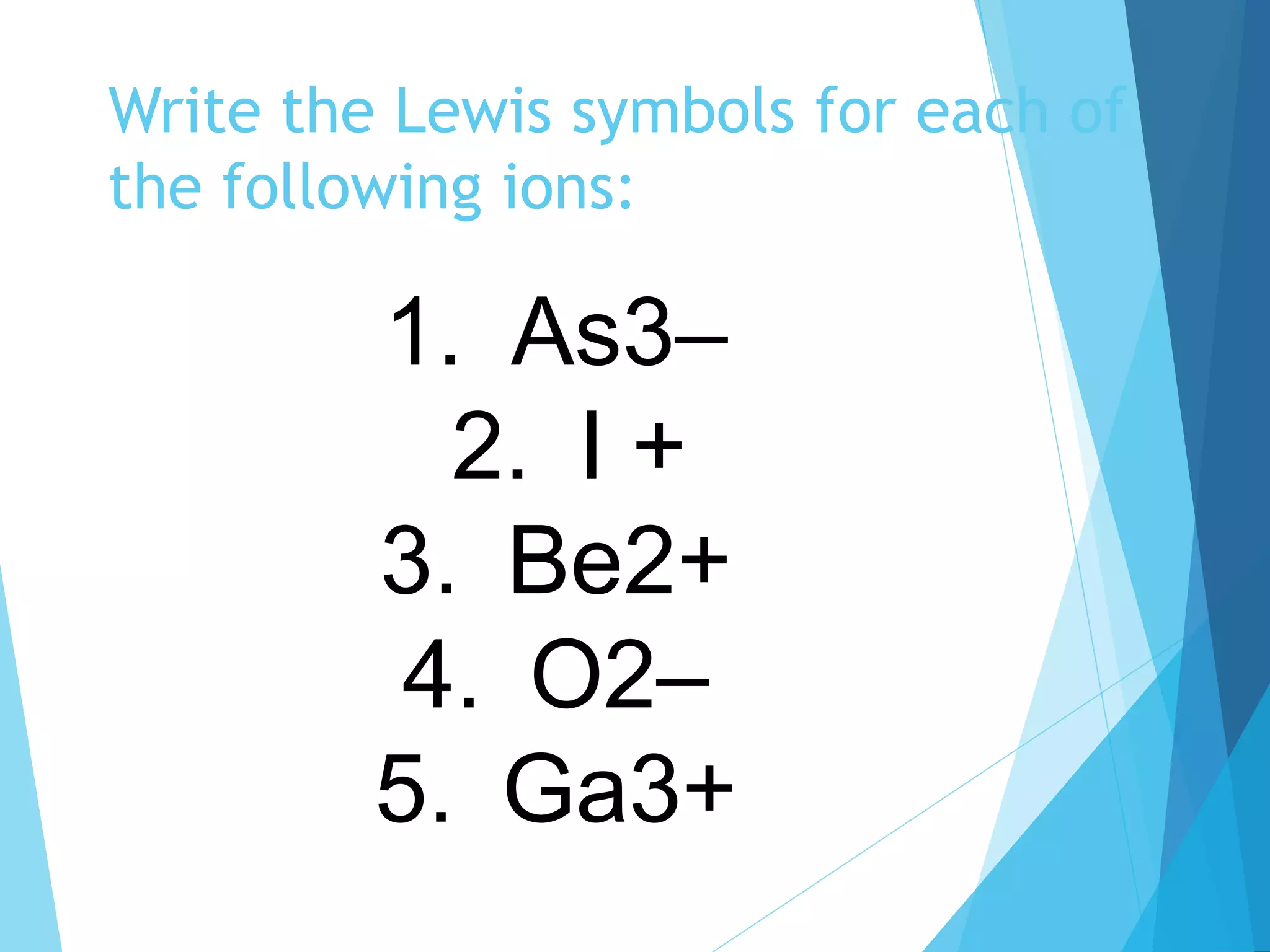This document discusses chemical bonding and Lewis dot structures. It explains that atoms combine to achieve stable electron configurations, often those of noble gases. Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred between atoms, creating ions. Covalent bonds form through electron sharing between nonmetals. Lewis dot structures represent valence electrons and can show electron transfers in ion formation. Different bond types - ionic, covalent, and metallic - depend on differences in electronegativity between atoms. Practice problems are provided to determine bond type based on electronegativity values.