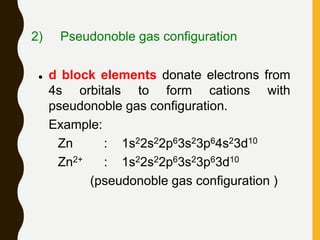
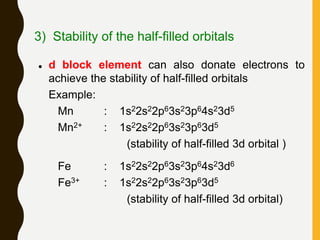
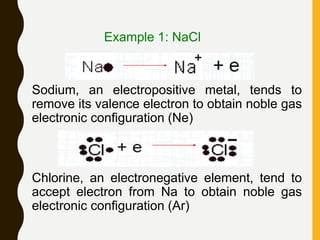
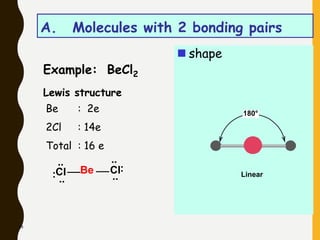
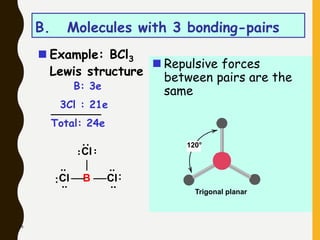
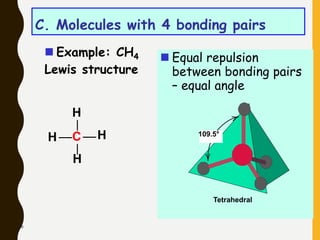
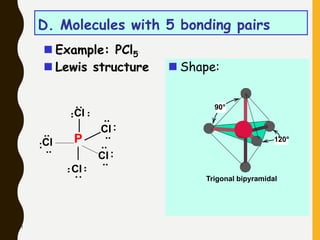
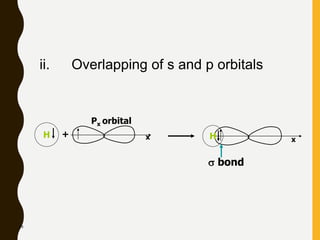
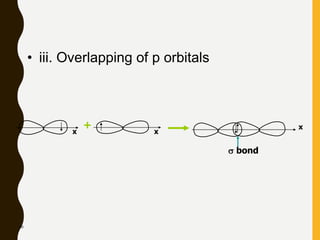
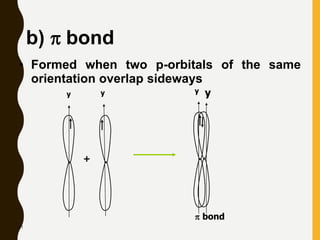
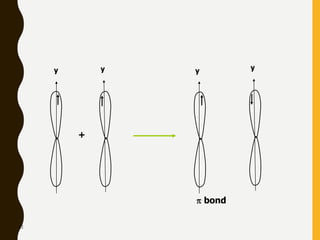
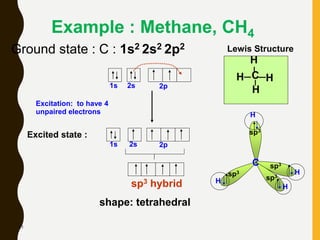
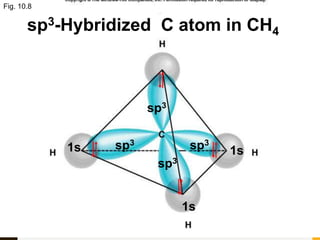
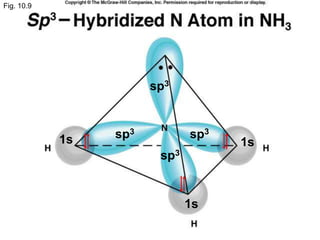
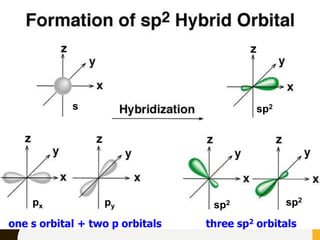
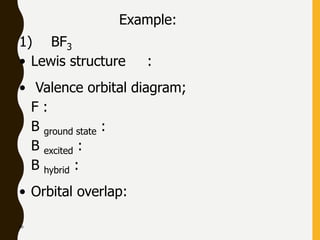
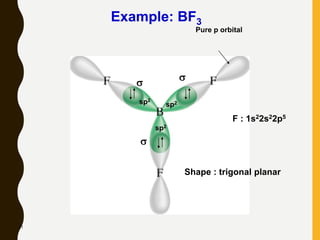
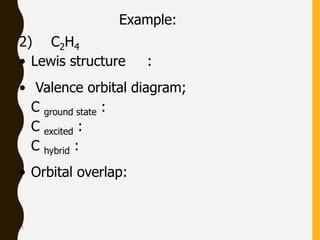
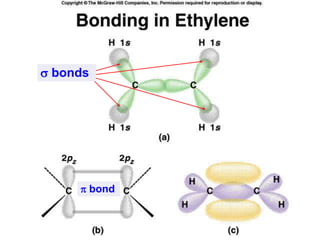
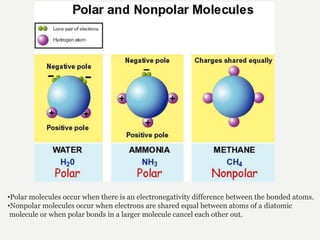
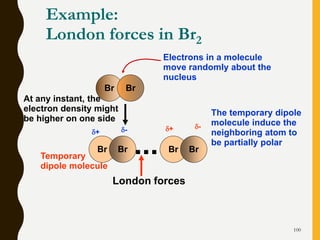
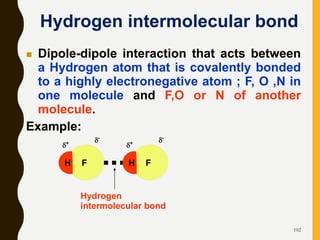
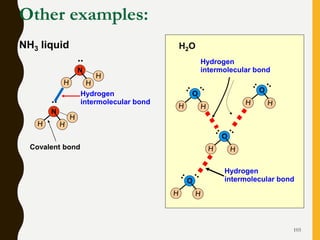
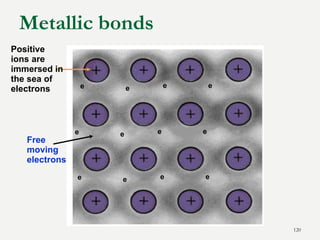
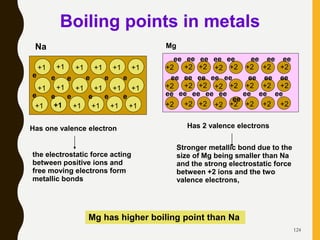
Chemical bonds are formed by the sharing or transfer of valence electrons between atoms. Valence electrons play an important role in bond formation as atoms seek to achieve stable electronic configurations like noble gases. There are two main types of bonds:
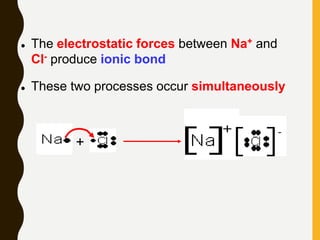
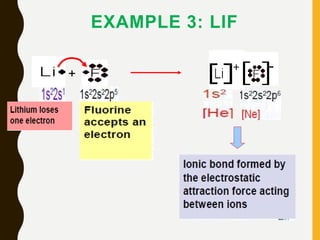
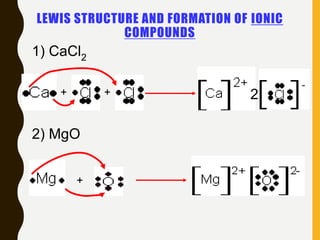
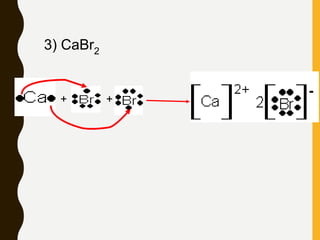
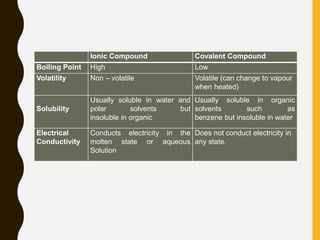
1) Ionic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons from metals to nonmetals, resulting in positively charged cations and negatively charged anions that are attracted to each other.
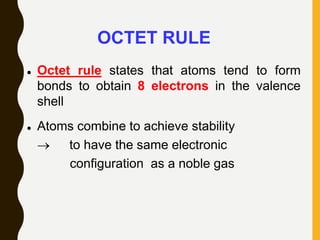
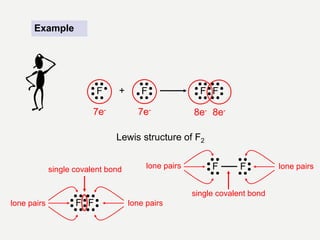
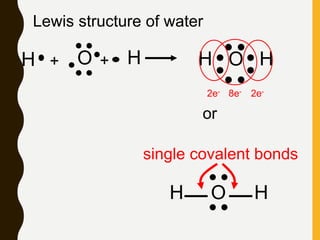
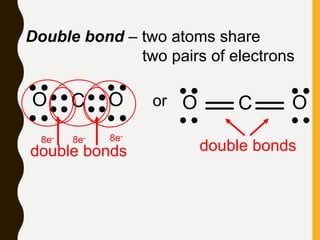
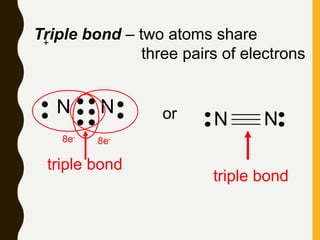
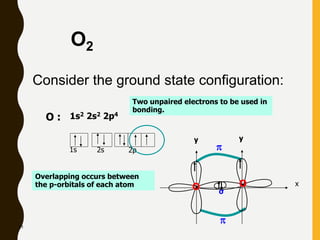
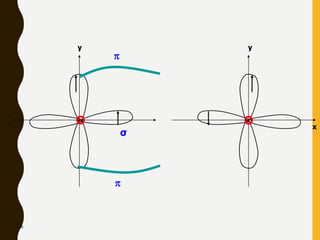
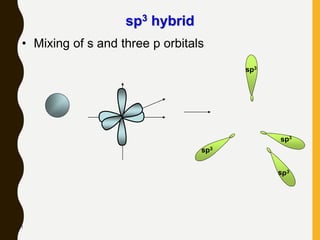
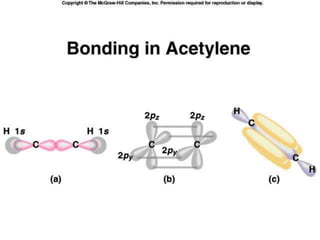
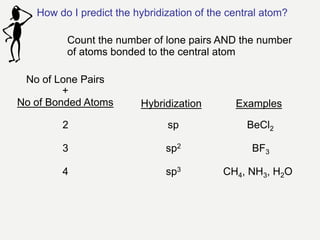
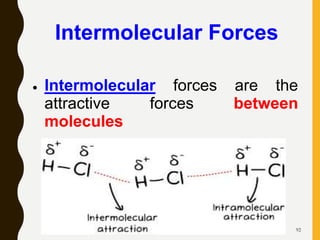
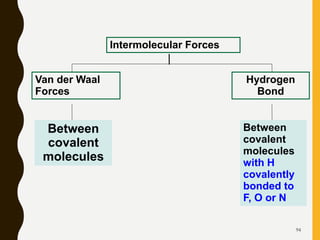
2) Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between nonmetals. Atoms share electrons to achieve stable octet configurations. Single, double, and triple covalent bonds are distinguished by the number of electron pairs shared.
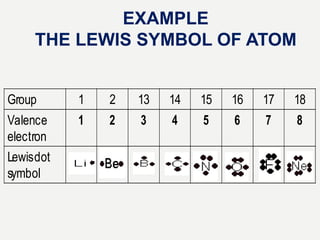
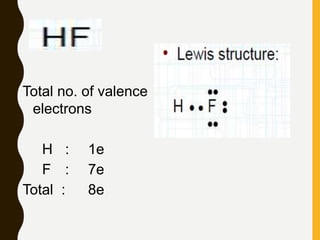
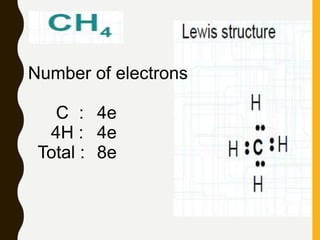
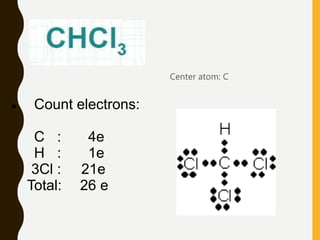
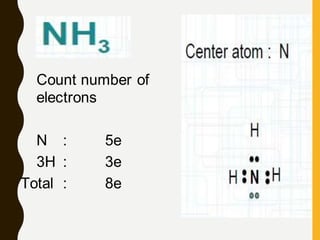
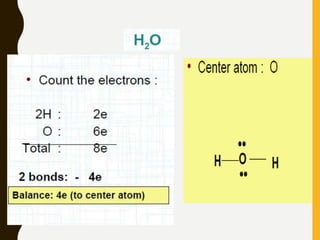
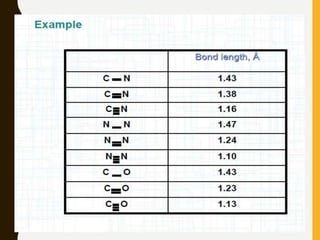
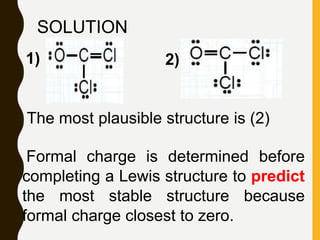
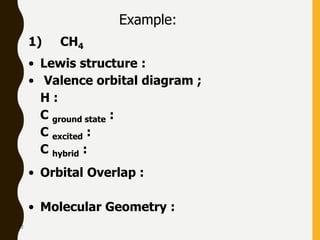
Lewis structures use dots or crosses to represent valence