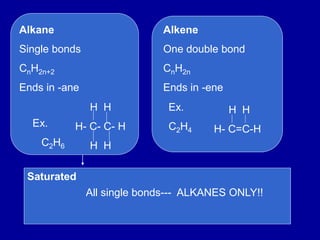
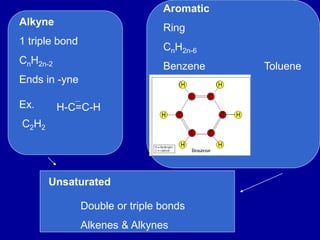
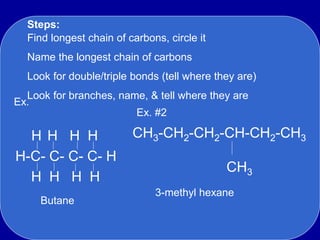
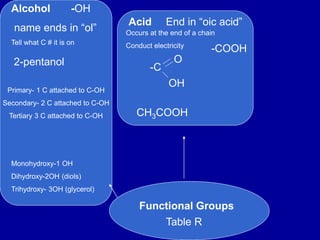
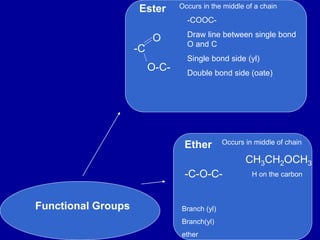
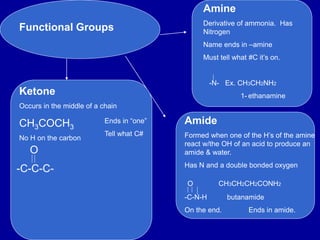
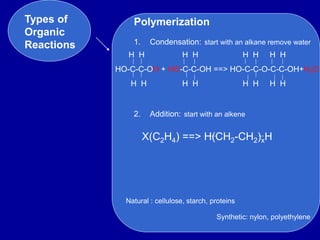
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-containing compounds. Hydrocarbons only contain carbon and hydrogen, forming chains and branches with single, double, or triple bonds between carbons. Functional groups include alcohols, acids, esters, ethers, amines, amides, ketones, and aldehydes. Organic reactions include substitution, addition, fermentation, saponification, polymerization, esterification, combustion, cracking, and fractional distillation. Hydrocarbons have low melting points and are nonpolar and nonconductive.