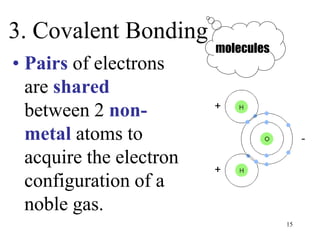
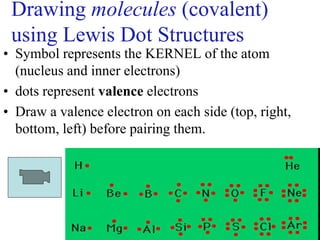
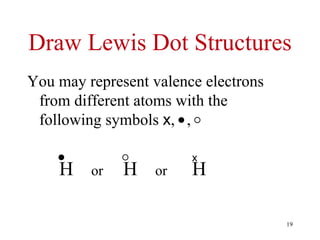
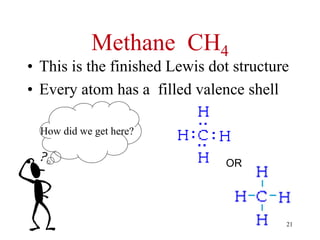
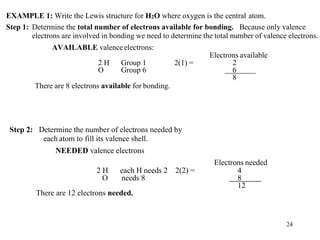
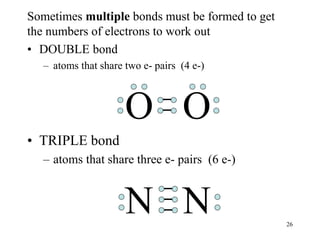
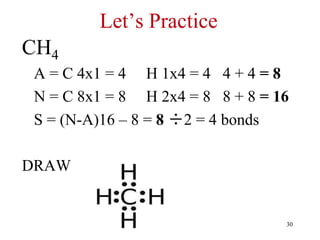
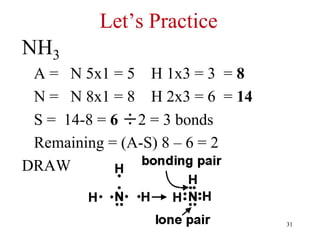
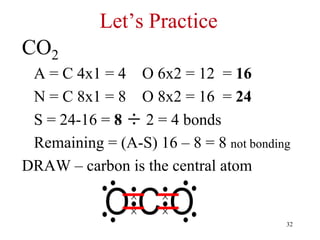
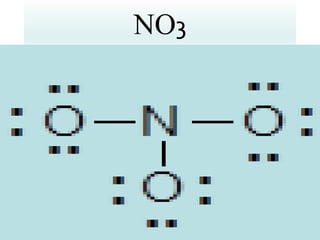
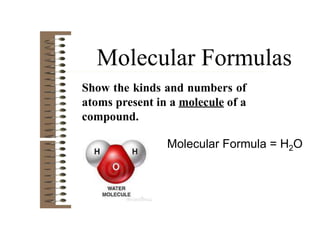
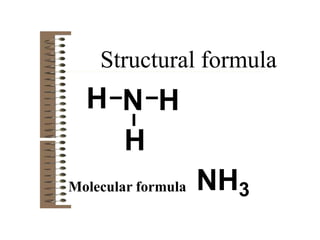
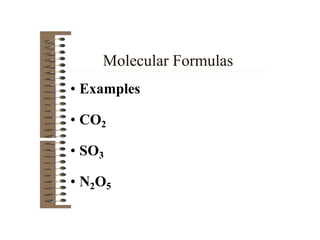
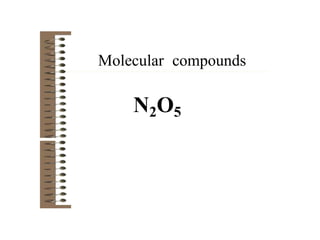
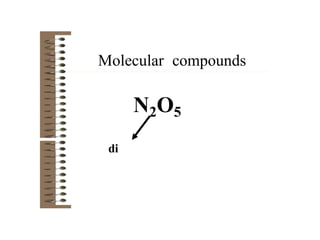
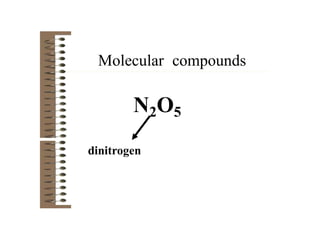
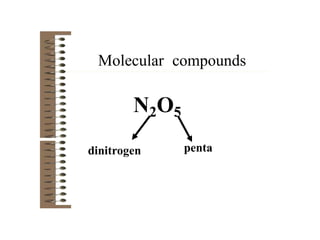
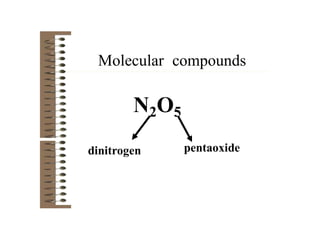
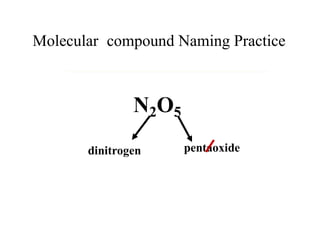
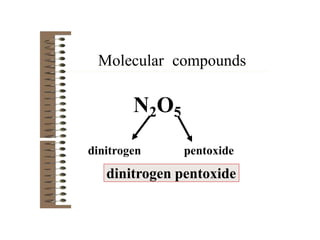
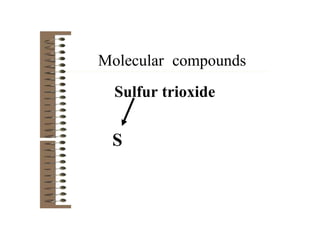
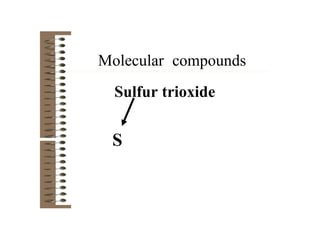
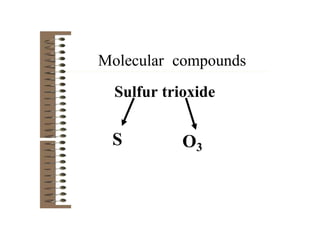
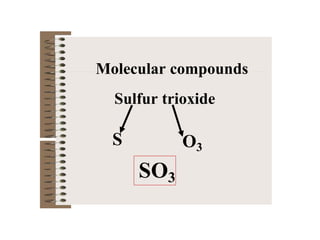
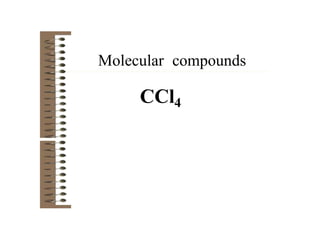
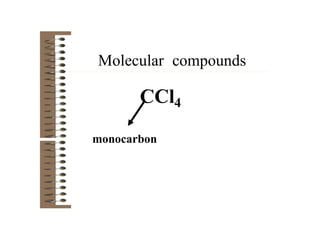
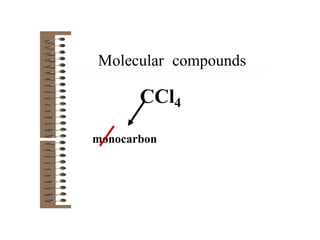
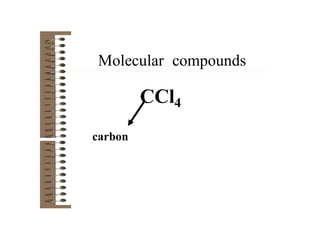
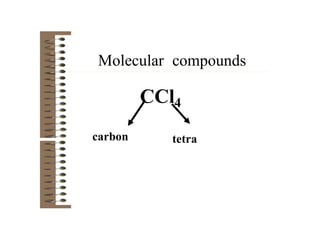
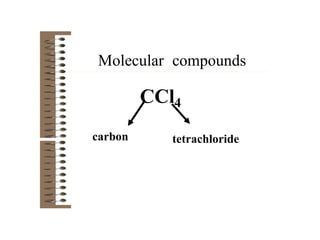
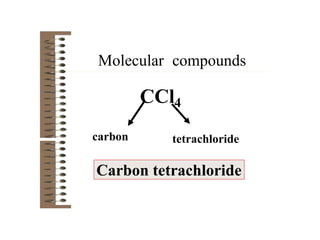
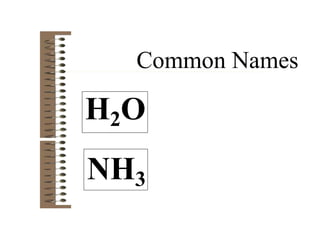
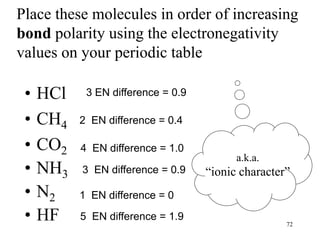
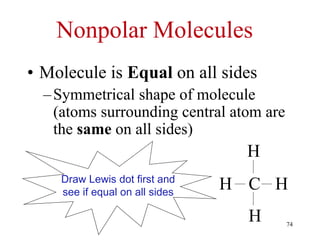
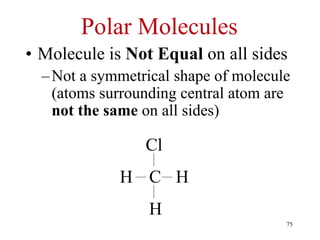
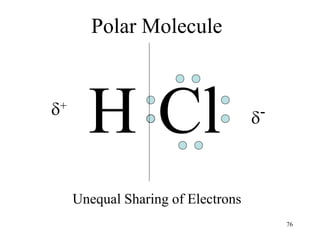
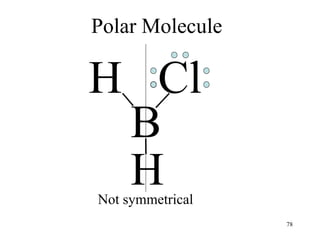
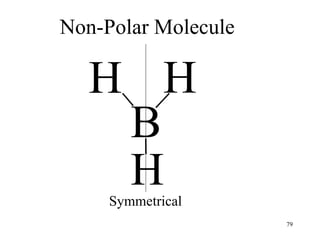
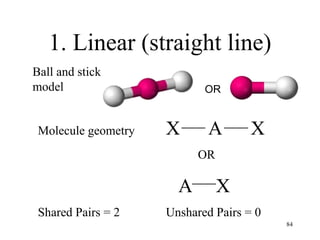
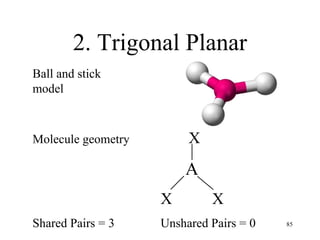
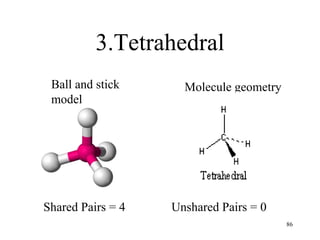
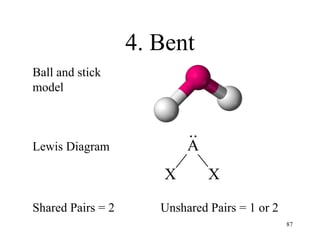
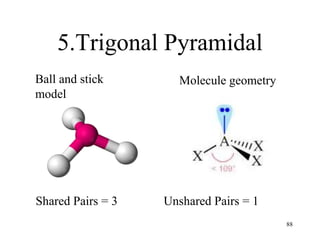
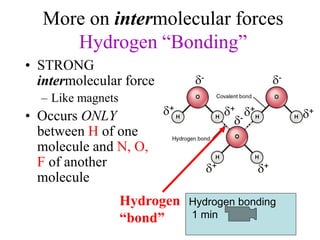
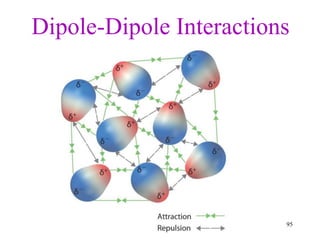
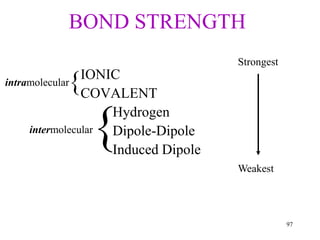
Chemical bonds result from the attraction between positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons. There are three main types of bonding: ionic, metallic, and covalent. Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms to form ions with opposite charges that are attracted to each other. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between nonmetal atoms. Molecules form through covalent bonds and have molecular formulas that describe the number and type of atoms present. The shape and polarity of molecules can be predicted from their Lewis structures.





![1. Ionic Bonding
• Always formed between metal cations
and non-metals anions
• Cations are ions that are positively
charged. Anions are ions that are
negatively charged
• The oppositely charged ions stick like
magnets
[METALS ]+ [NON-METALS ]-
Lost e- Gained e- 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/covalentbonding-230320031753-b4800104/85/Covalent-Bonding-pptx-6-320.jpg)