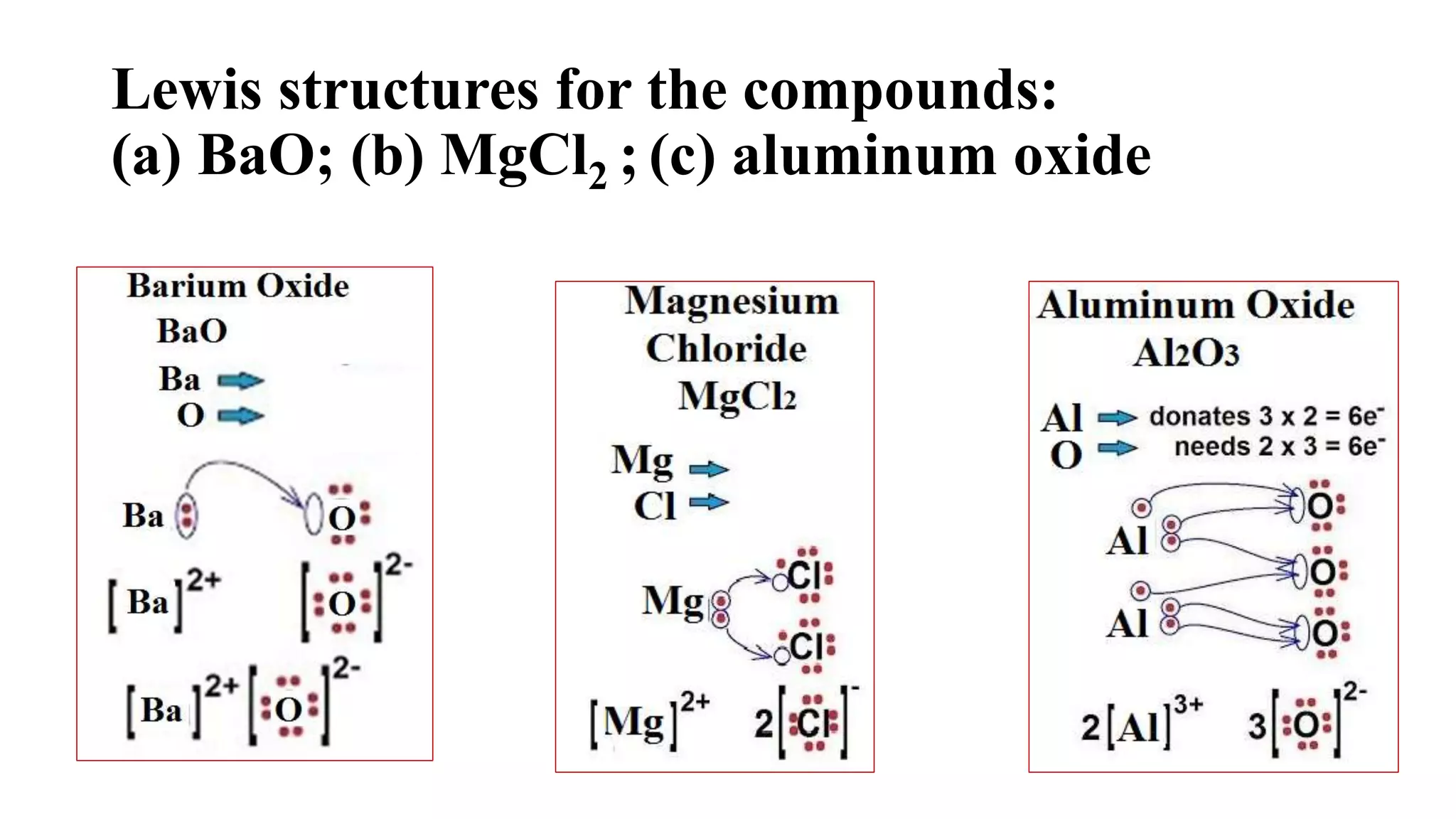
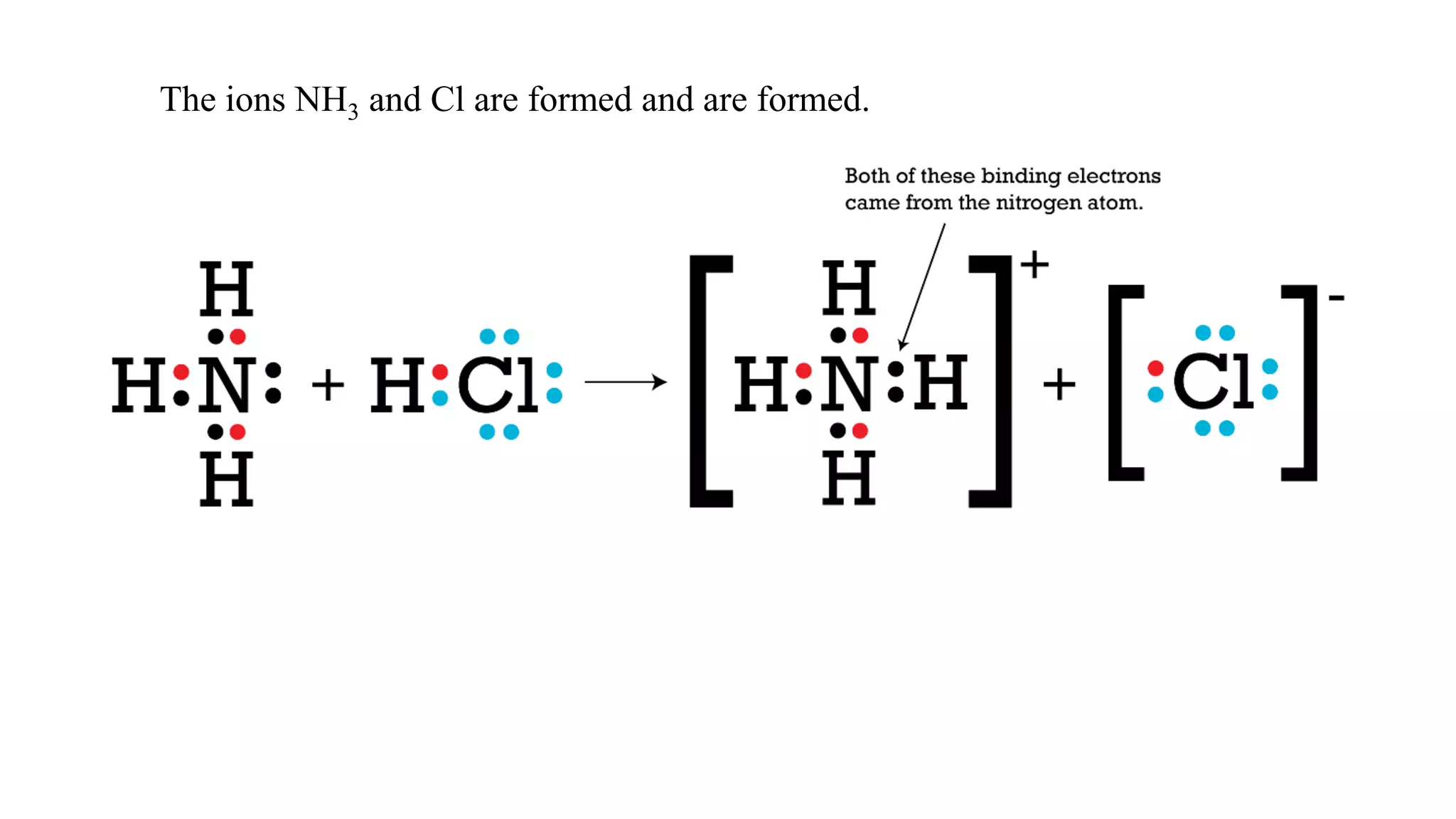
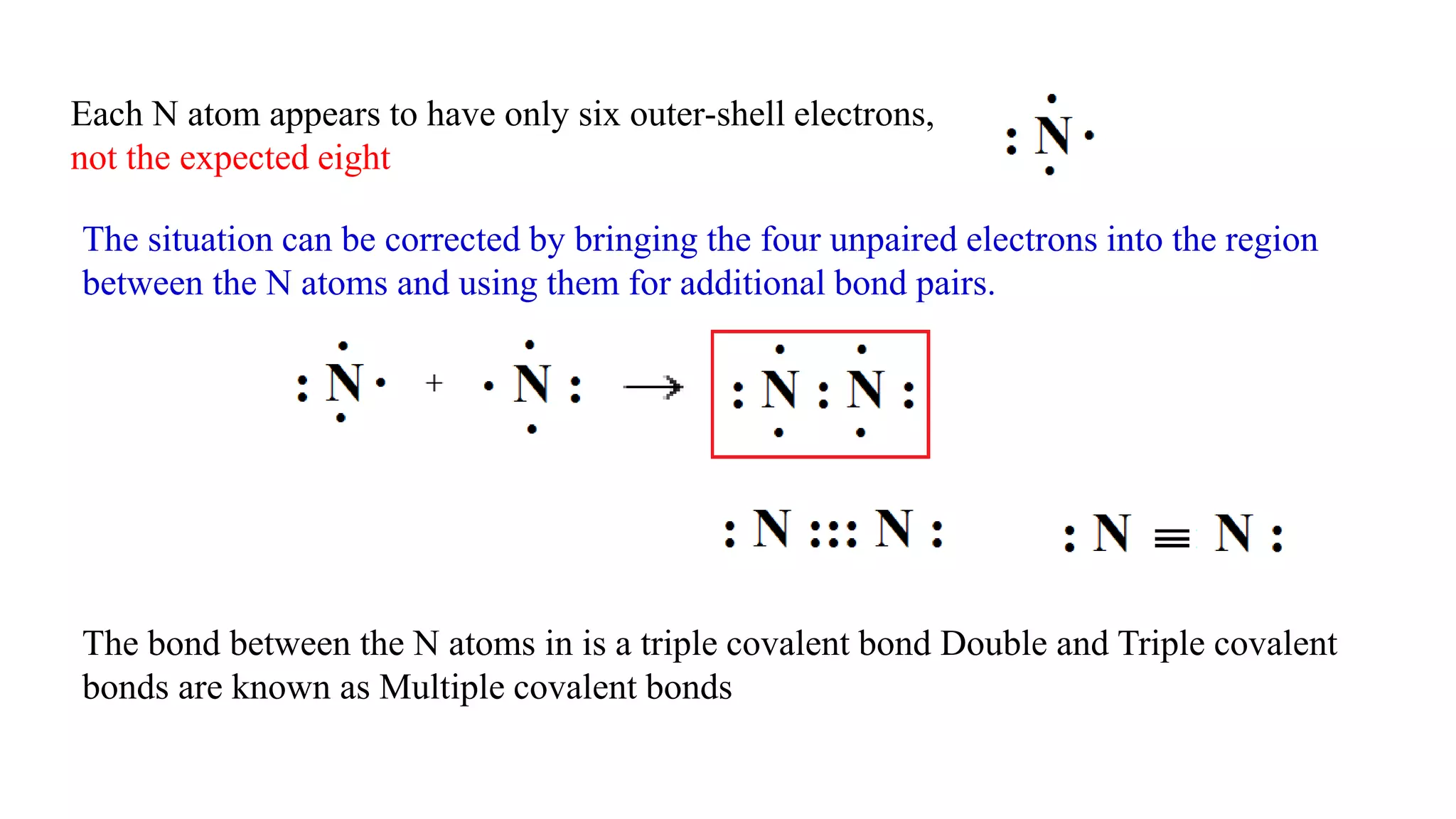
The document discusses chemical bonding theories, primarily focusing on Lewis's theory, which explains how electrons are transferred or shared to form ionic and covalent bonds. It includes details about Lewis structures, coordinate covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds, and electronegativity, emphasizing how these concepts impact the stability and characteristics of molecules. Additionally, it notes the relationship between electronegativity and the metallic/nonmetallic character of elements in the periodic table.