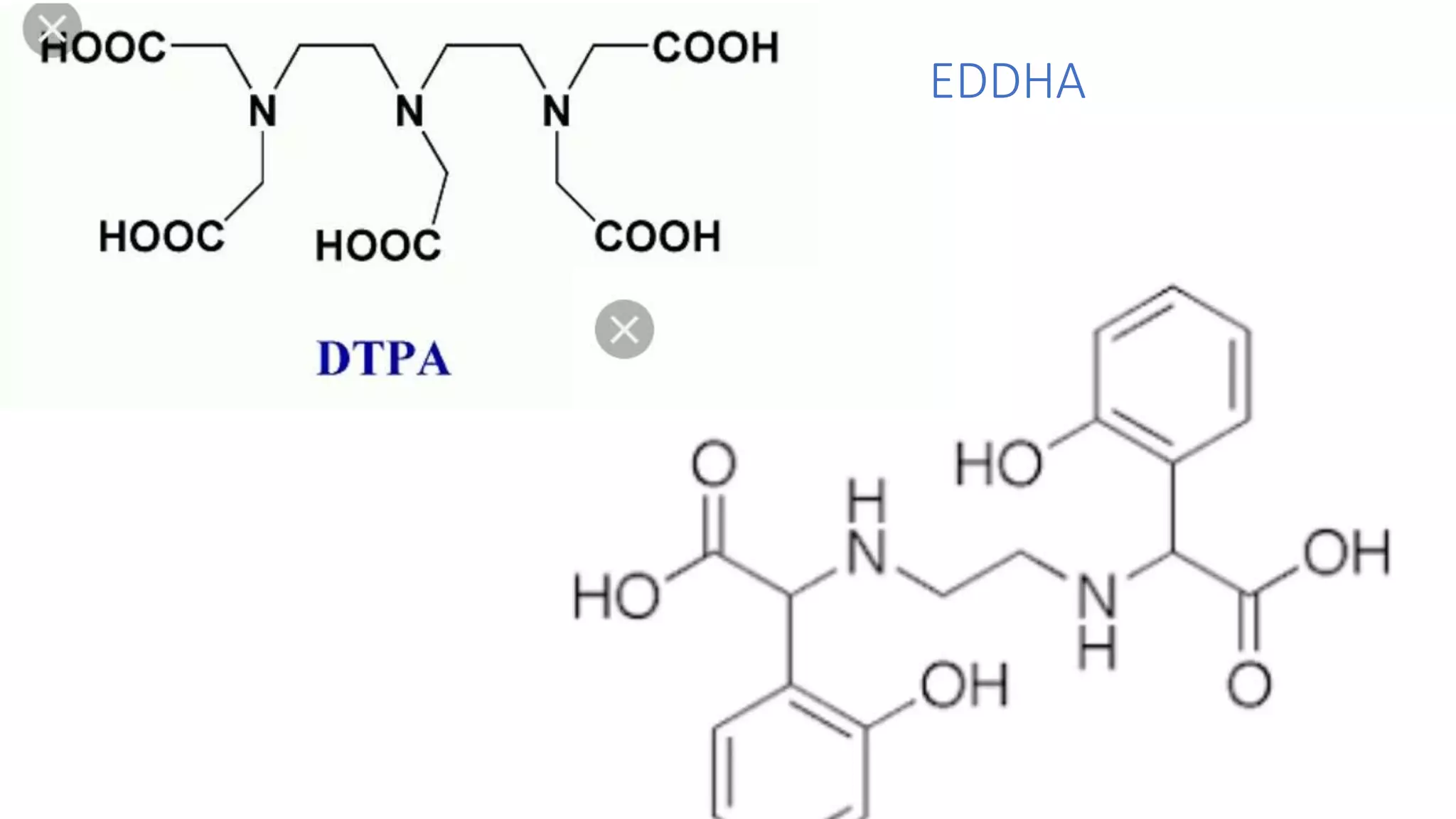
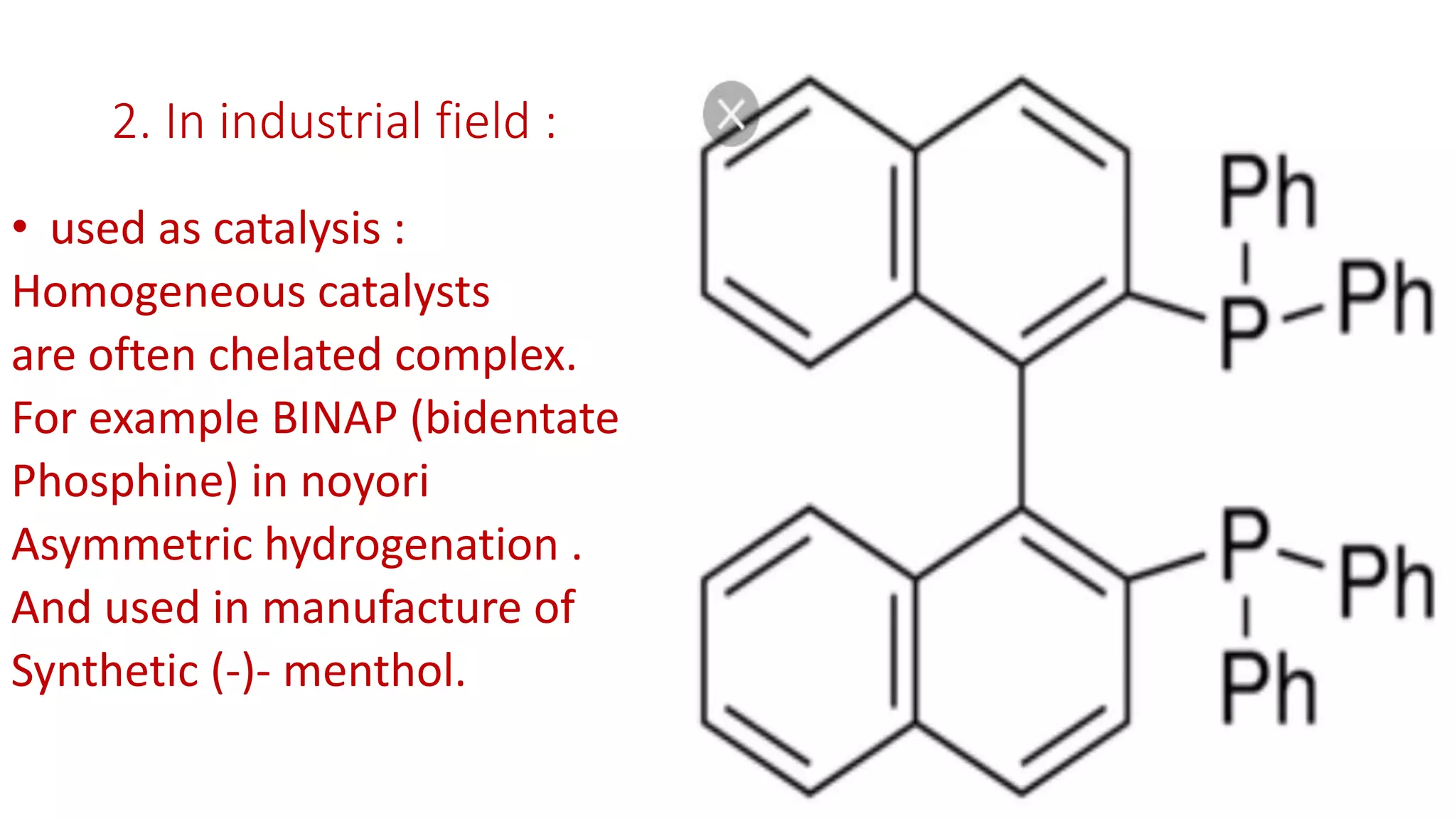
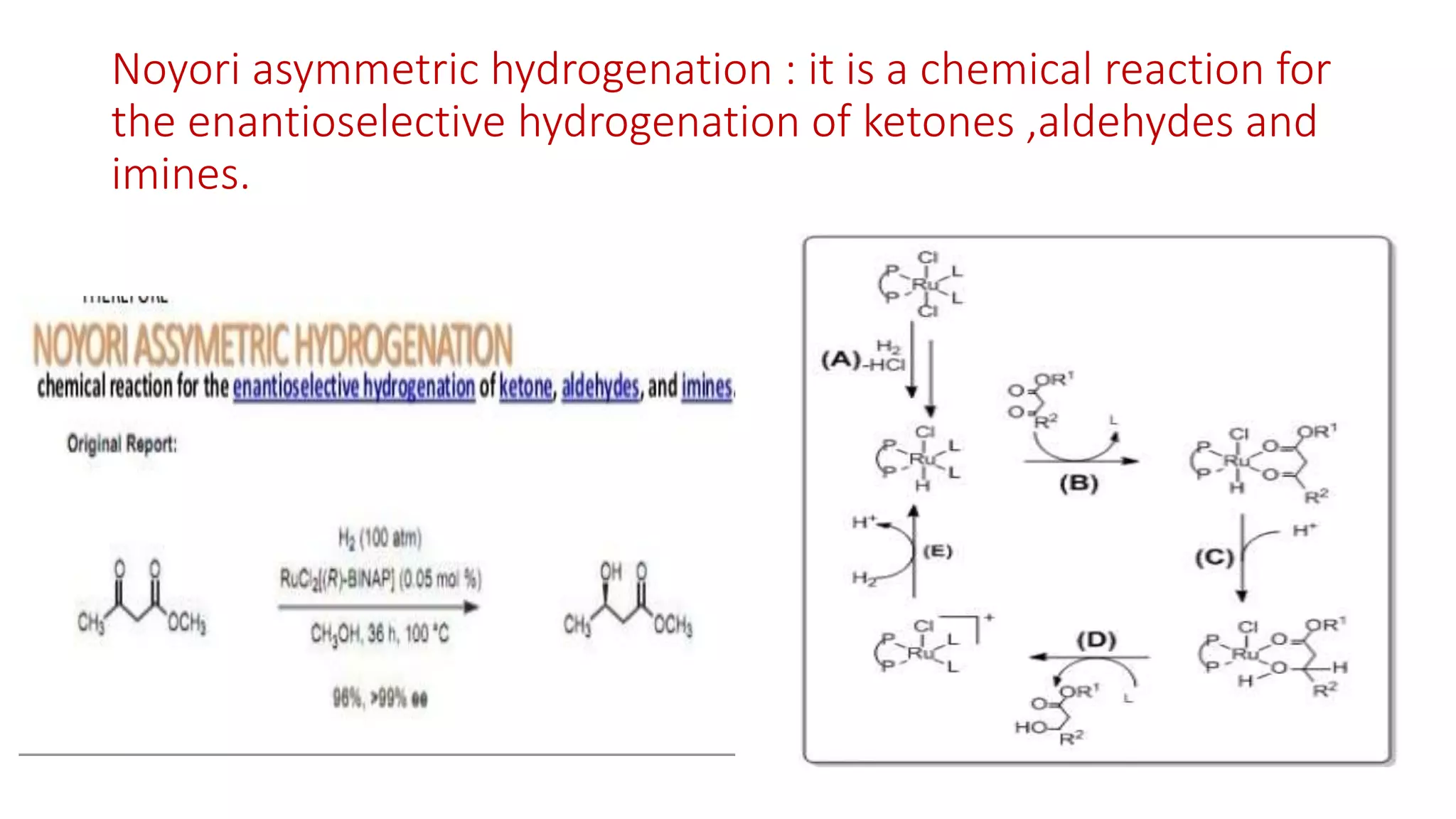
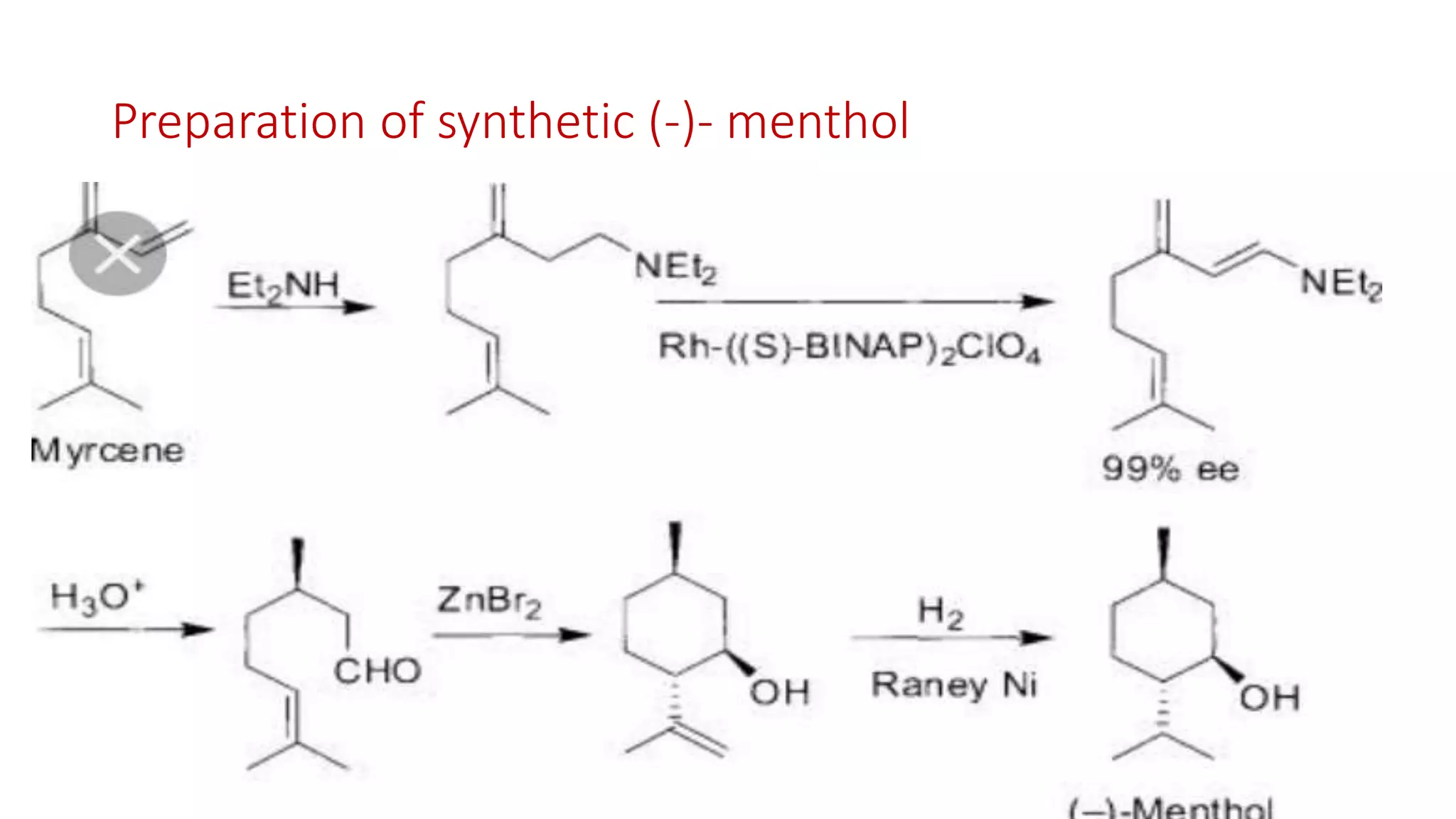
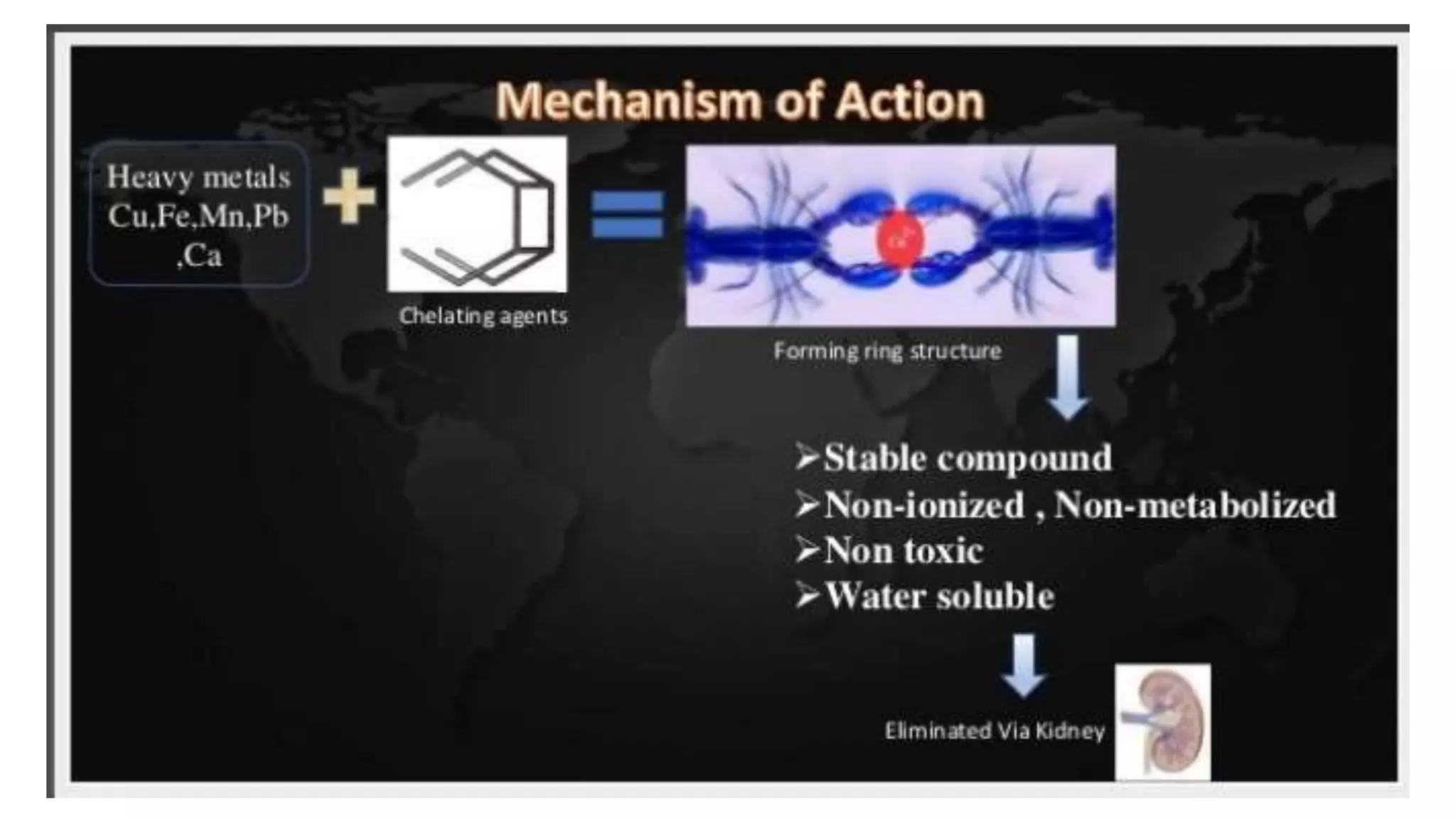
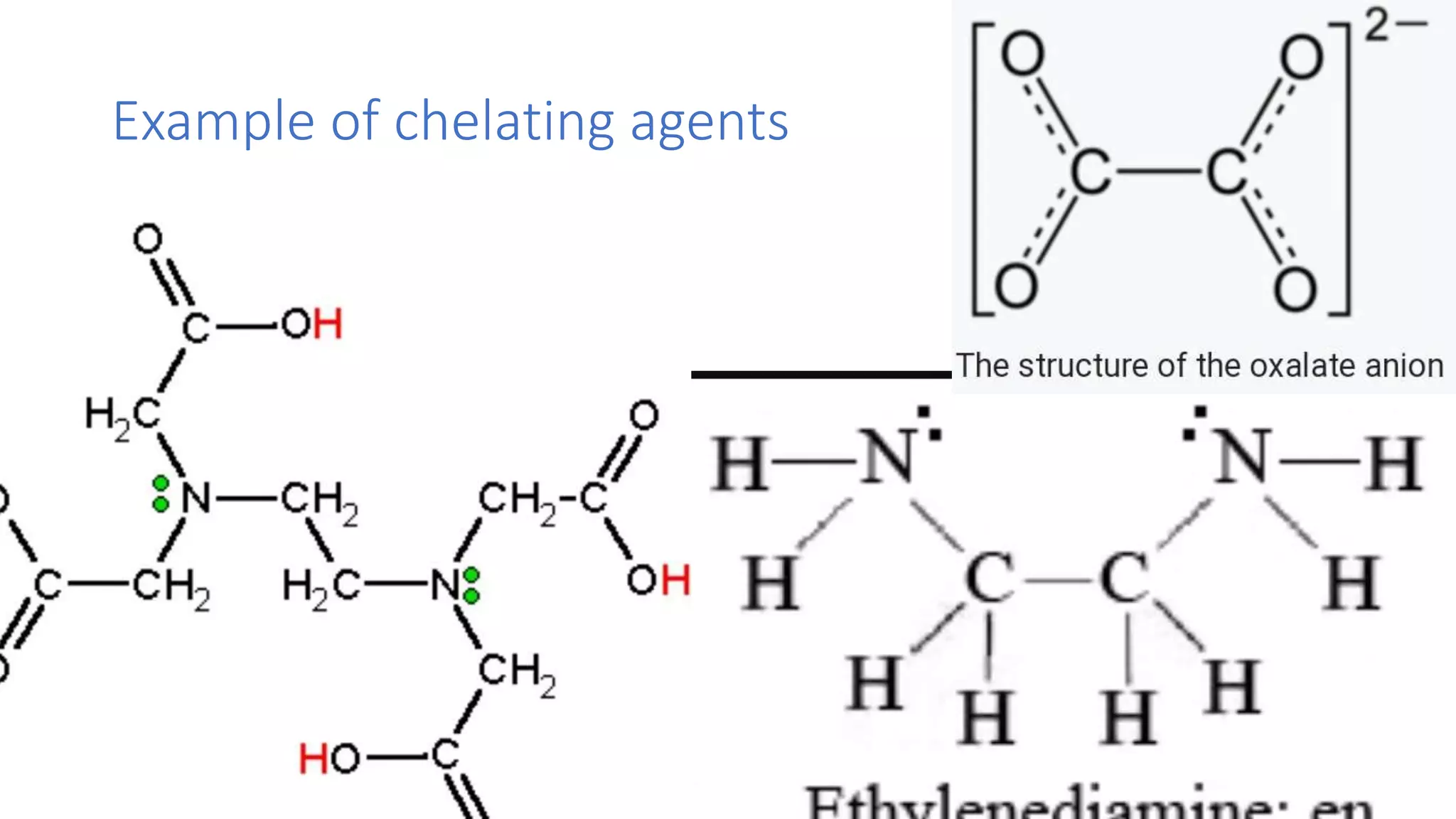
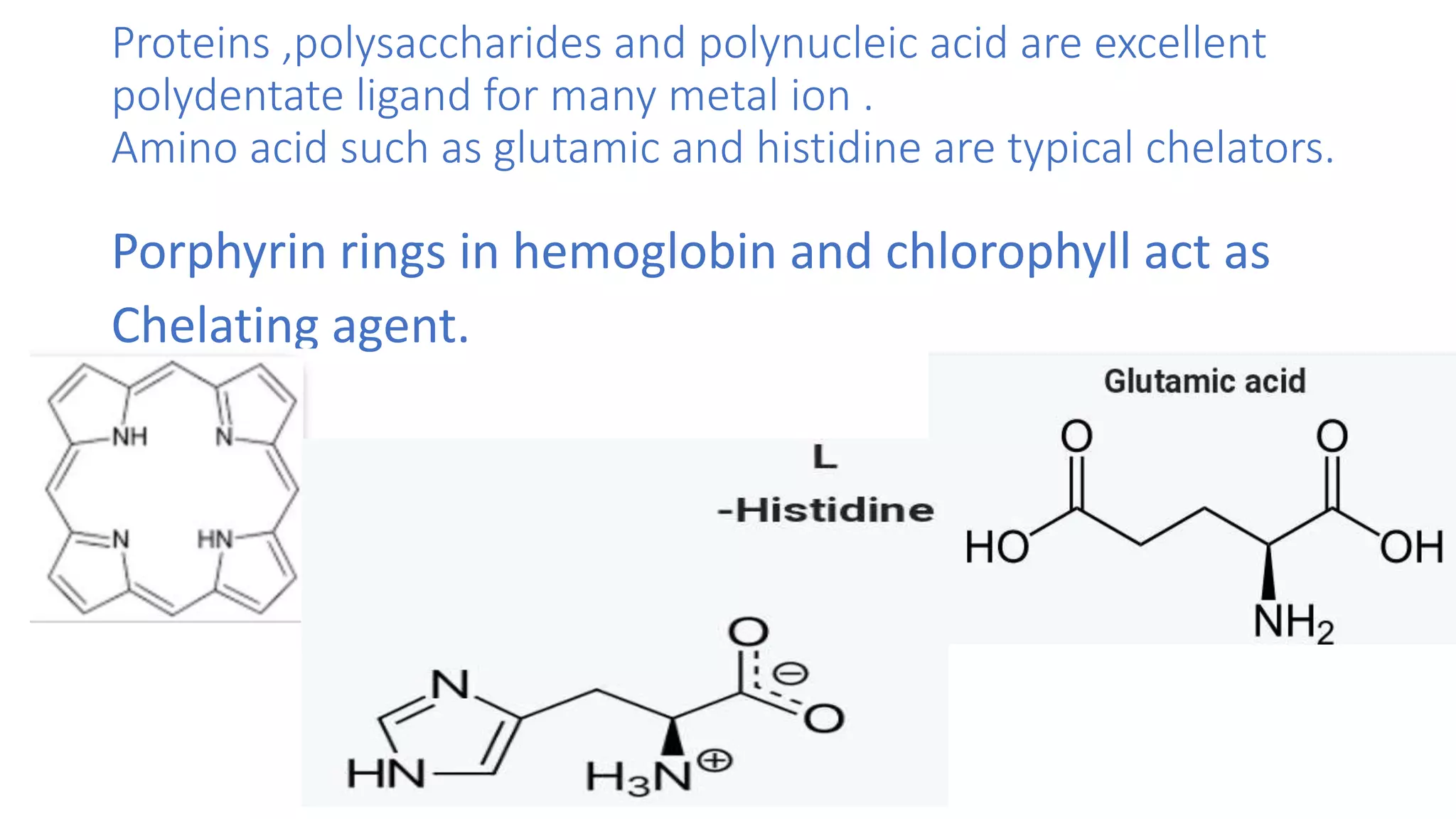
The document discusses chelating agents, which are chemical compounds that can form multiple bonds to a single metal ion, forming stable, soluble complexes. It provides examples of chelating agents like ethylenediamine and EDTA. Chelating agents are classified based on the number of atoms that coordinate with the metal ion, and have properties like high solubility in water and low affinity for calcium. Applications of chelating agents include use in agriculture to provide micronutrients to plants, industrial uses like catalysis and metal extraction, and medical uses such as chelation therapy to remove heavy metals from the body. However, chelating agents can also have drawbacks like redistributing toxic metals or losing essential metals.



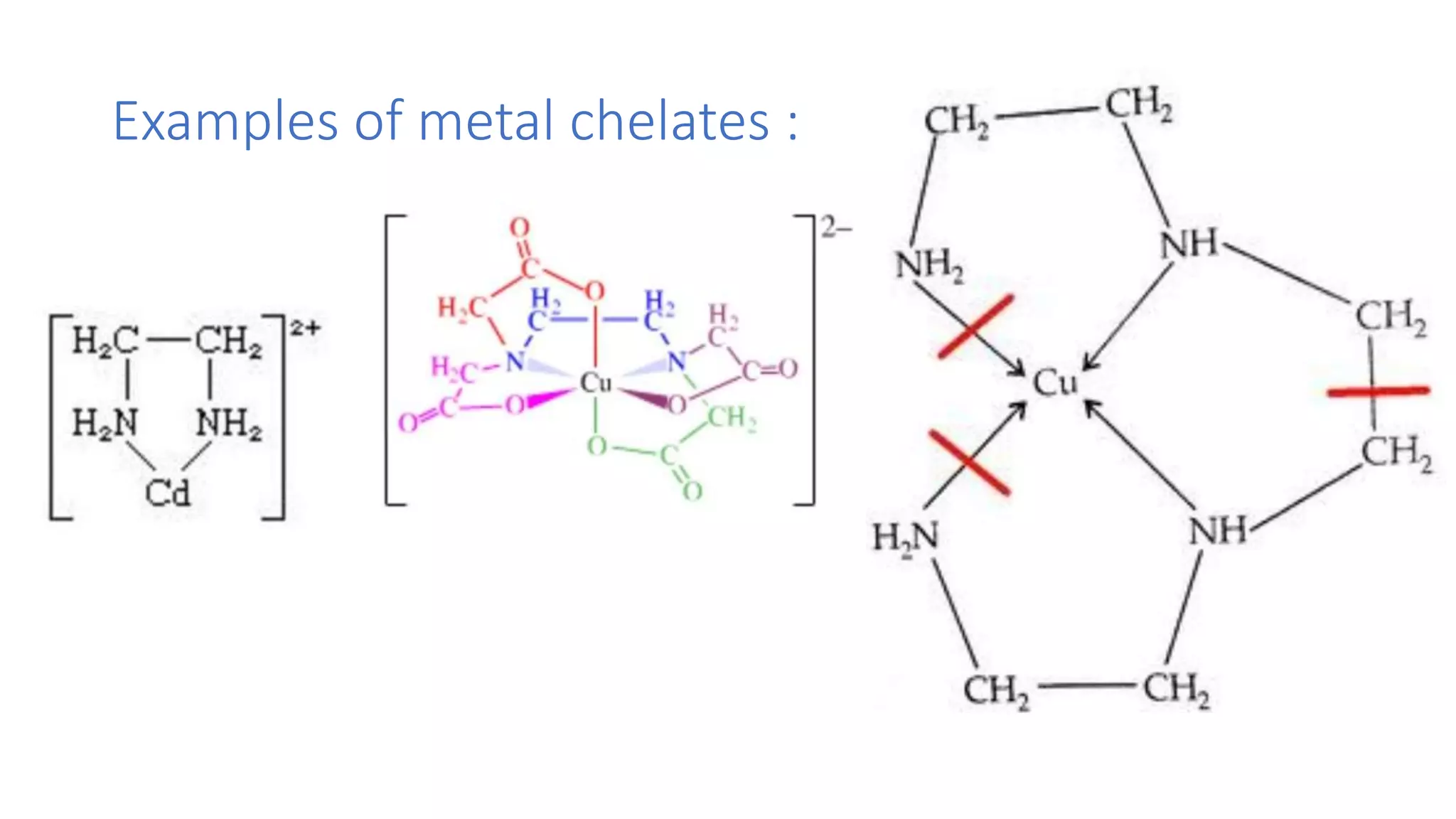

![Chelating effect :chelating effect is the enhanced affinity of
chelating ligands for a metal ion compared to the affinity of
non chelating (monodentate) ligand for the same metal.greater
the chelating effect greater will be stability of the resulting
complex. For example [cu(en)] have higher stability constant
than [cu(Me NH2)].
Some properties of an ideal chelating agent are
1. Highly soluble in water.
2. Low affinity for calcium .
3. form non toxic complex with toxic metal.
4. They are biologically inert.
5. More affinity for metals than the endogenous
ligand.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-191111131623/75/Chelating-agents-and-it-s-application-8-2048.jpg)