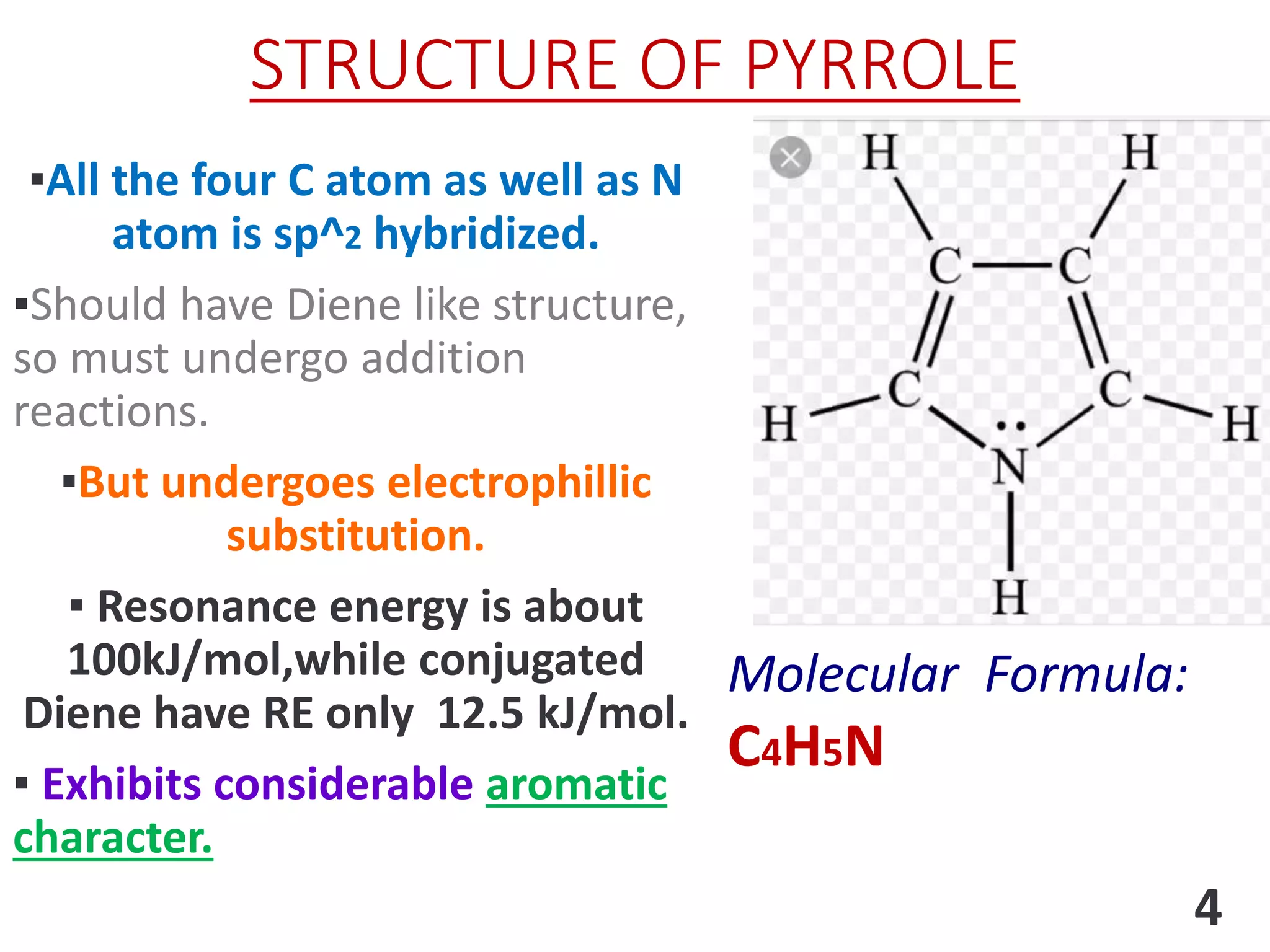
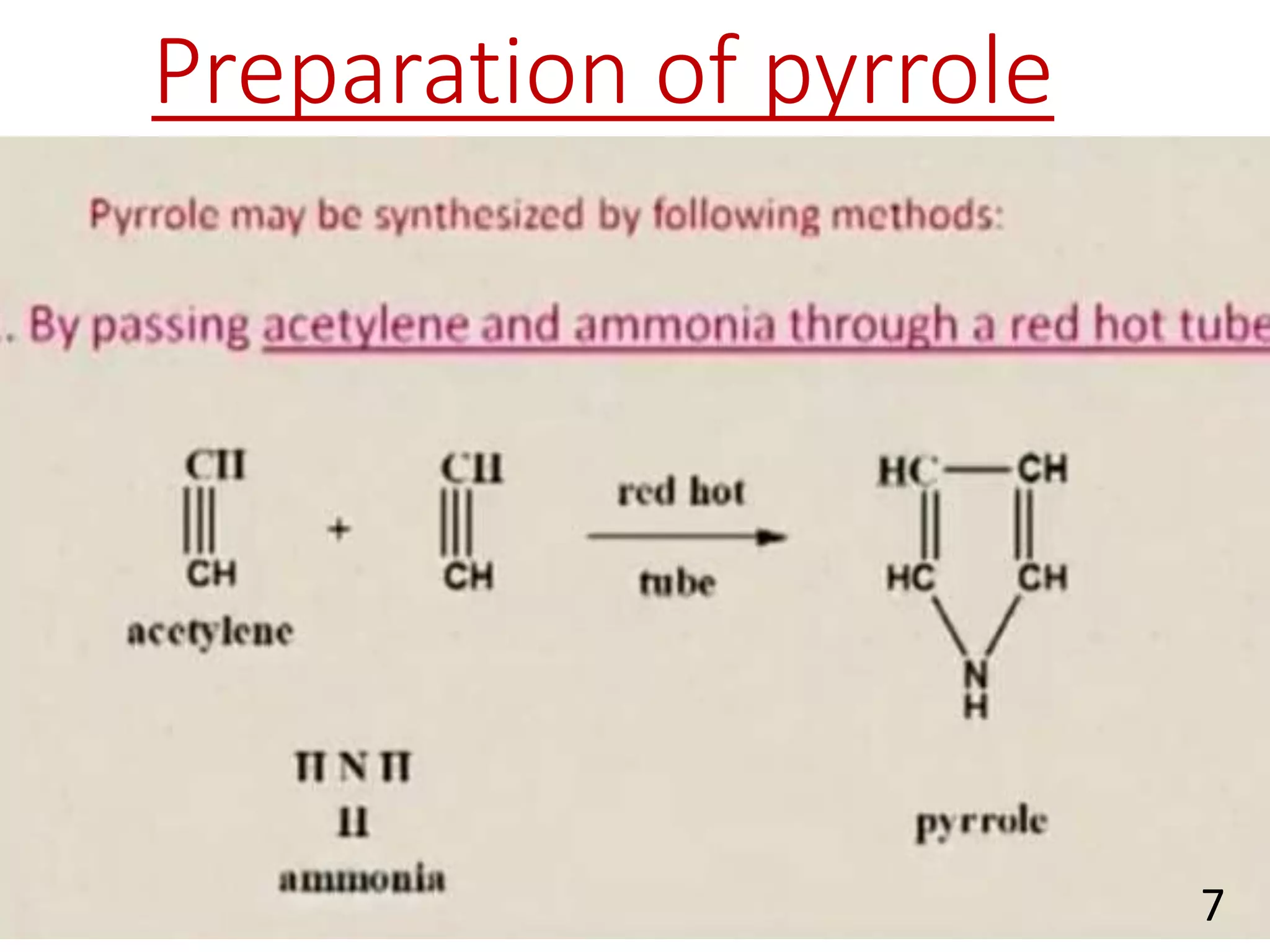
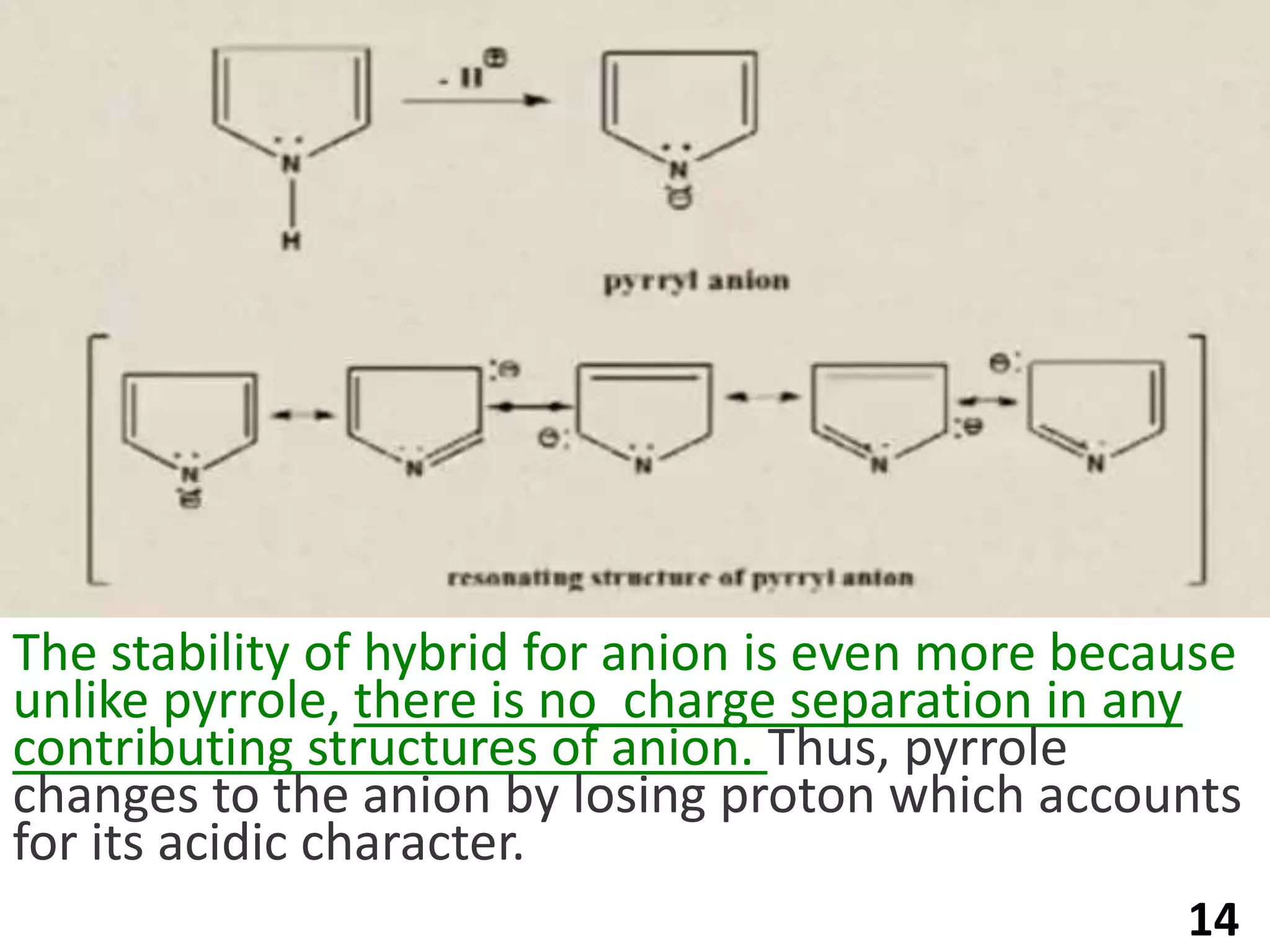
Pyrrole is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic compound with the formula C4H4NH. It has a planar structure that is aromatic due to delocalized pi electrons. Pyrrole is prepared through various methods and undergoes electrophilic substitution and other reactions. It is a weak base and acid and has applications as an intermediate in pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other organic compounds.