Embed presentation
Downloaded 54 times

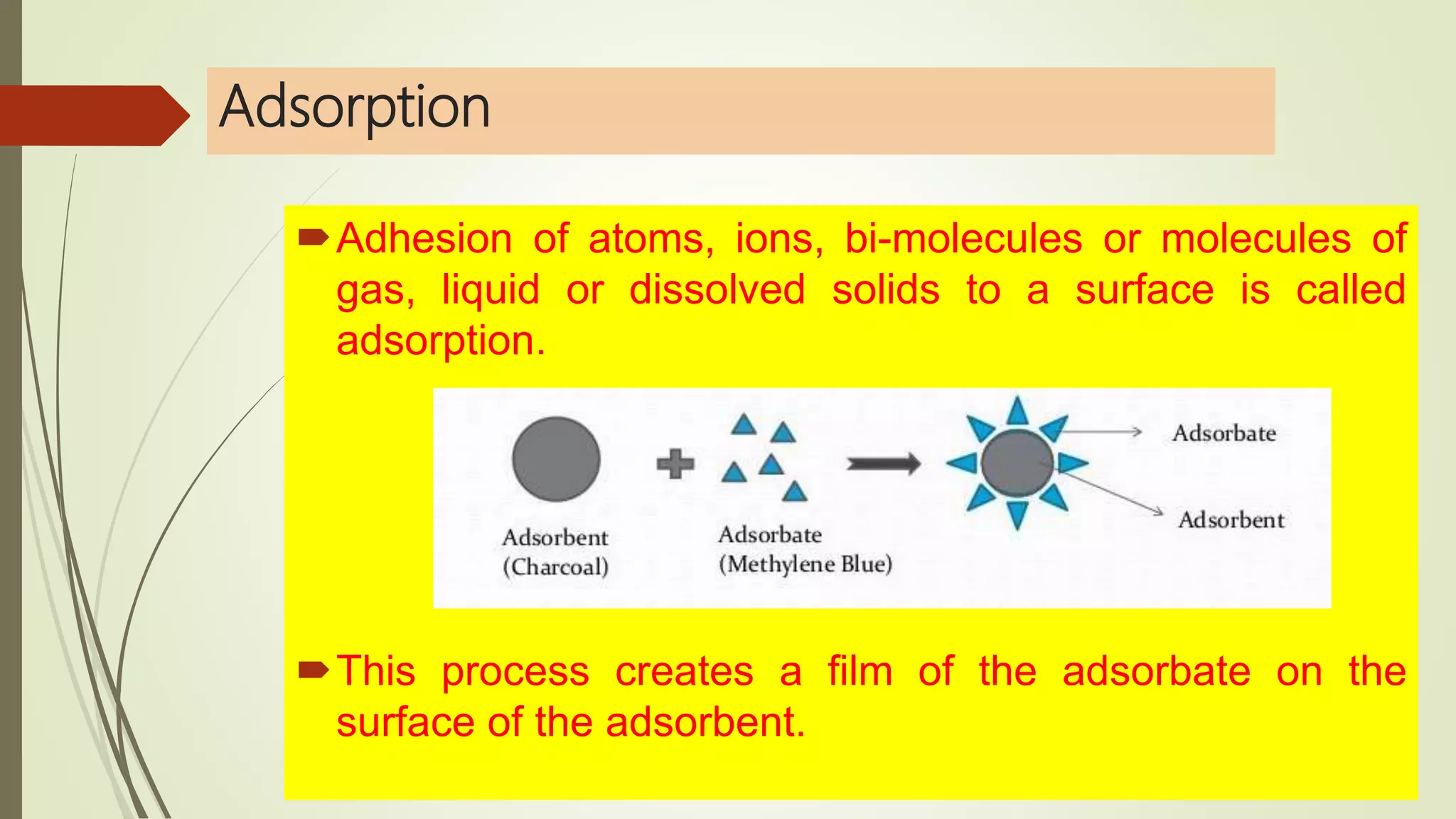

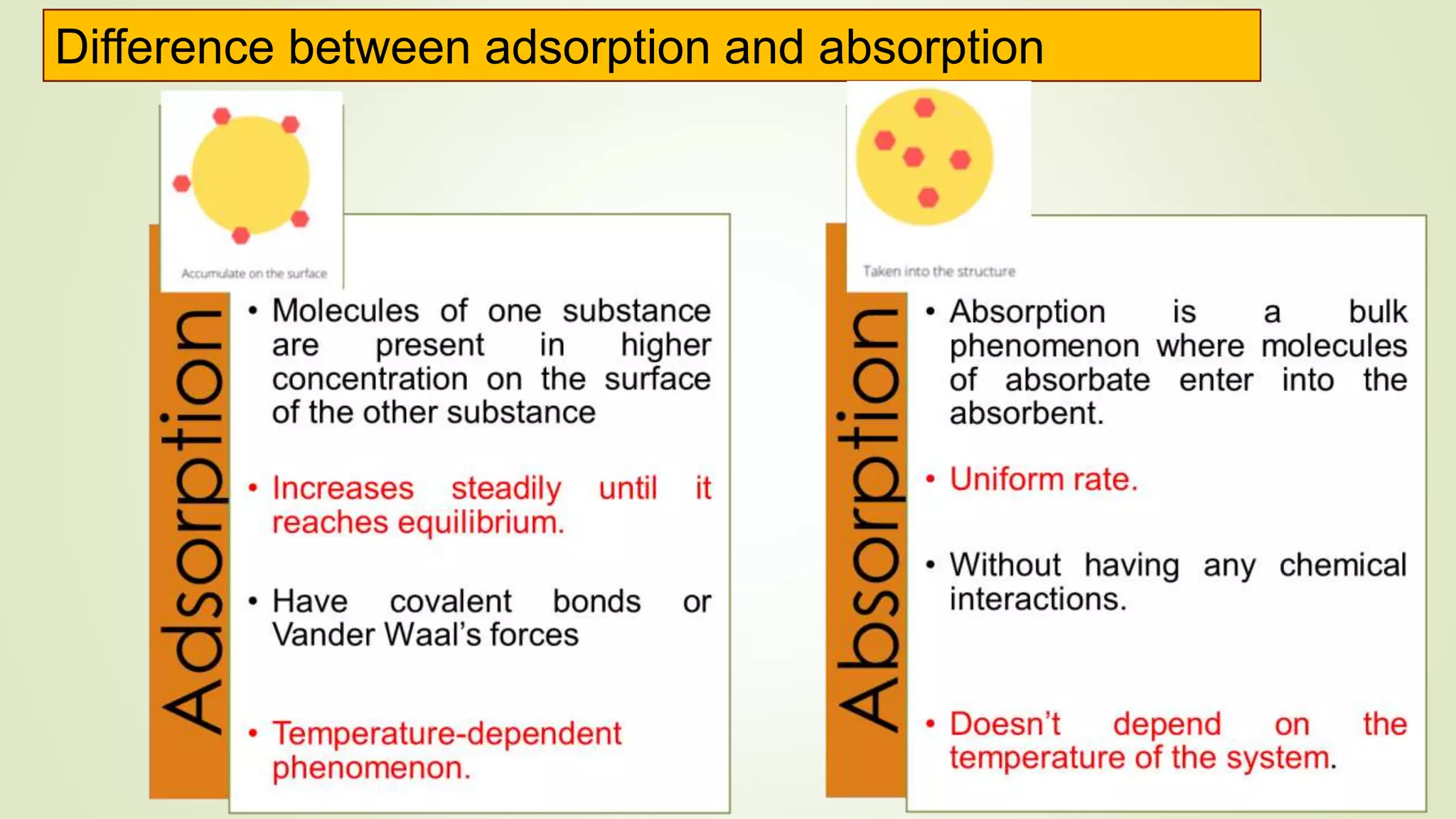



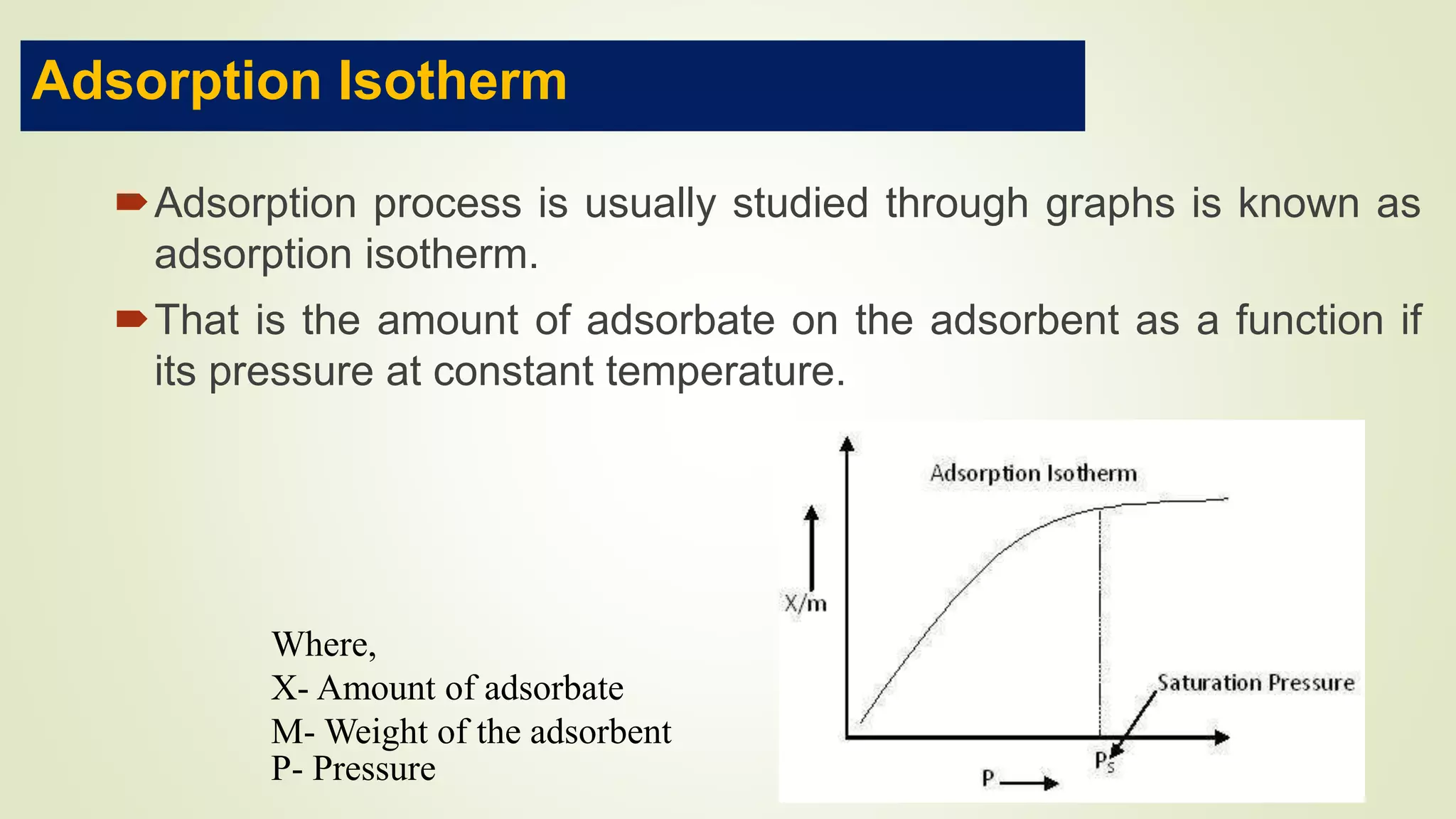
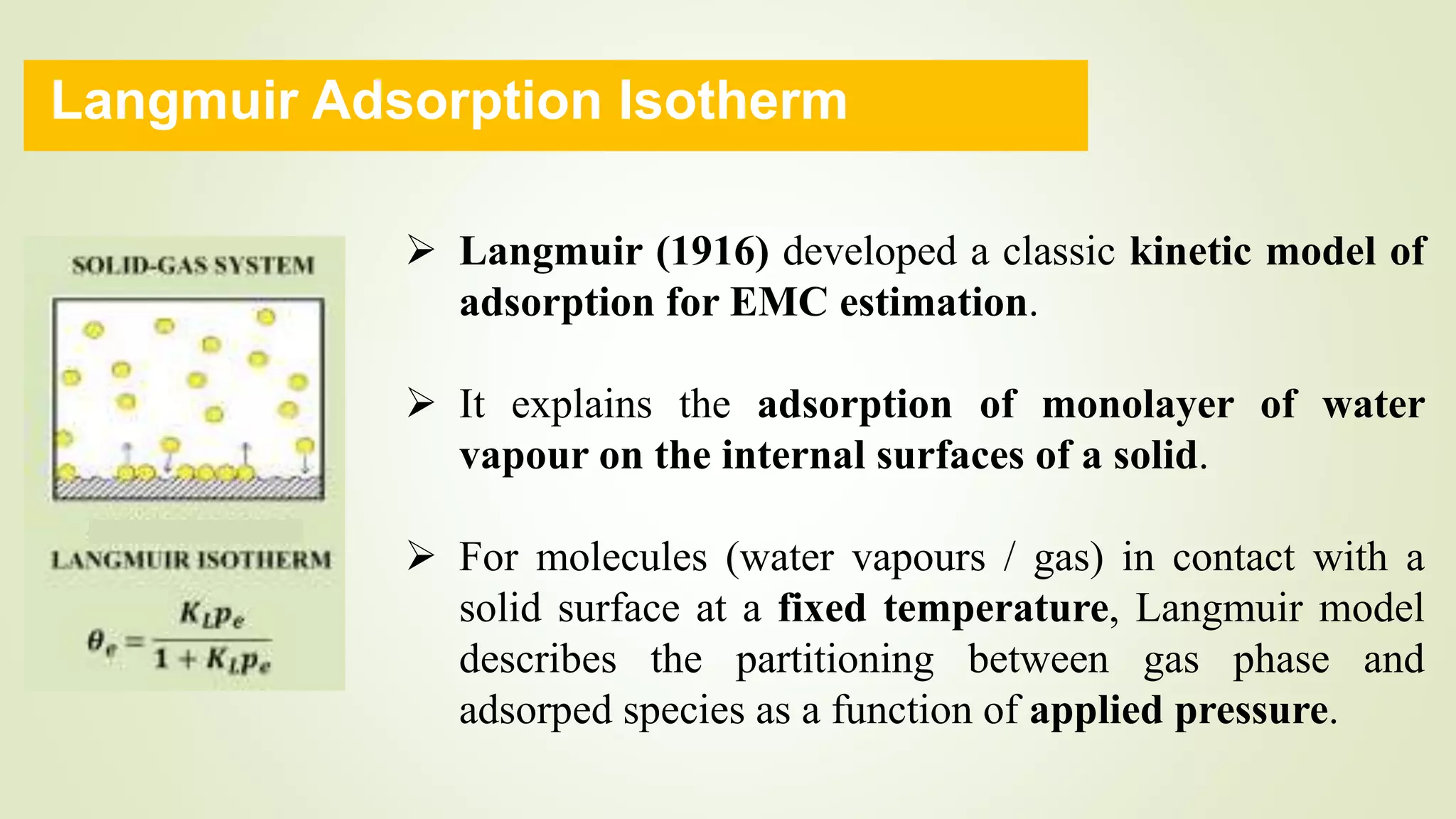

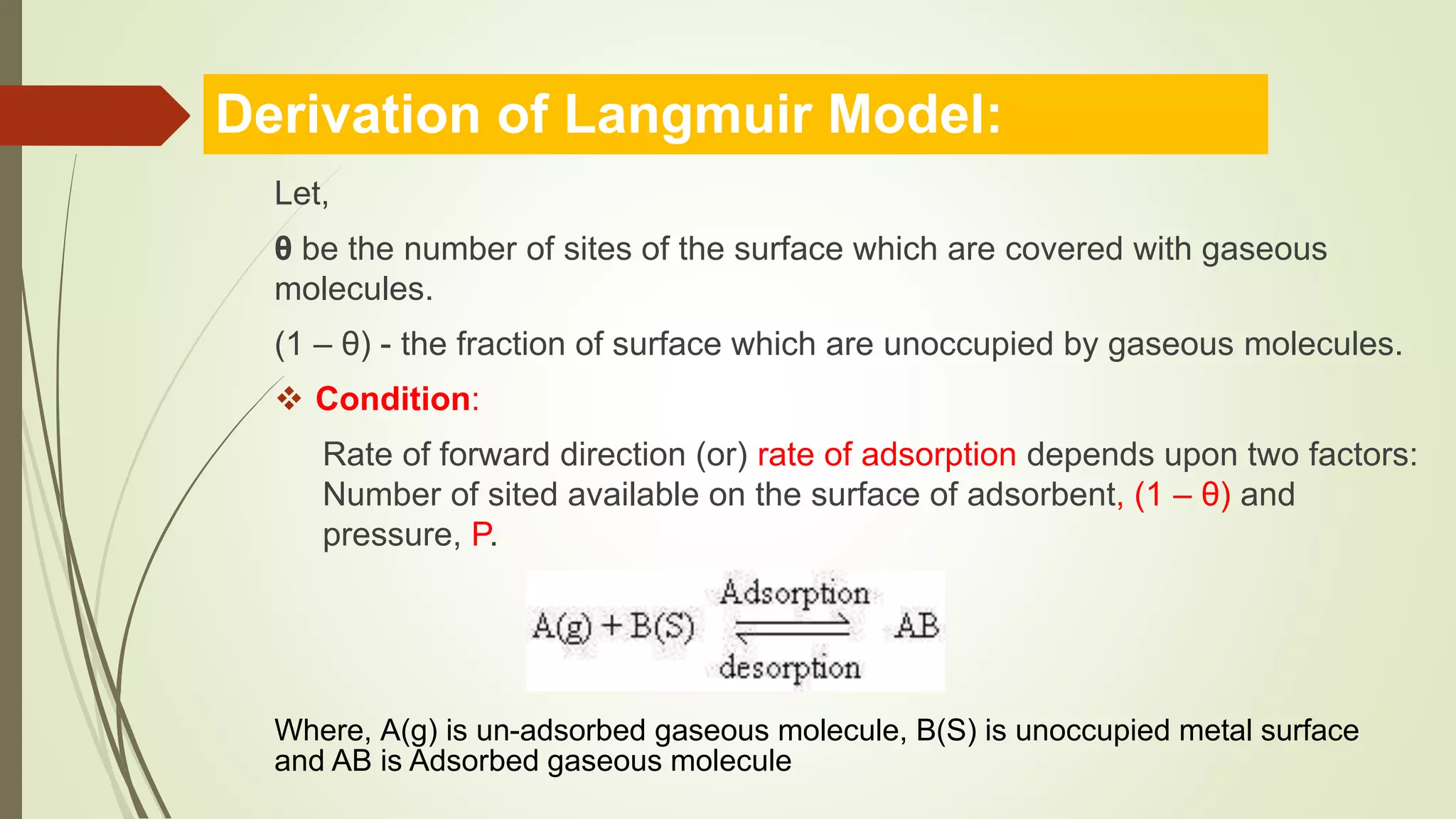







This document discusses Langmuir adsorption isotherm, which explains monolayer adsorption of gases onto surfaces. It assumes adsorption occurs at specific identical sites, with no lateral interactions between adsorbed molecules. Langmuir derived an equation showing the relationship between fraction of surface coverage (θ) and gas pressure (P), based on equilibrium between adsorption and desorption rates. This model applies at low pressures and assumes only monolayer coverage, with limitations at high pressures where multilayers can form. The document also outlines assumptions, derivation of the Langmuir equation, and applications for measuring moisture adsorption.


















