1. The stability of metal complexes is affected by factors such as the nature of the central metal ion, the coordinating ligand, and the presence of ring structures. The charge, size, and ionization energy of the metal ion influence stability, as do the size, charge, and basic strength of the ligand.
2. Chelation, where a multidentate ligand bonds to the metal ion at multiple sites, generally enhances stability. Five-membered rings formed by chelation are most stable due to reduced strain. An increase in the number of chelate rings or delocalized π-electrons in ring structures also increases stability.
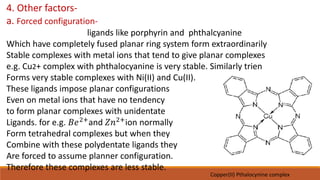
3. Other factors like forced ligand configurations, the solvent environment, and










![c. Ligand Concentration:
Some coordination complexes exist in aqueous solution only in presence of
higher concentration of coordination group. In some cases aqueous molecules
show greater coordinating tendency than the coordinating group which is
originally present.
e.g. in presence of highly concentrated solution of SCN- (thiocynate ion), the Co2+
metal ion
forms a stable blue colored coordination complex but on dilution in aqueous medium the blue
complex is destroyed and a pink aqua complex [Co(H2O)6]2+ is formed and then by further
addition of ligand (SCN-) pink colour disappears.
[Co(SCN)4]2−
+ H2O → [Co(H2O)6]2+
+ + 4SCNˉ
Blue Pink
The colour change indicates that there is a competition between H2O/SCN- in
formation of complex with Co(II) ion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idbqwu2eracae3qdmac9-factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-lokesh-jangid-sem-2-230203155121-8a9e8a04/85/Factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-11-320.jpg)
![3. Presence of ring structure (chelation)-
a. Chelate Effect:
The process of forming metal chelate by the attachment of multidentate ligand
with central metal ion in which ligand act as chelating agent is known as
chelation. Chelation is expressed by the following unidentate and bidentate
ligand reaction.
M + 2L→ ML2 K=[ML2]/[M][𝐿]2
M + L-L → M-L-L or K=
[𝑀−𝐿−𝐿]
𝑀 [𝐿−𝐿]
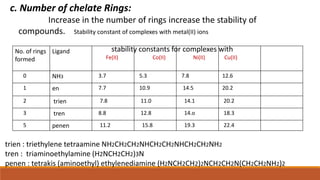
Multidentate ligands form more stable coordination compounds than
monodentate ligands. Following factors are of great importance in chelate
formation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idbqwu2eracae3qdmac9-factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-lokesh-jangid-sem-2-230203155121-8a9e8a04/85/Factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-12-320.jpg)



![d. Entropy Effect –
the chief factor responsible for the stability of the chelate
ring is the entropy change. Considering the electronic effect of the
donor atom to be the same in the monodentate and the bidentate
ligands, it can be seen that the dissociation of a monodentate from
the complex will be higher than that in the chelating bidentate.
The dissociation of the M-L bond in monodentate will release
The ligand completely from the coordination sphere of the metal,
So that it can be easily swept off by the solvent. but the dissociation
Of one M-L bond for the bidentate ligand does not release the ligand
Completely (for which simultaneous dissociation at both ends is
required).hence the stability constant for metal chelate must be
Higher.
[Co(NH3)6]3++ 3en → [𝐶𝑜 𝑒𝑛 3]2++ 6NH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idbqwu2eracae3qdmac9-factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-lokesh-jangid-sem-2-230203155121-8a9e8a04/85/Factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-17-320.jpg)

![c. Steric effect-
In some cases the clashing of groups on two coordinated
ligands will result in distortion of bond angles and a decrease in stability is
the phenomenon of F-strain, described by Brown [27], as applied to
coordination compounds.
As steric effect is decreasing, the stability of a complex is increasing.
Due to steric effect in Ni(II) complexes with 2-methyl 8- hydroxy quinoline
are less stable than complexes with 8-hydroxy quinoline because of the
steric hindrance caused by the methyl
group adjacent to the site of coordination.
Similarly complexes of ethylene diamine are more stable than its
tetramethyl derivatives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idbqwu2eracae3qdmac9-factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-lokesh-jangid-sem-2-230203155121-8a9e8a04/85/Factors-affecting-stability-of-metal-complexes-20-320.jpg)

