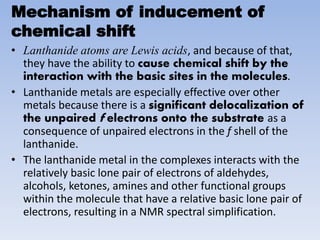
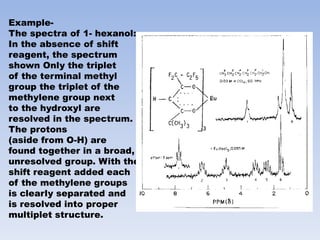
The document discusses the importance of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and the use of shift reagents to resolve signal overlap in complex organic compounds. It details the history, mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages of lanthanide shift reagents, which enhance spectral resolution by causing chemical shifts through interactions with specific nuclei. Ultimately, these reagents simplify the interpretation of NMR spectra, allowing for more accurate structural analysis of organic and organometallic compounds.