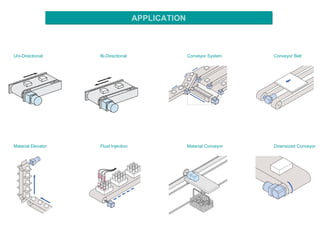
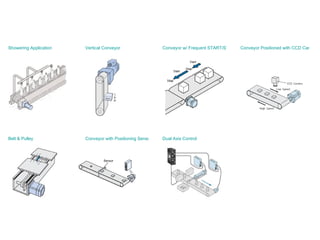
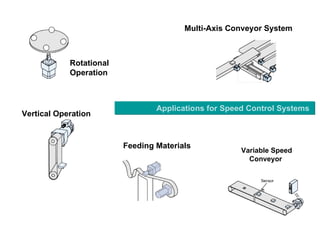
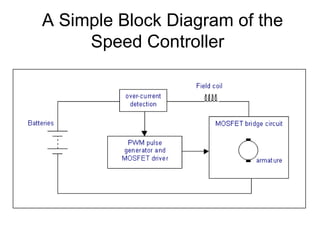
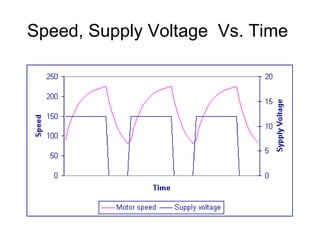
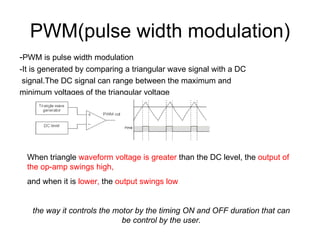
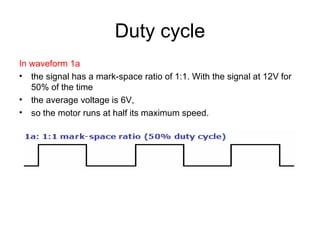
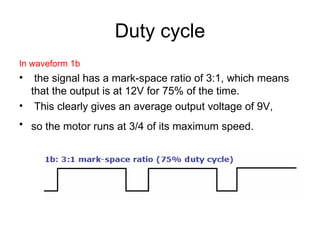
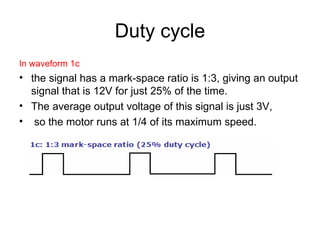
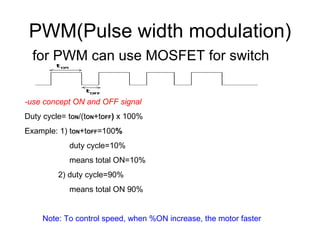
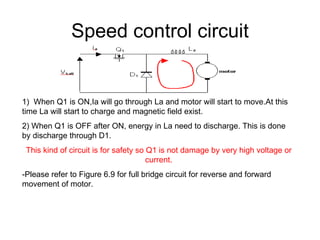
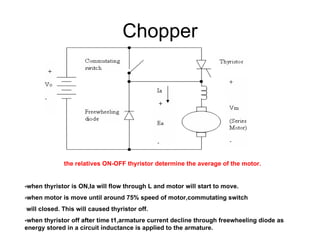
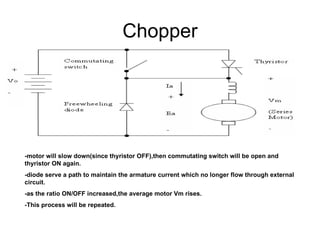
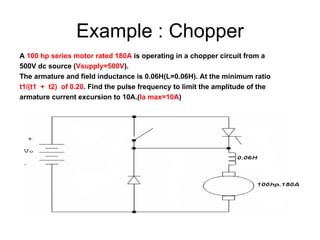
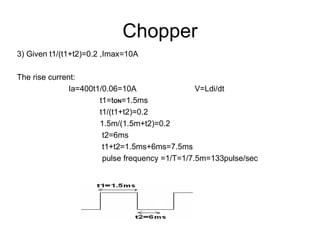
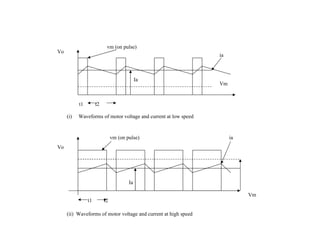
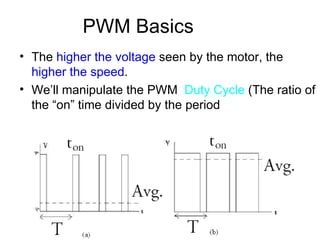
The document discusses speed control of DC motors using pulse width modulation (PWM). PWM controls motor speed by varying the duty cycle, or ratio of on/off time, of a pulsed voltage signal provided to the motor. A higher duty cycle results in a higher average voltage and faster motor speed. Specific applications discussed include conveyor systems and examples of calculating duty cycle and pulse frequency needed to control motor current within limits.