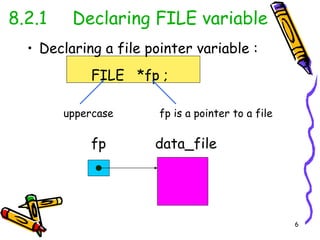
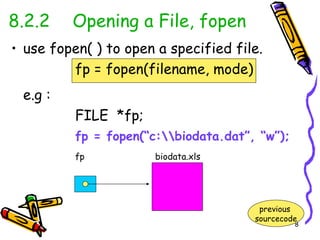
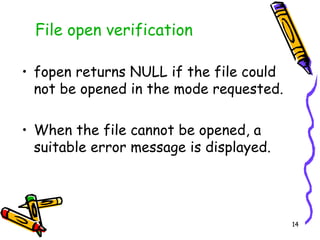
This chapter discusses file processing in C programming. It introduces file input/output (I/O) operations, including declaring FILE variables, opening and closing files, reading from and writing to files, and checking for end of file. The key steps are to declare a FILE pointer variable, use fopen() to open a file, perform file I/O operations like fprintf() and fscanf(), and close the file using fclose(). File opening is verified by checking if fopen() returns NULL. End of file is detected using the feof() function.




![/*a program that able to read name & age and print the data in data file named biodata.dat*/ #include<stdio.h> void main() { FILE *failnama; failnama=fopen("c:\\biodata2.dat","w"); char nama[20]; int umur; fputs("Nama\t umur\n",failnama); fputs("=========================\n",failnama); for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) { printf("Nama:"); scanf("%s",nama); printf("Umur:"); scanf("%d",&umur); fprintf(failnama,"%s\t %d\n",nama,umur); } fclose(failnama); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-7-320.jpg)


![mode (r) /*a program that read the data from biodata.dat*/ #include<stdio.h> void main(){ char nama[30]; int umur; FILE *failnama; failnama=fopen("c:\\biodata.dat","r"); printf("Nama\t umur\n"); printf("--------------------\n"); for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) { fscanf(failnama,"%s\t %d\n",nama,&umur); printf("%s\t %d\n",nama,umur); } fclose(failnama); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-11-320.jpg)
![mode (a) //a program that able to append the data into biodata.dat #include<stdio.h> void main(){ FILE *failnama1; FILE *failnama2; failnama1=fopen("c:\\biodata.dat","a+"); failnama2=fopen(“c:\\student.xls”,”w+”); char nama[20]; int umur; for(int i=0;i<=2;i++) { printf("Nama:"); scanf("%s",nama); printf("Umur:"); scanf("%d",&umur); fprintf(failnama1,"%s\t %d\n",nama,umur); fprintf(failnama2,"%s\t %d\n",nama,umur); } fclose(failnama1); fclose(failnama2); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-12-320.jpg)

![File open verification (cont..) #include<stdio.h> #define NULL 0 void main( ) { char nama[30]; int umur; FILE *failnama; failnama = fopen("c:\\biodata.dat","r+"); if (failnama == NULL) printf("\n ERROR - Can't open the file\n"); else { printf("Nama\tumur\n"); printf("--------------------\n"); for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) { fscanf(failnama,"%s\t %d\n",nama,&umur); printf("%s\t %d\n",nama,umur); } } fclose(failnama); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-15-320.jpg)

![fgets( ) #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void main ( ) { FILE *filePtr; char person[100]; int bil; filePtr=fopen("menteri.dat","r"); /*baca string dari fail*/ for (bil=1;bil<=7;bil++) { fgets(person,strlen(person),filePtr); puts(person); } fclose(filePtr); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-19-320.jpg)
![End of File (EOF) (cont..) #include<stdio.h> #define NULL 0 void main( ) { char nama[30]; int umur; FILE *pelajar; pelajar = fopen("c:\\biodata2.dat","w+"); if (pelajar == NULL) printf("\n ERROR - Can't open the file\n"); else{ printf("Enter eof to end input\n"); printf("Nama\tumur\n"); printf("--------------------\n"); //while not end of file while ( ! feof( stdin ) ) { fprintf( pelajar, "%s %d \n", nama, umur ); printf("Nama:"); scanf("%s",nama); printf("Umur:"); scanf("%d",&umur); }//end while fclose(pelajar); }//end else }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8fileprocessing-111203174215-phpapp01/85/Ch8-file-processing-22-320.jpg)