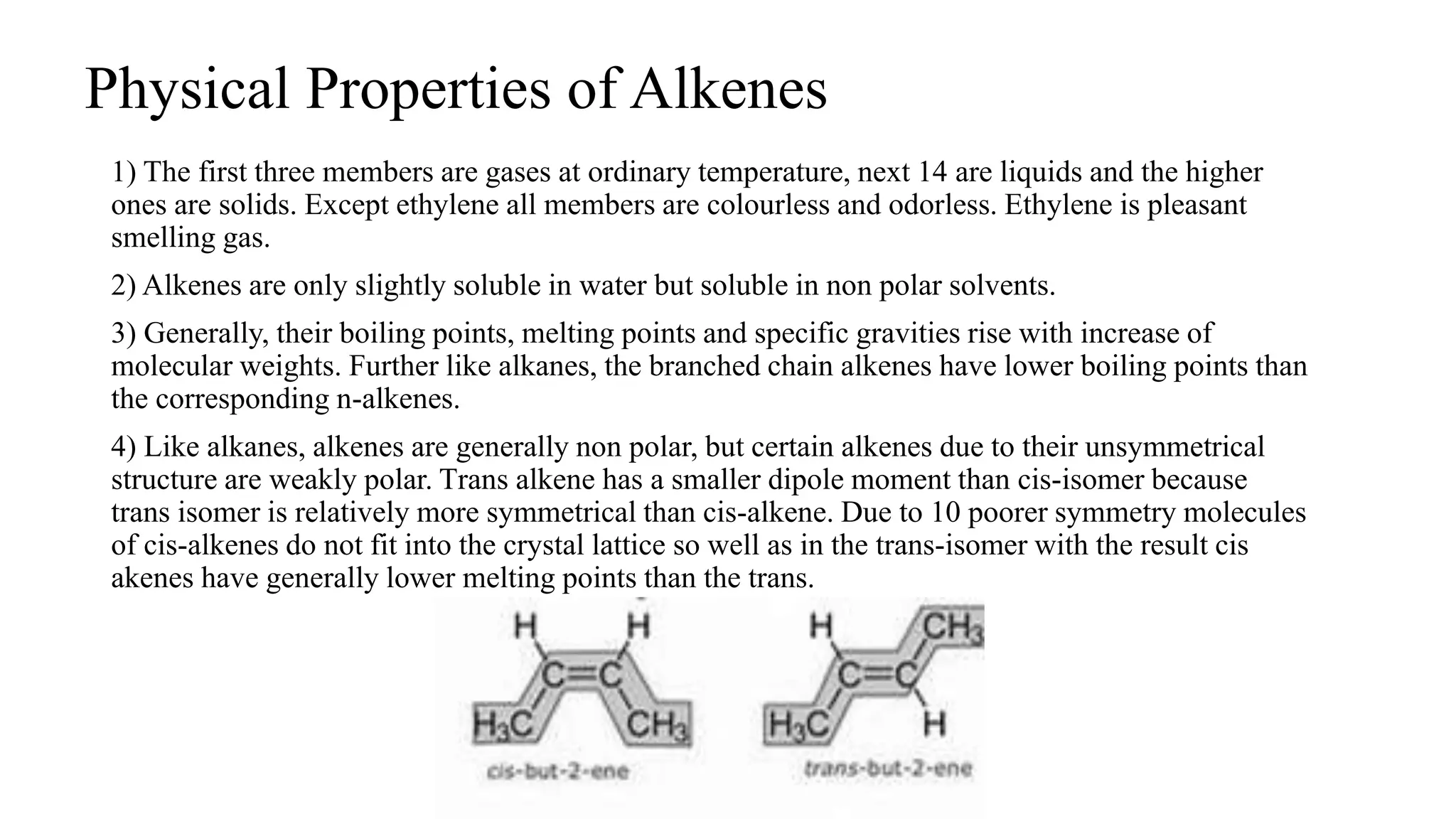
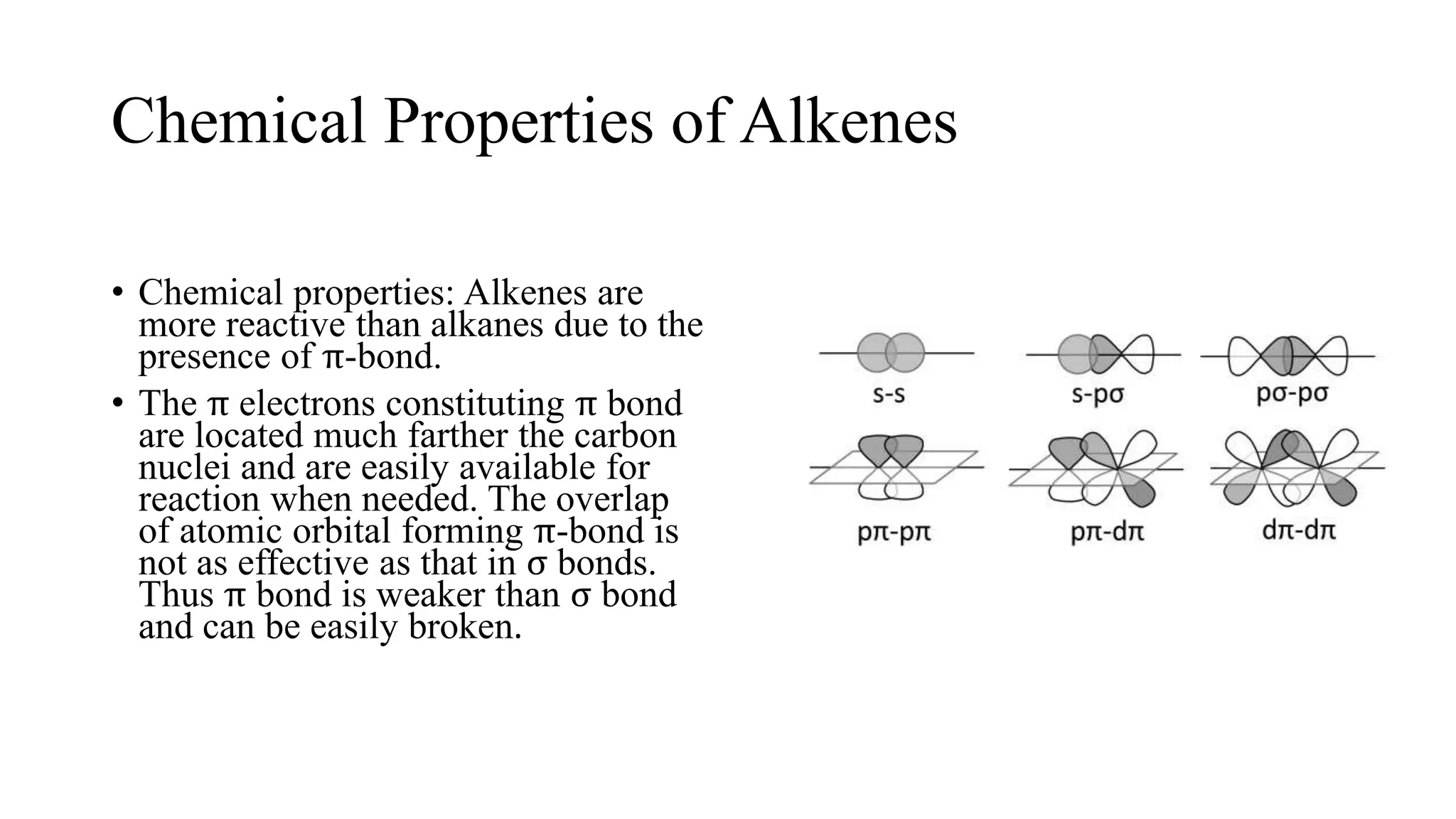
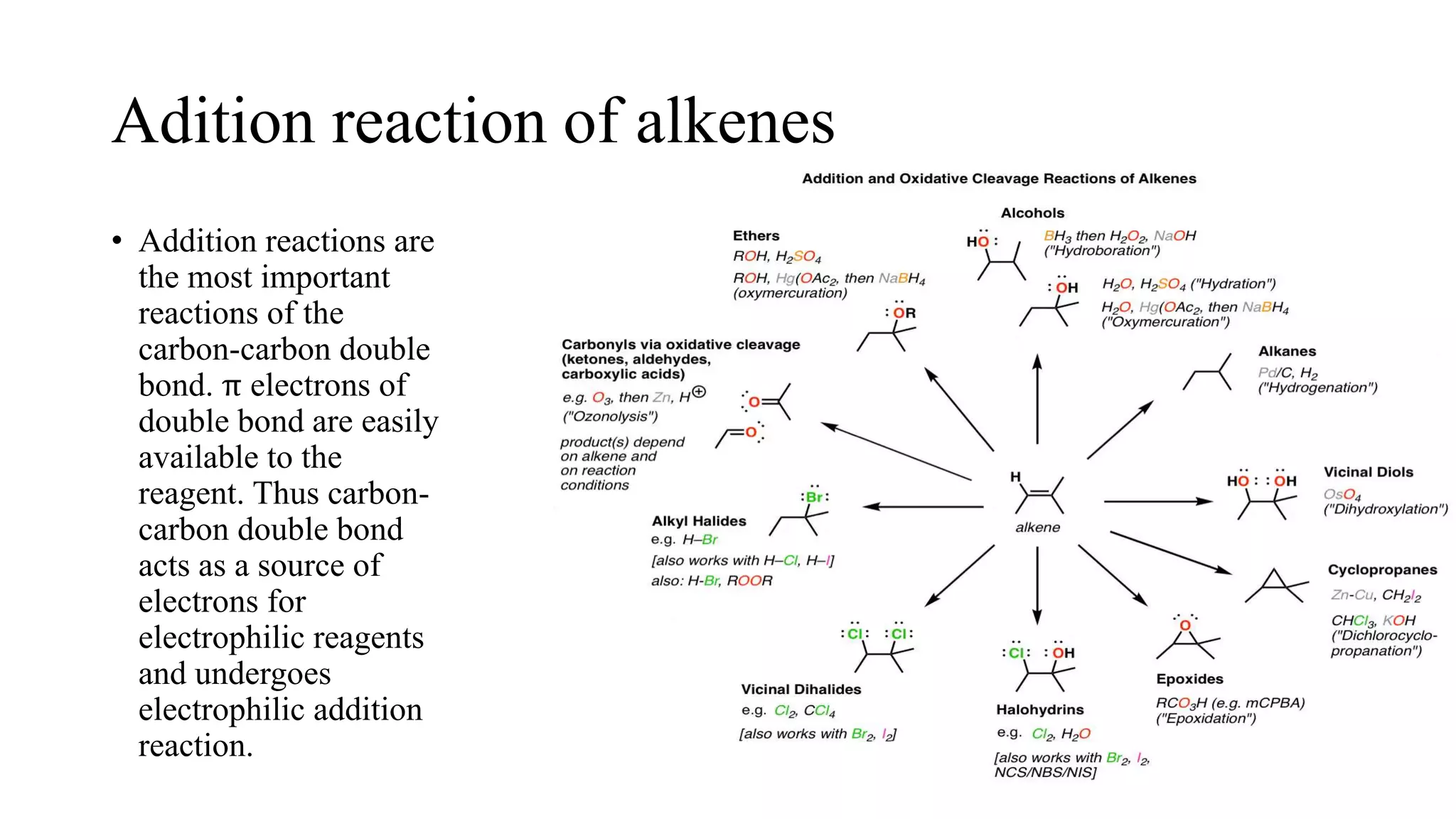
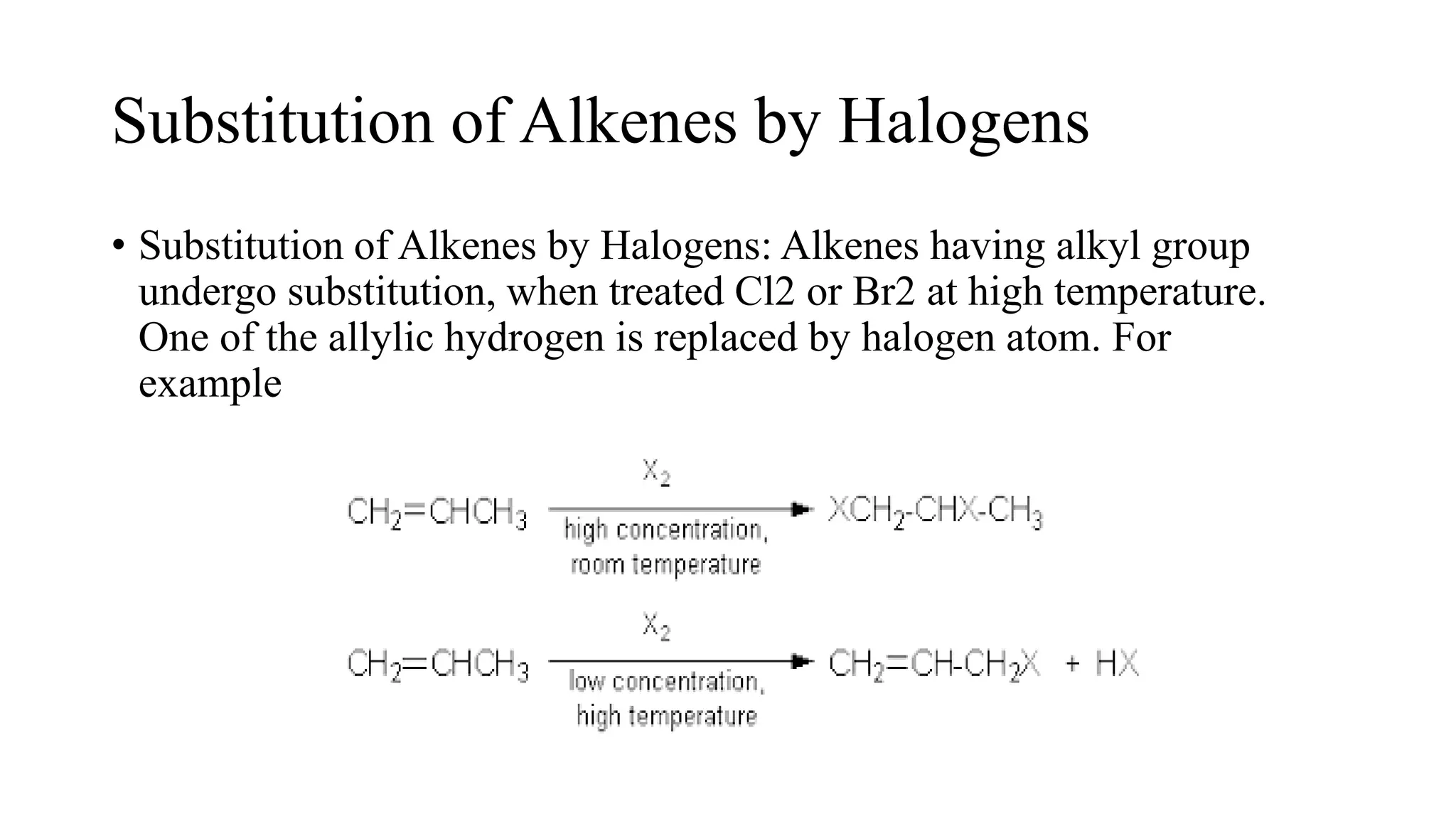
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon double bond. They are more reactive than alkanes due to the availability of pi electrons. Alkenes undergo addition reactions and can be prepared through dehydration of alcohols, dehydrogenation of alkyl halides, and cracking of alkanes. Their properties include being less dense than water and soluble in nonpolar solvents.