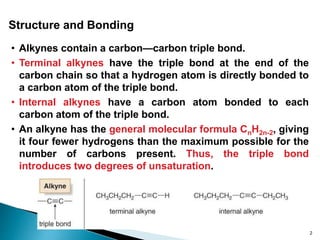
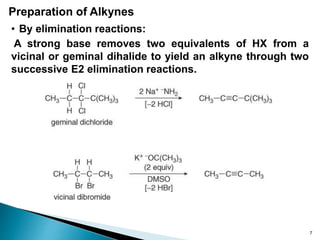
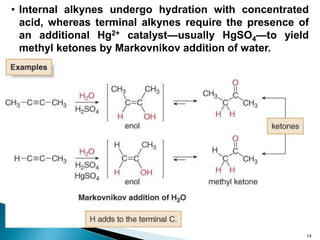
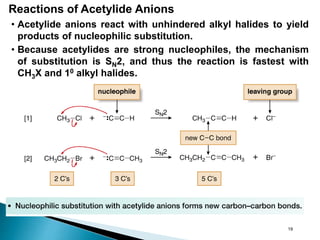
Alkynes are hydrocarbons characterized by a carbon-carbon triple bond, categorized as terminal or internal based on the position of the bond. They follow the molecular formula CnH2n-2, have unique nomenclature in the IUPAC system, and exhibit physical properties similar to hydrocarbons. Various chemical reactions, including hydrohalogenation, hydration, and hydroboration-oxidation, are utilized to prepare and modify alkynes, with terminal alkynes being particularly reactive in Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions.