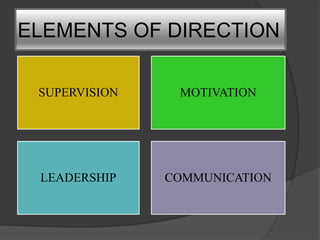
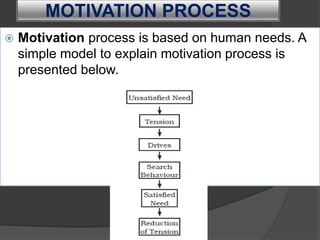
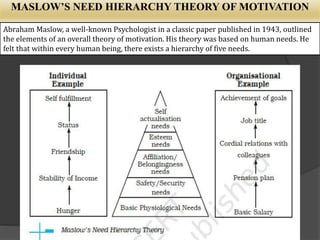
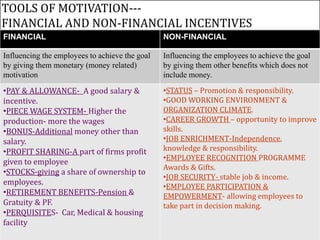
Directing involves guiding and instructing employees to complete work tasks. It is a continuous managerial process that occurs at all levels of an organization. Effective directing helps initiate action, integrate employee efforts, guide employees to reach their potential, and facilitate organizational changes. Key elements of directing include supervision, motivation, leadership, and communication. Supervision involves overseeing employee work, motivation inspires employees to achieve goals, leadership influences employees, and communication involves sharing information between managers and staff. Directing works best when managers follow principles like ensuring each employee contributes fully and objectives are harmonized.