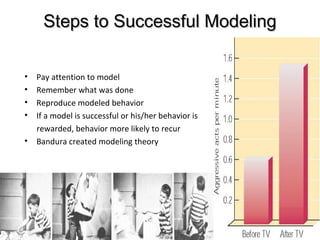
The document outlines various aspects of personal accountability, management effectiveness, and employee behavior, highlighting the influence of attitudes, perceptions, and communication in workplace dynamics. It discusses the importance of goal setting, self-assessment, and the interplay of classical and operant conditioning in behavior management. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of leaders in fostering positive relationships and feedback within teams to enhance productivity and job satisfaction.