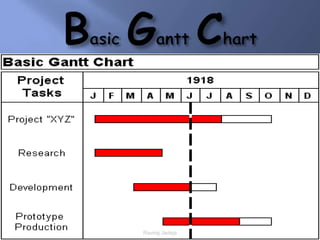
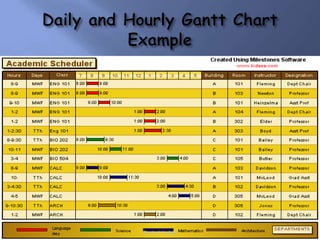
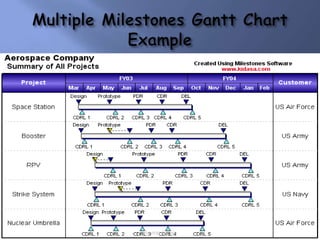
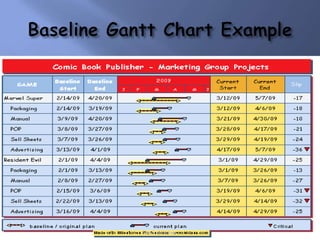
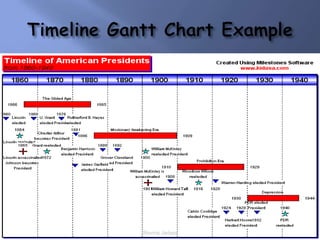
Scientific management was a theory developed in the late 19th/early 20th century to improve economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It involved determining the most efficient ways to perform tasks through time and motion studies. Key figures who developed it included Frederick Taylor, Henry Gantt, and Frank and Lillian Gilbreth. While it increased productivity and standardization, it was also criticized for being exploitative and depersonalizing work. Elements of scientific management like standardization and productivity studies are still used in management today.