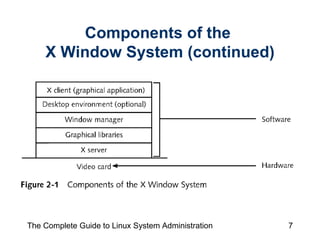
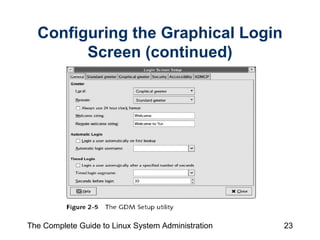
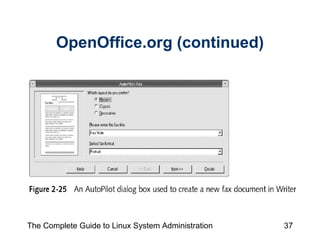
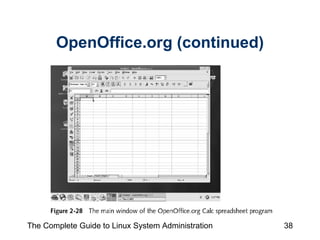
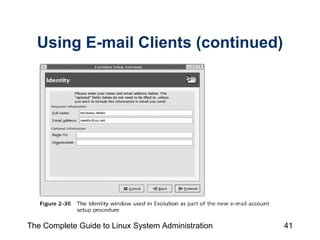
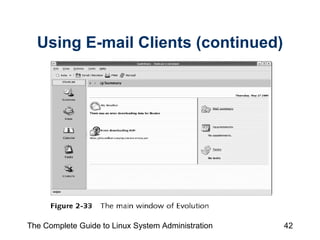
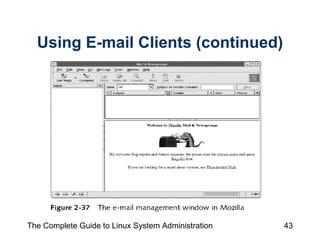
The document discusses the graphical desktop environment in Linux. It describes the X Window System and its components including the X server, X clients, window managers and graphical libraries. It discusses the KDE and GNOME desktop interfaces, their components like panels and taskbars, and how to configure features. It also summarizes popular graphical utilities for file management, text editing, web browsing, productivity apps like OpenOffice, and email clients.