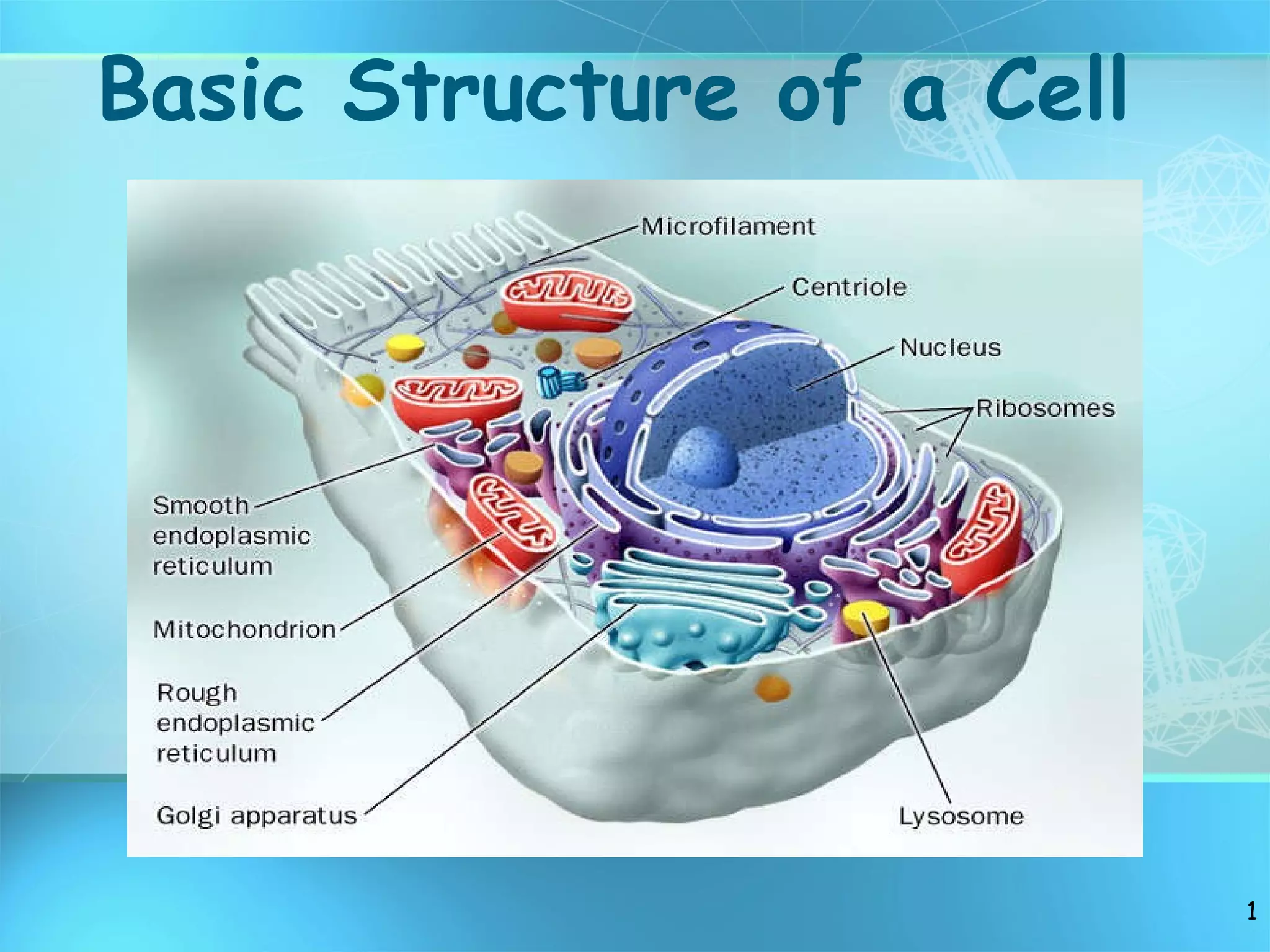
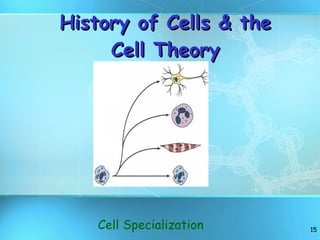
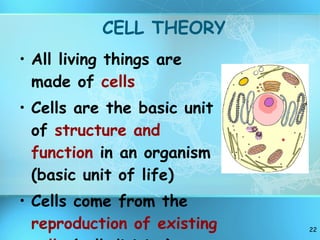
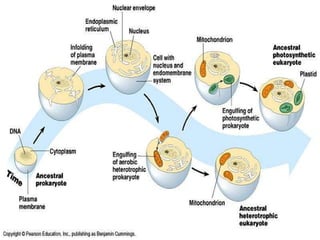
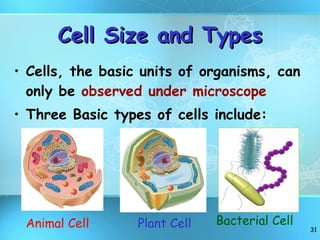
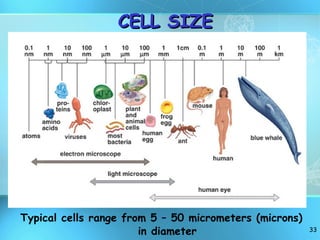
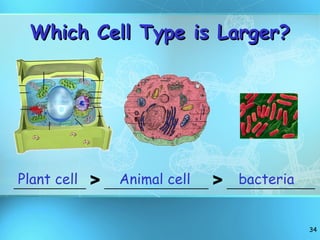
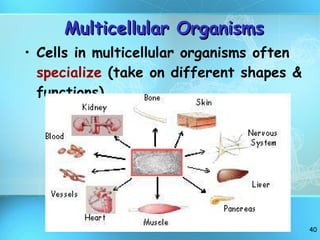
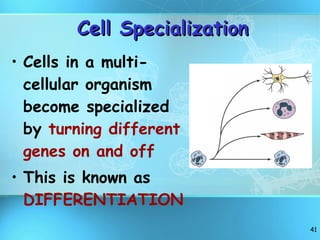
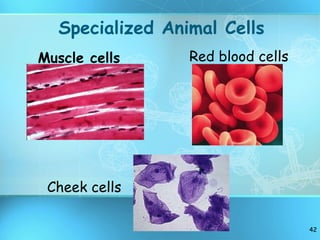
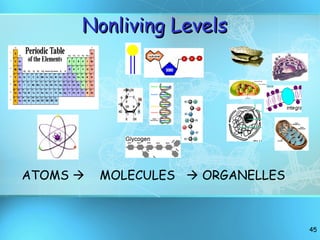
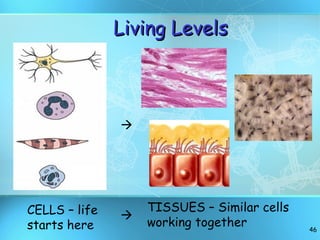
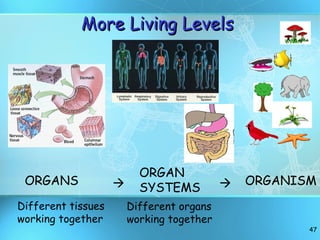
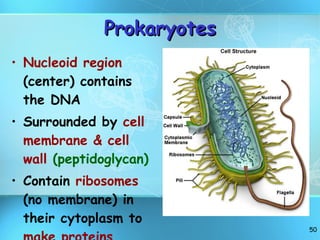
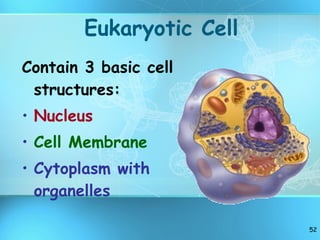
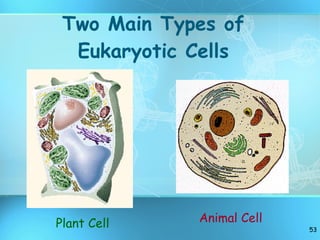
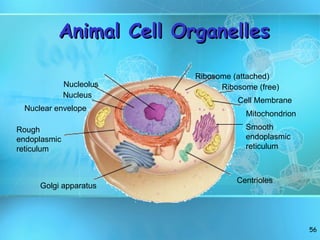
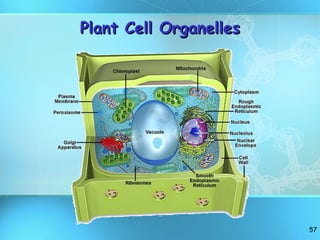
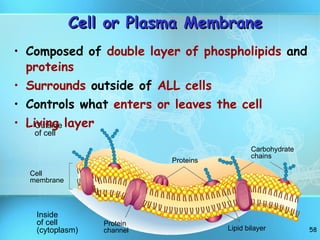
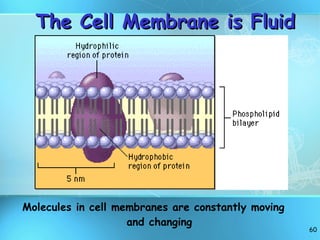
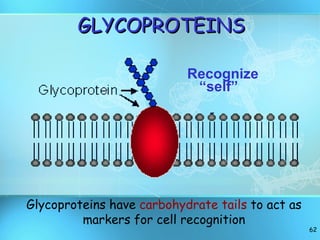
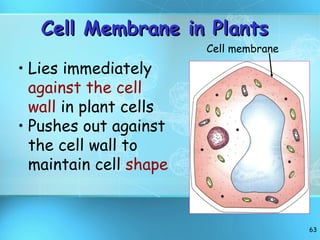
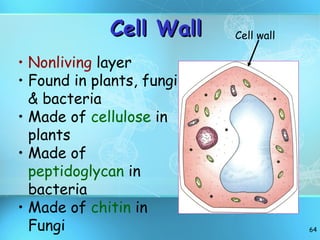
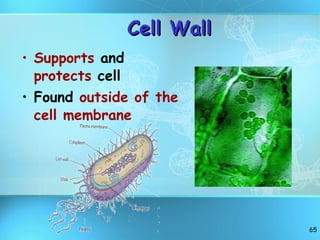
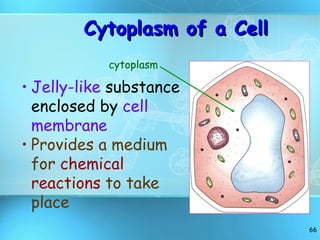
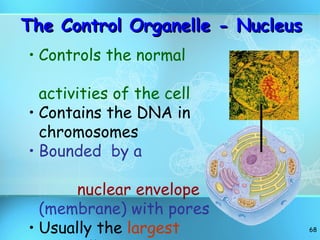
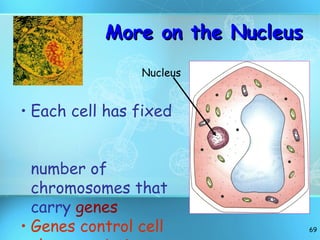
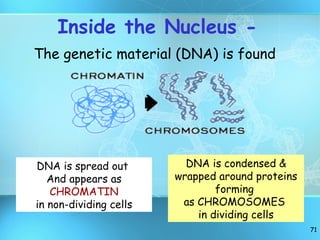
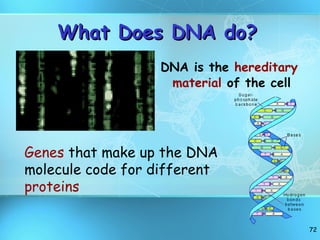
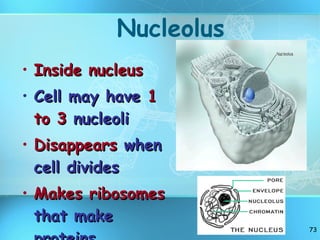
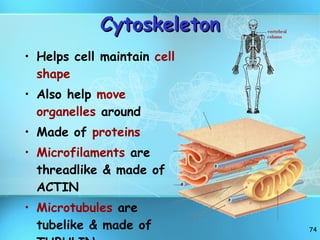
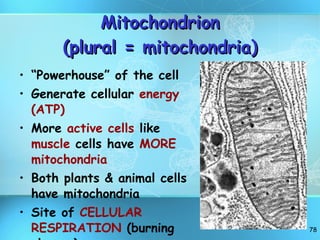
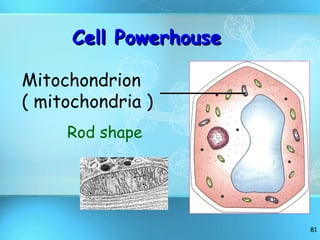
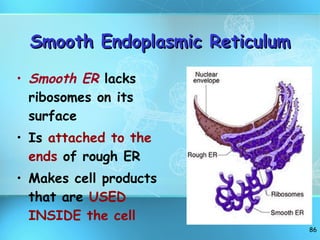
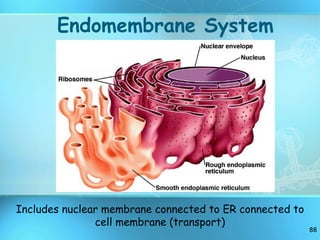
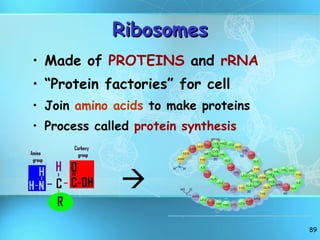
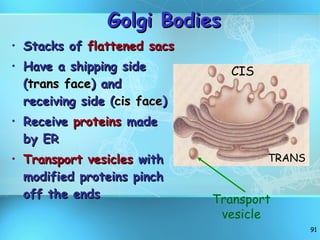
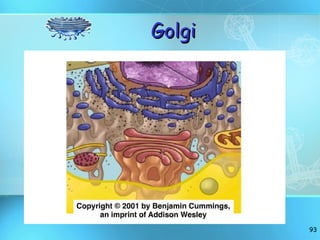
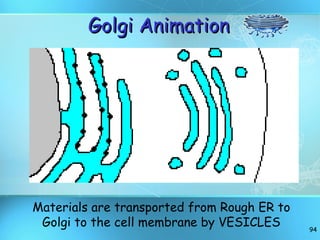
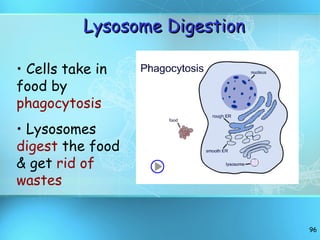
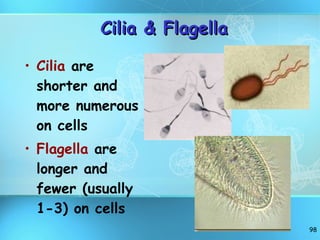
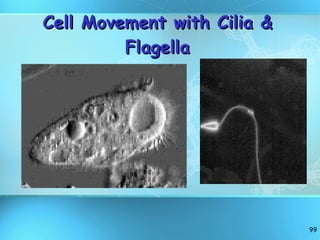
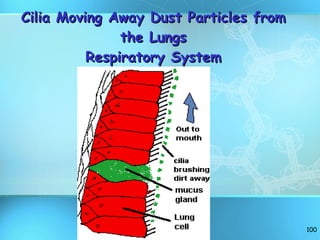
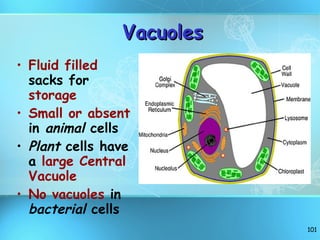
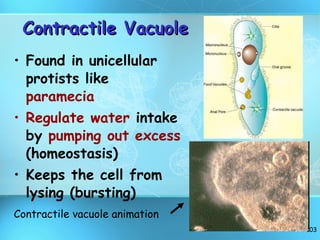
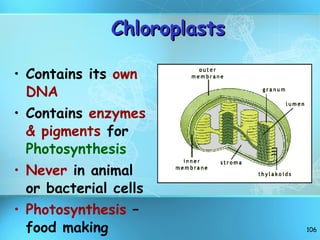
The document discusses the basic structure and organization of cells. It begins by outlining the main characteristics of living things and then describes the different levels of organization, from atoms and molecules up to biomes and the biosphere. It then provides details on the basic structure of plant and animal cells, including the organelles and their functions. It discusses the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and describes specialized cell types.