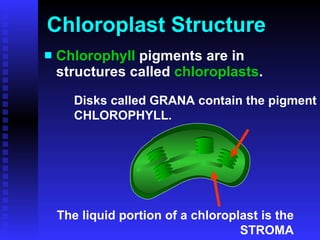
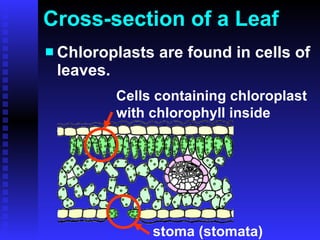
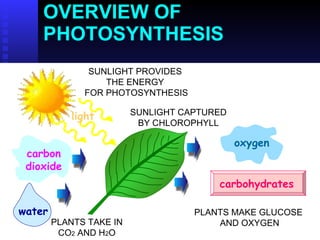
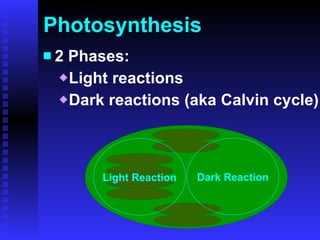
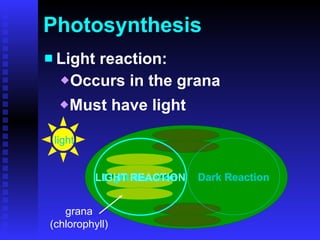
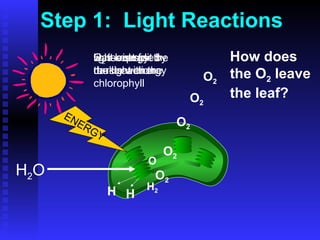
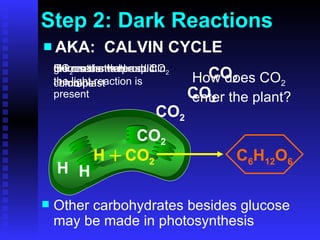
This PowerPoint presentation covers photosynthesis and was last revised in June 2008. It contains 27 slides discussing topics like the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis, chloroplast structure, and how plants use light energy from the sun to produce glucose and oxygen from water and carbon dioxide. The document provides an overview of photosynthesis and its key stages and equations.