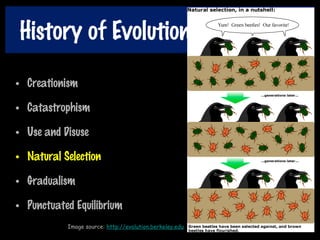
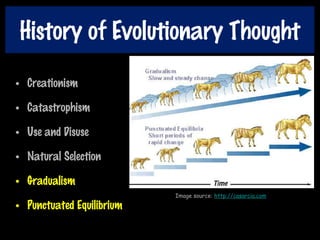
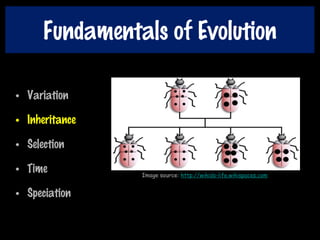
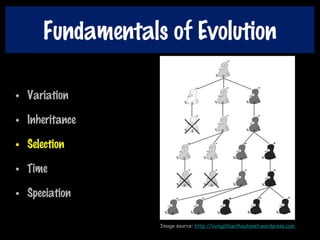
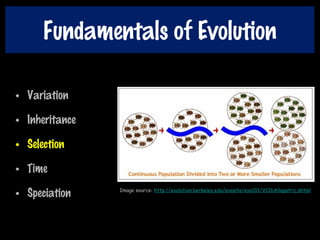
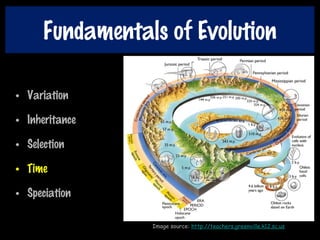
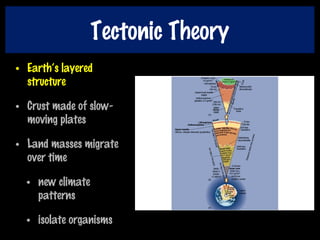
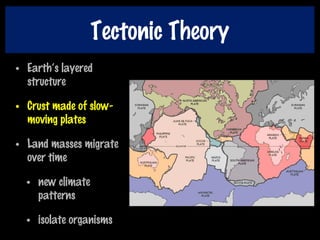
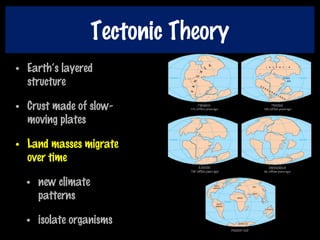
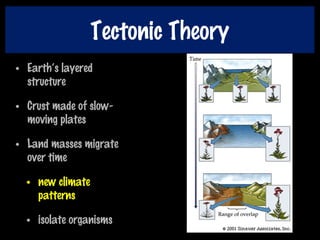
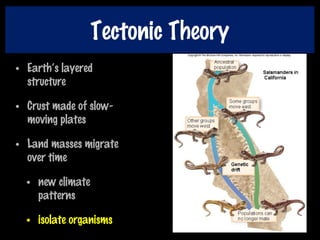
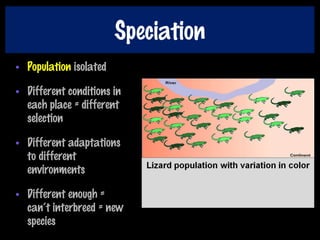
This document discusses key concepts of evolution including the history of evolutionary theories from creationism to modern ideas like punctuated equilibrium. It covers Darwin and Wallace's model of natural selection and how environmental pressures can lead to speciation. The fundamentals of evolution are explained including variation, inheritance, selection over time. The role of tectonic plate movement in genetic isolation and speciation is described. Various forms of evidence for evolution are listed such as the fossil record, present-day examples, and molecular clocks using mitochondrial DNA.