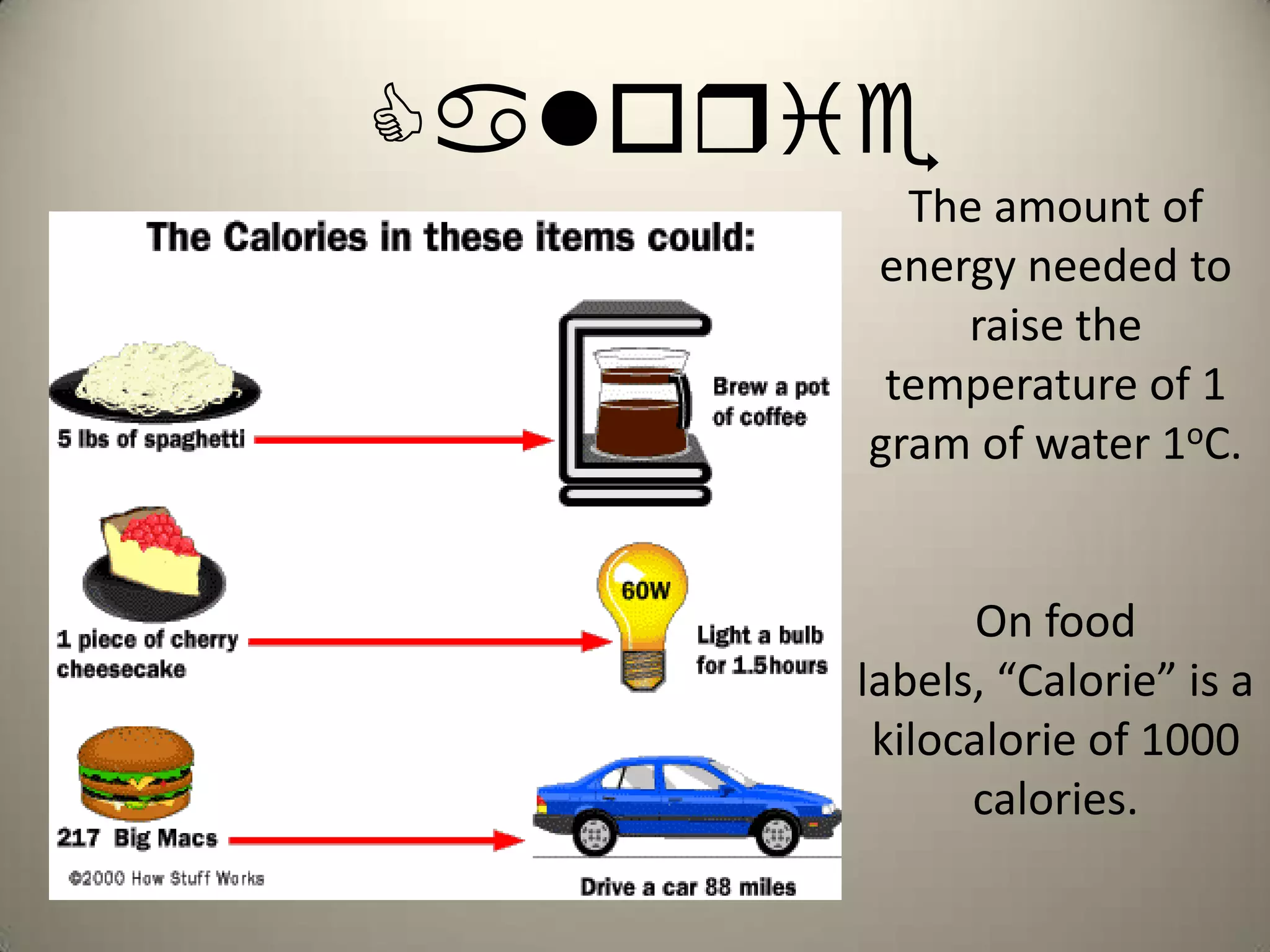
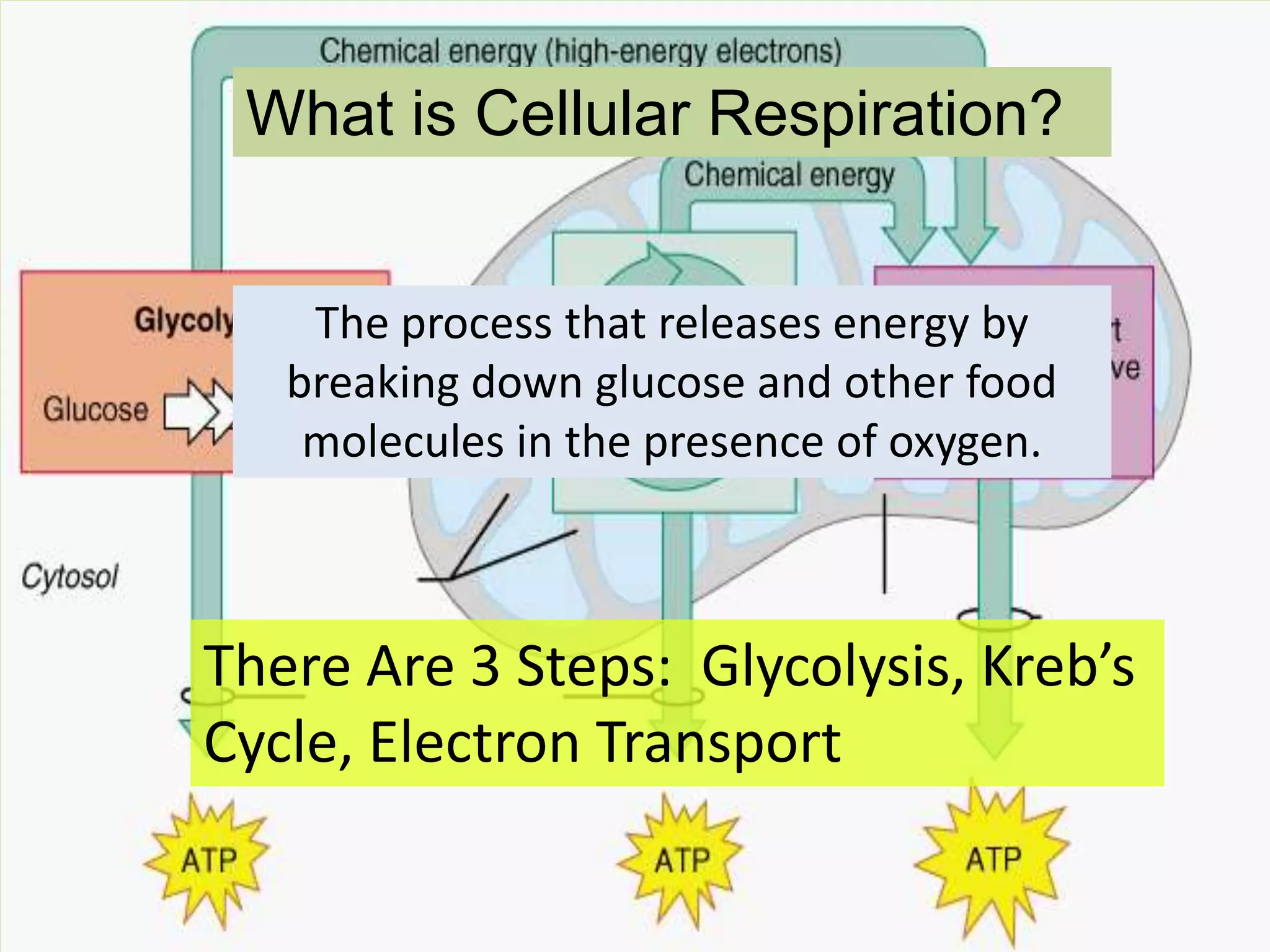
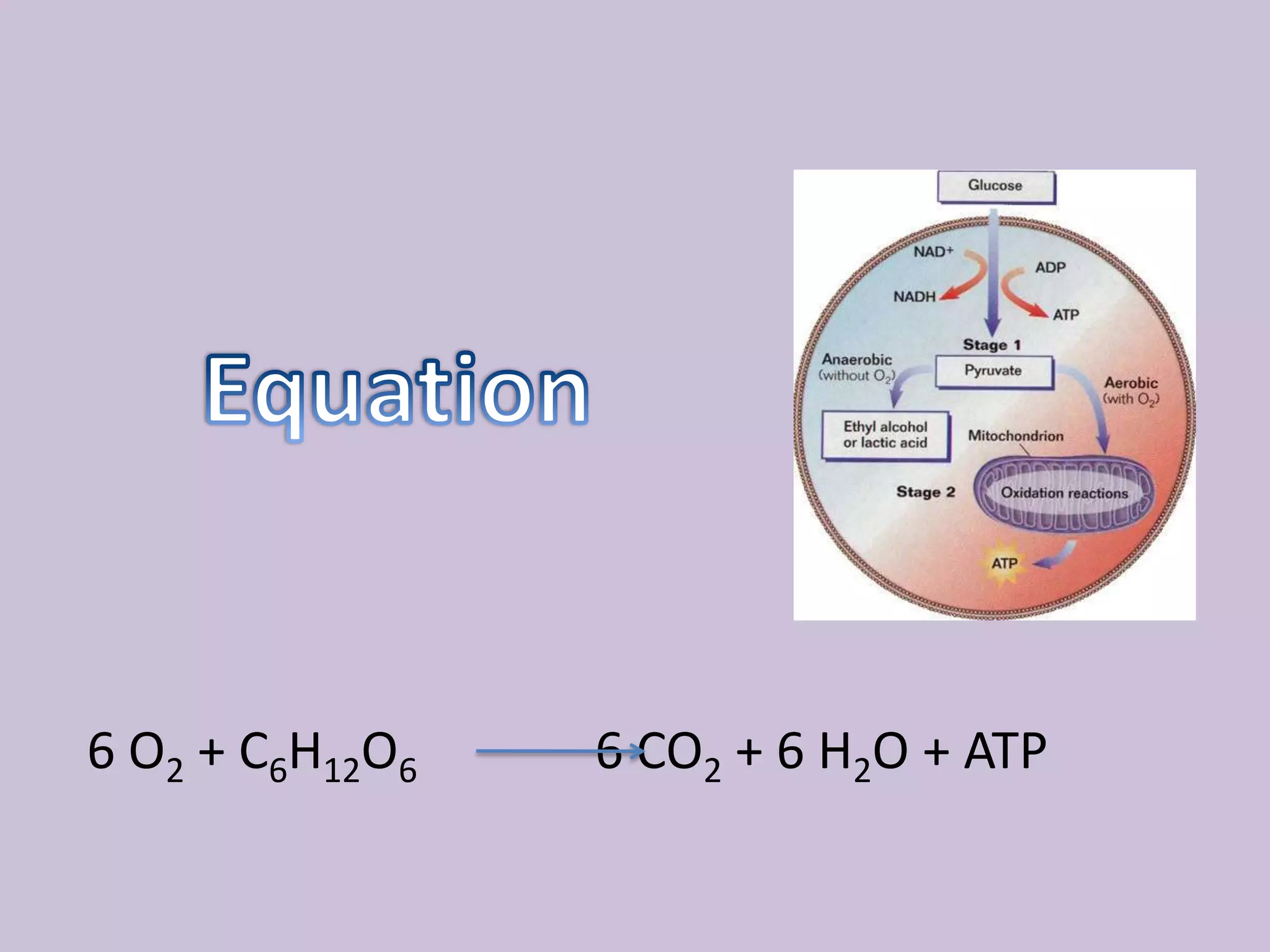
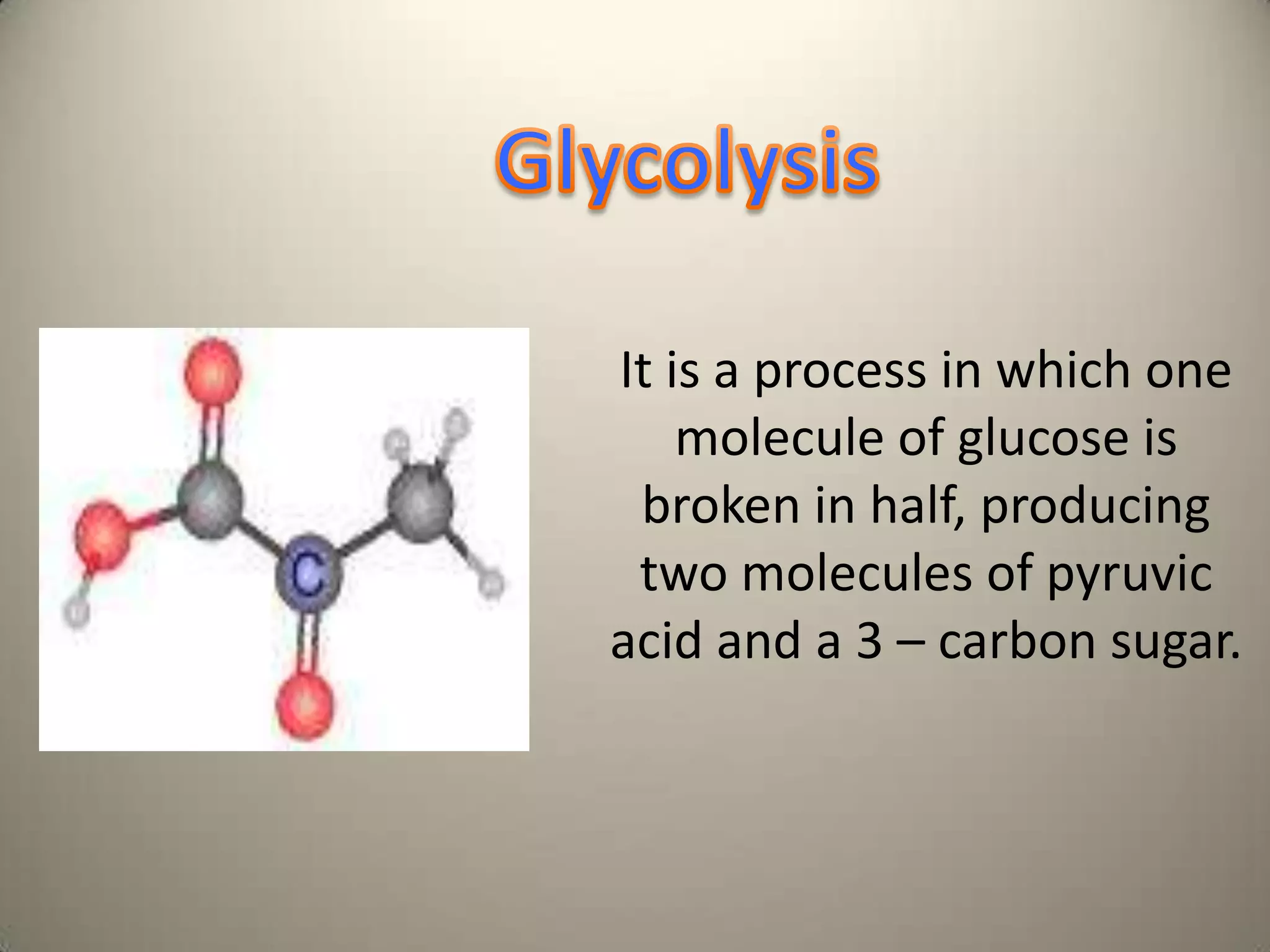
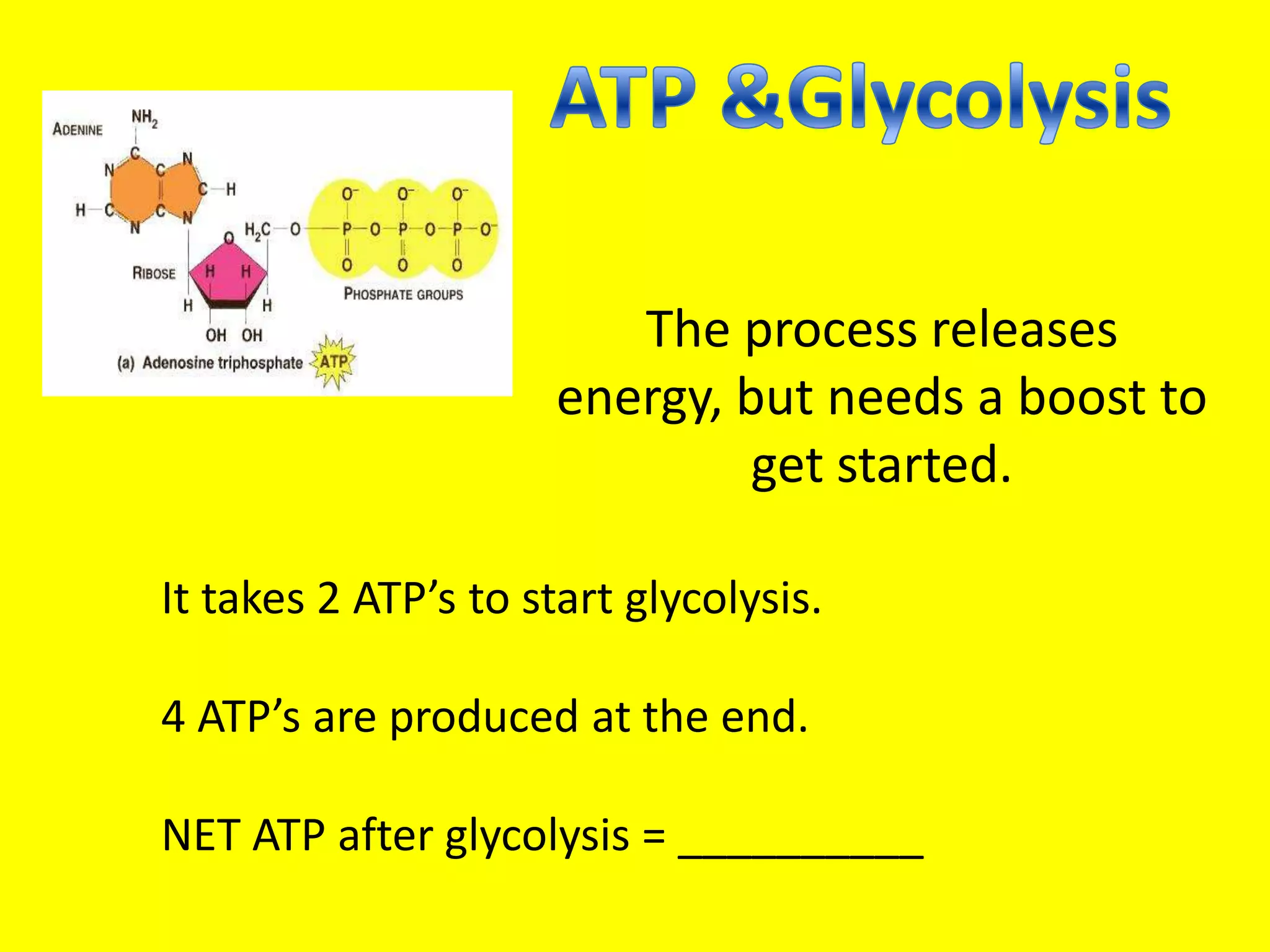
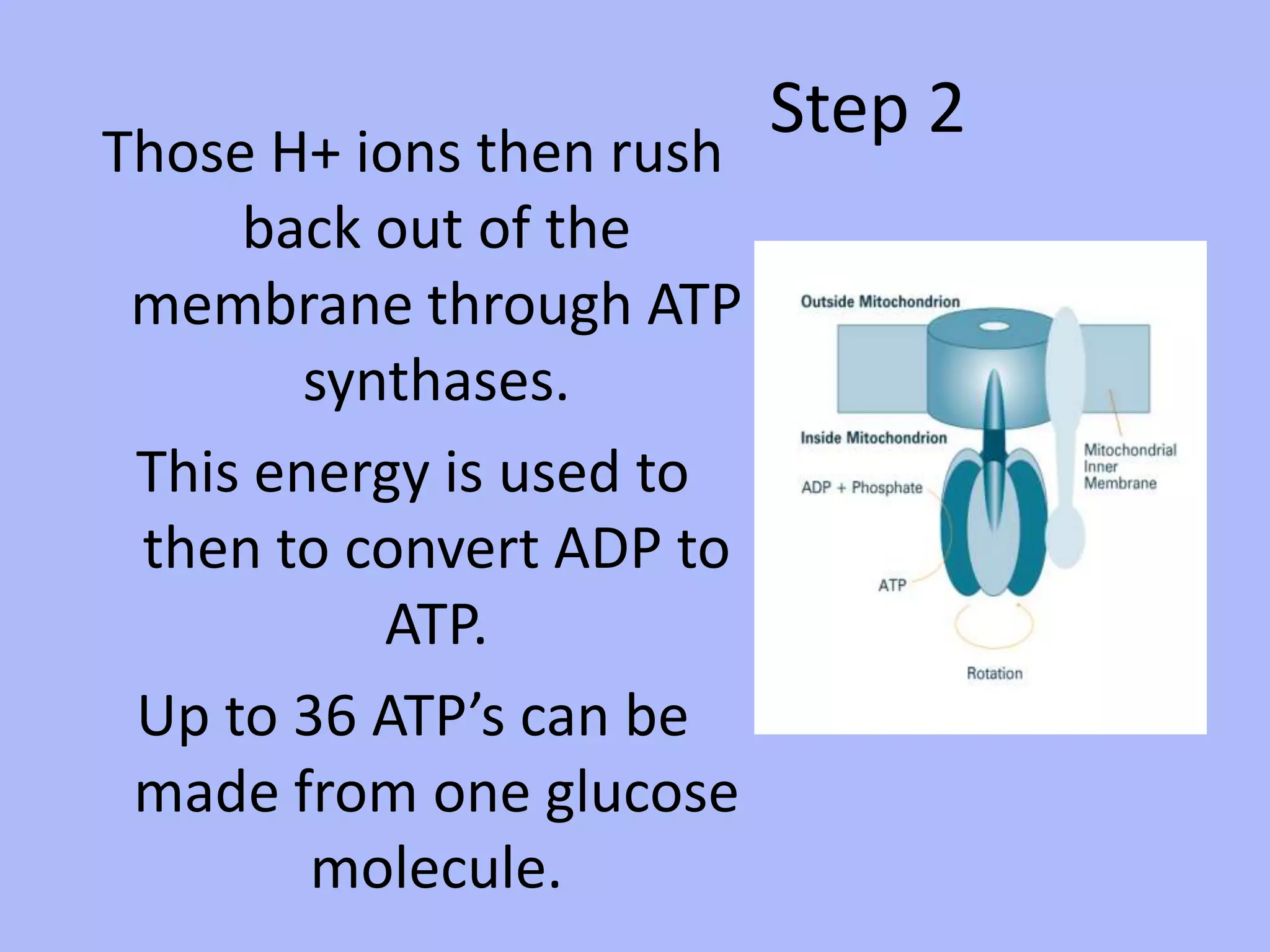
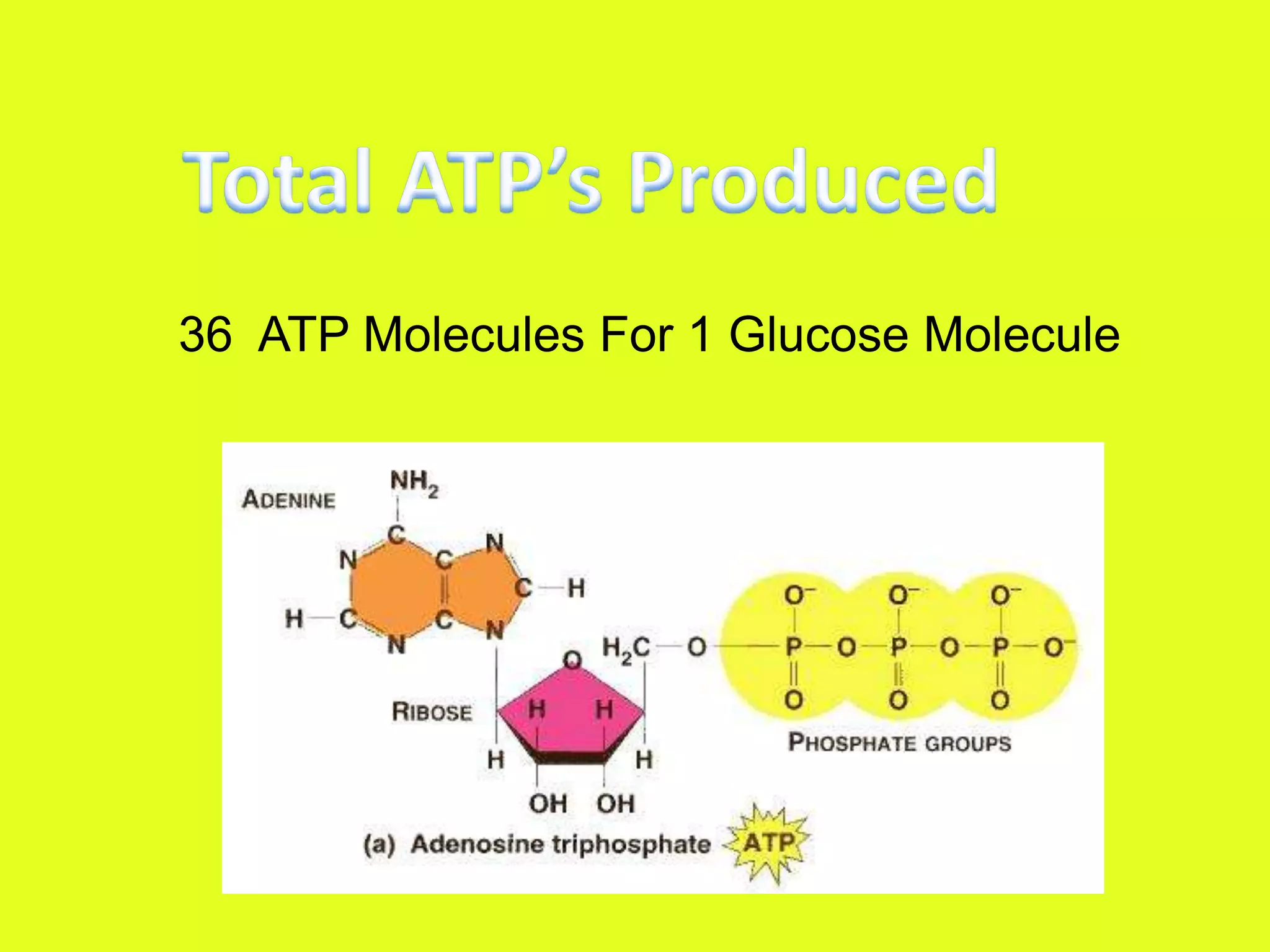
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen to release energy. It occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and produces a small amount of ATP. The Krebs cycle further breaks down these products and produces more ATP and electron carriers. Finally, the electron transport chain uses these carriers to power ATP synthase and produce the majority of ATP from glucose through chemiosmosis. In total, the complete breakdown of one glucose molecule via cellular respiration can produce up to 36 ATP molecules.