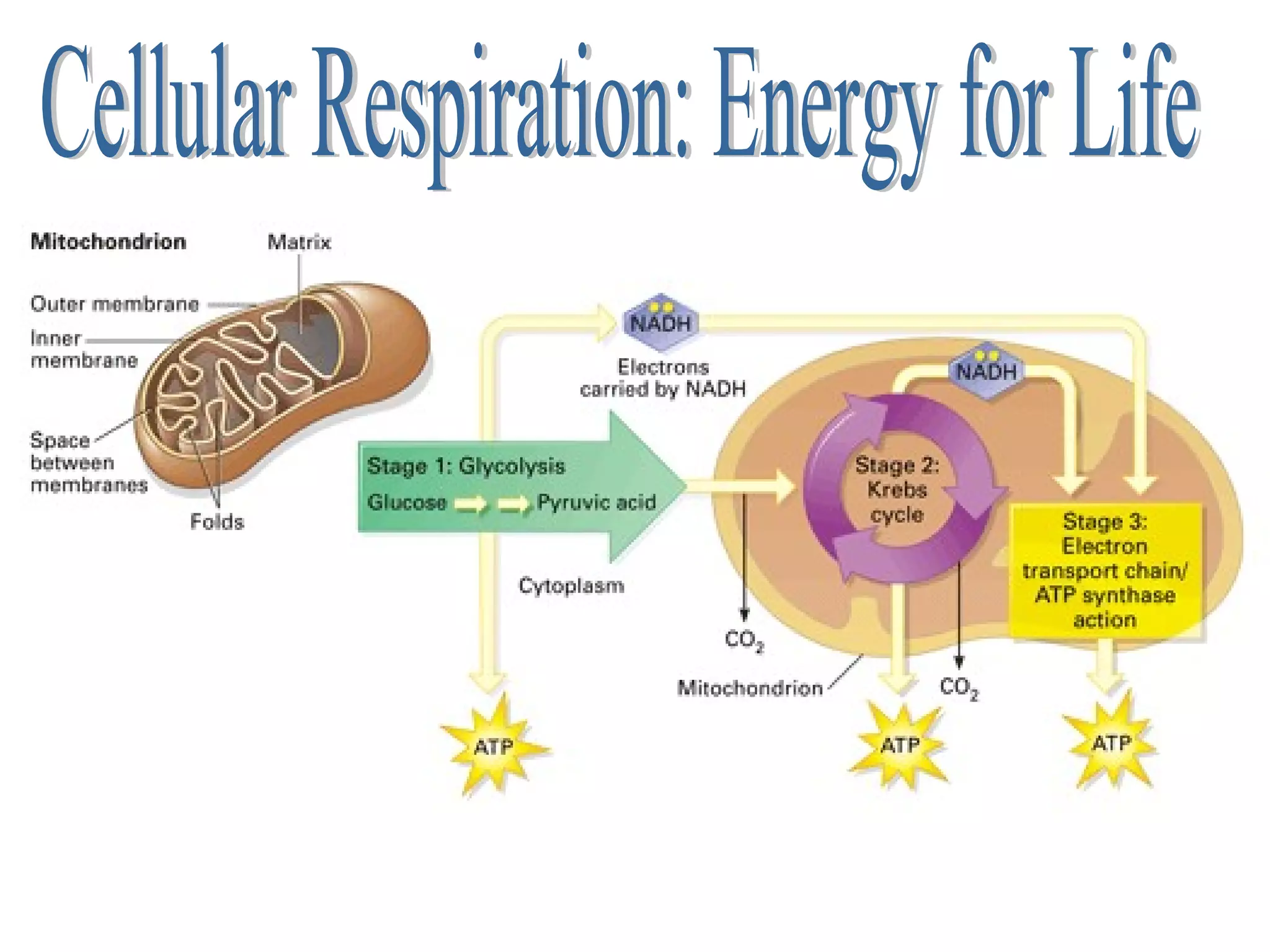
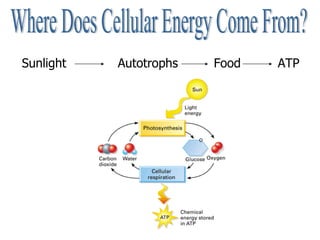
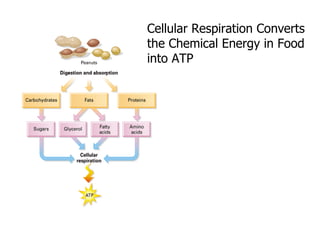
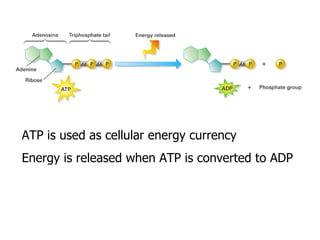
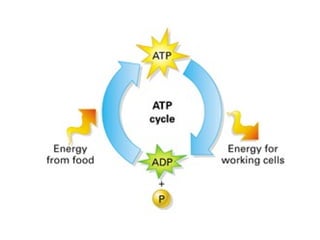
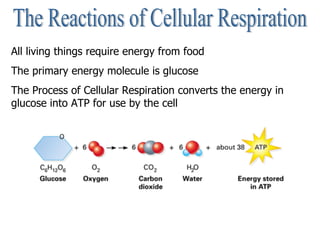
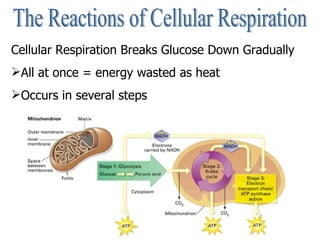
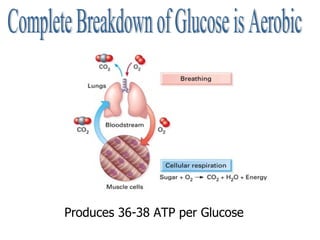
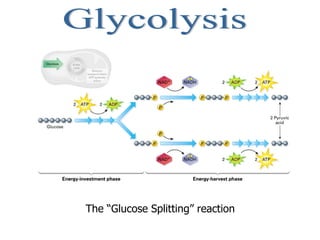
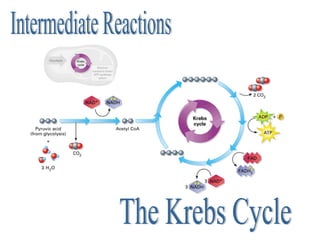
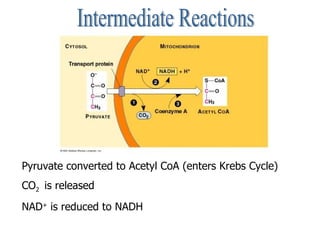
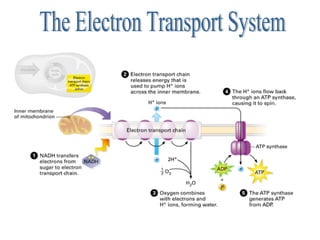
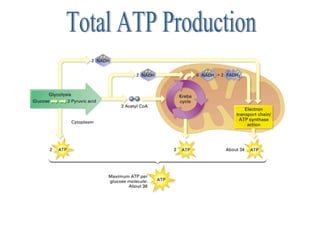
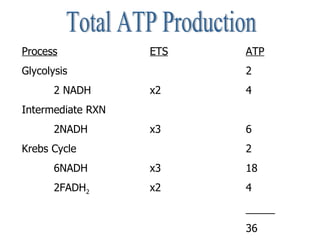
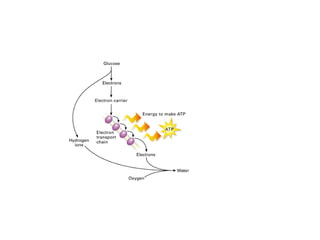
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert the chemical energy in food, primarily glucose, into ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The key stages include glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport system, which together produce 36-38 ATP per glucose molecule. Energy is released and captured through various phosphorylation processes, including substrate-level and oxidative phosphorylation.