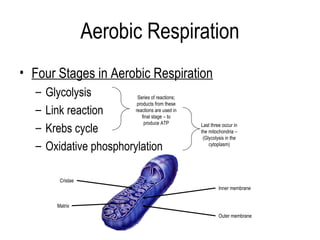
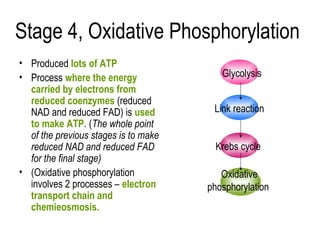
1) Aerobic respiration has four stages: glycolysis, the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
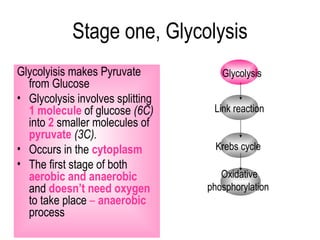
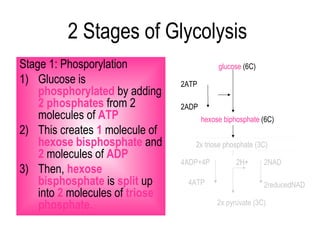
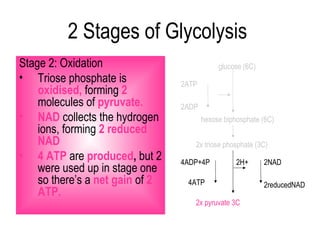
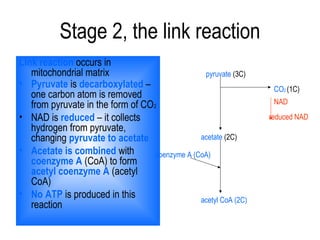
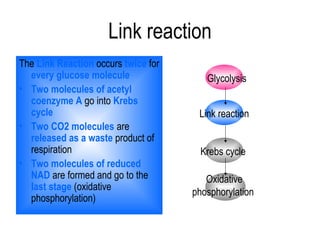
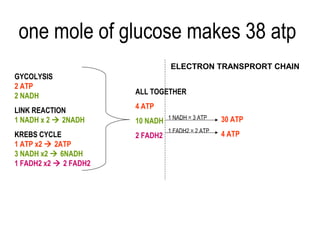
2) Glycolysis breaks down glucose and produces pyruvate and a small amount of ATP. The link reaction converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA.
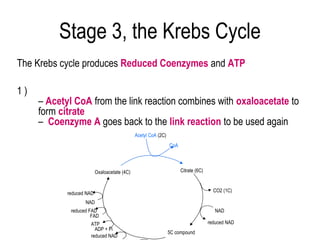
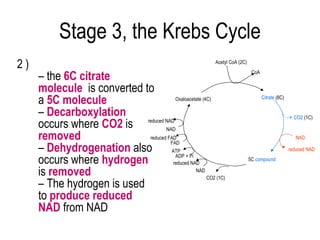
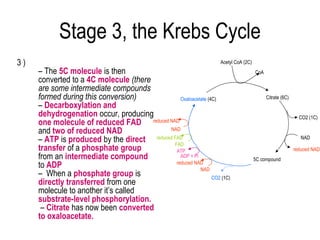
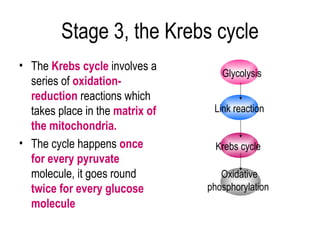
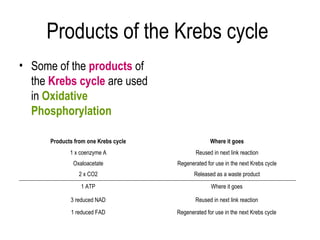
3) The Krebs cycle uses acetyl-CoA to generate ATP, reduced NADH, and reduced FADH2.
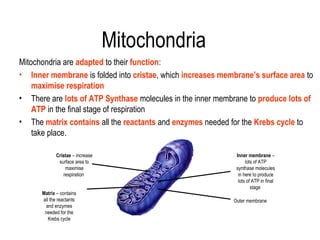
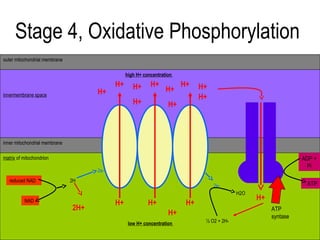
4) During oxidative phosphorylation, the electron transport chain uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to pump protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient. ATP synthase uses this gradient to produce large amounts of ATP through chemiosmosis.