1) Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and some other organisms use sunlight to produce food from carbon dioxide and water.
2) Autotrophs, like plants, can produce their own food using sunlight, while heterotrophs cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms.
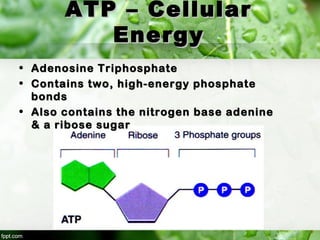
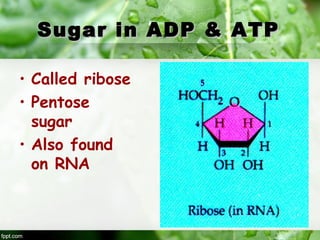
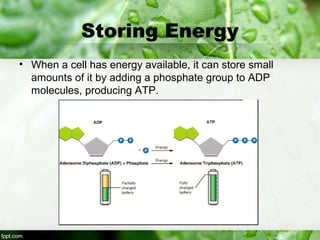
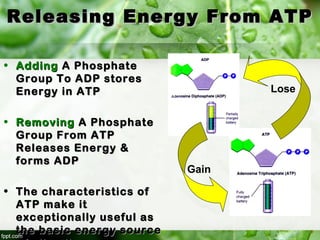
3) ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the main energy carrier in cells and is constantly being used and remade. ATP stores energy by bonding two phosphate groups to ADP, and releases energy when a phosphate group is removed, powering cellular reactions.