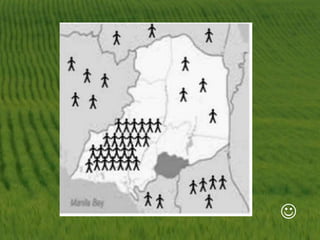
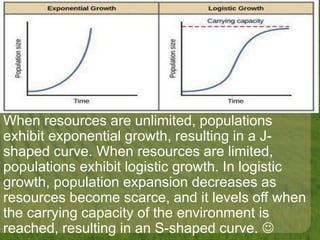
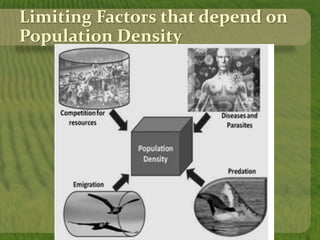
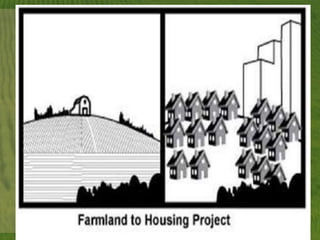
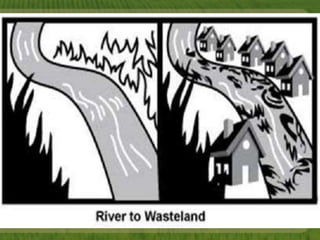
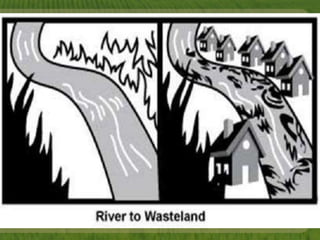
This document discusses biodiversity and ecosystems. It explains that species diversity increases adaptation and survival during environmental changes. Population growth follows a logistic curve as it approaches the carrying capacity of the environment. Maintaining biodiversity provides direct economic, indirect economic, and aesthetic value. It also contributes to ecosystem stability by increasing resilience to environmental changes.