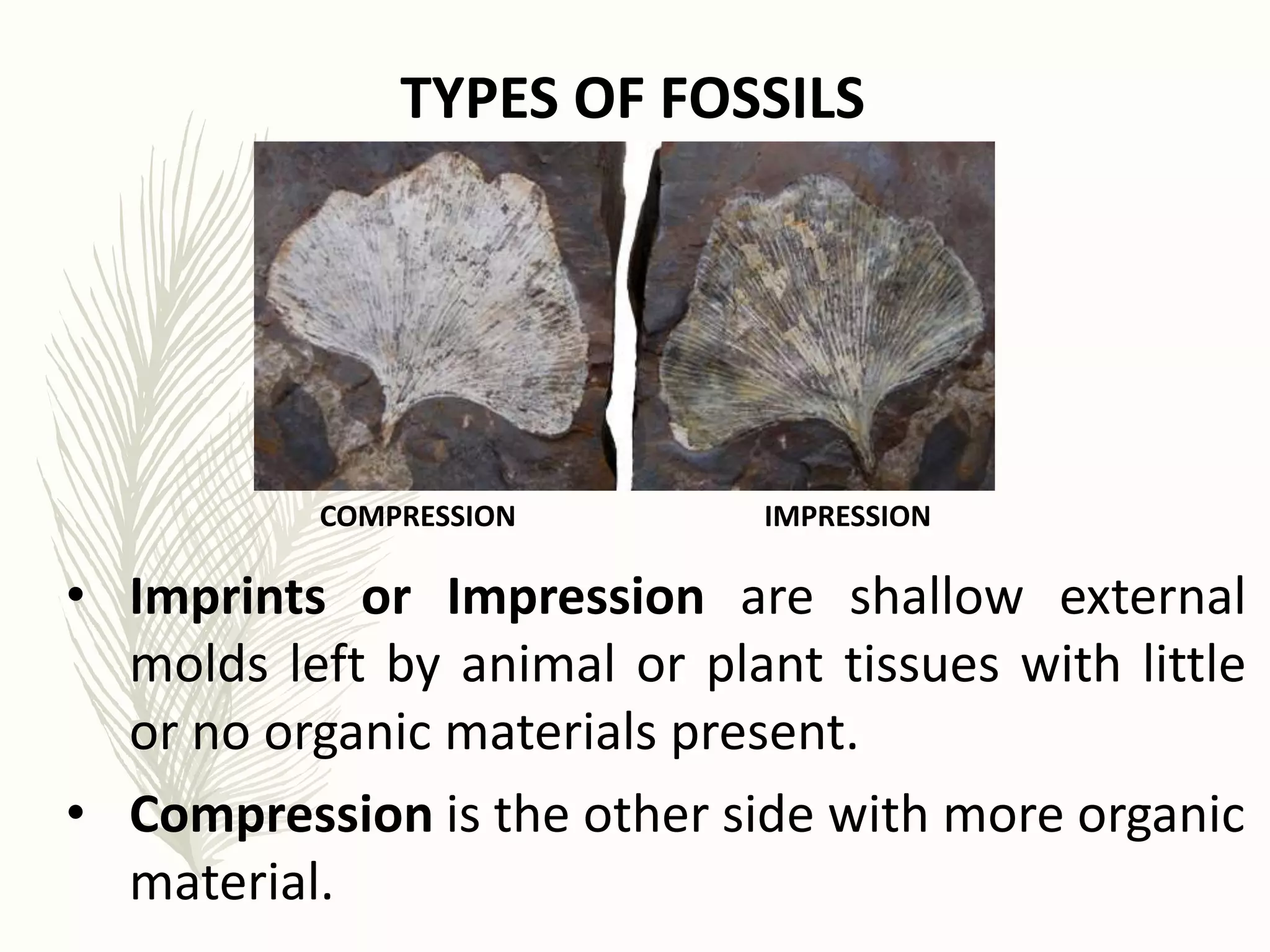
This document discusses sources of evidence for evolution from fossils found in sedimentary rocks. It describes how fossils provide evidence that organisms have changed over time by preserving their hard structures. It then explains different types of fossils and how scientists use relative and absolute dating methods like carbon-14 dating and potassium-argon dating to determine the age of fossils and place them within geological time periods.