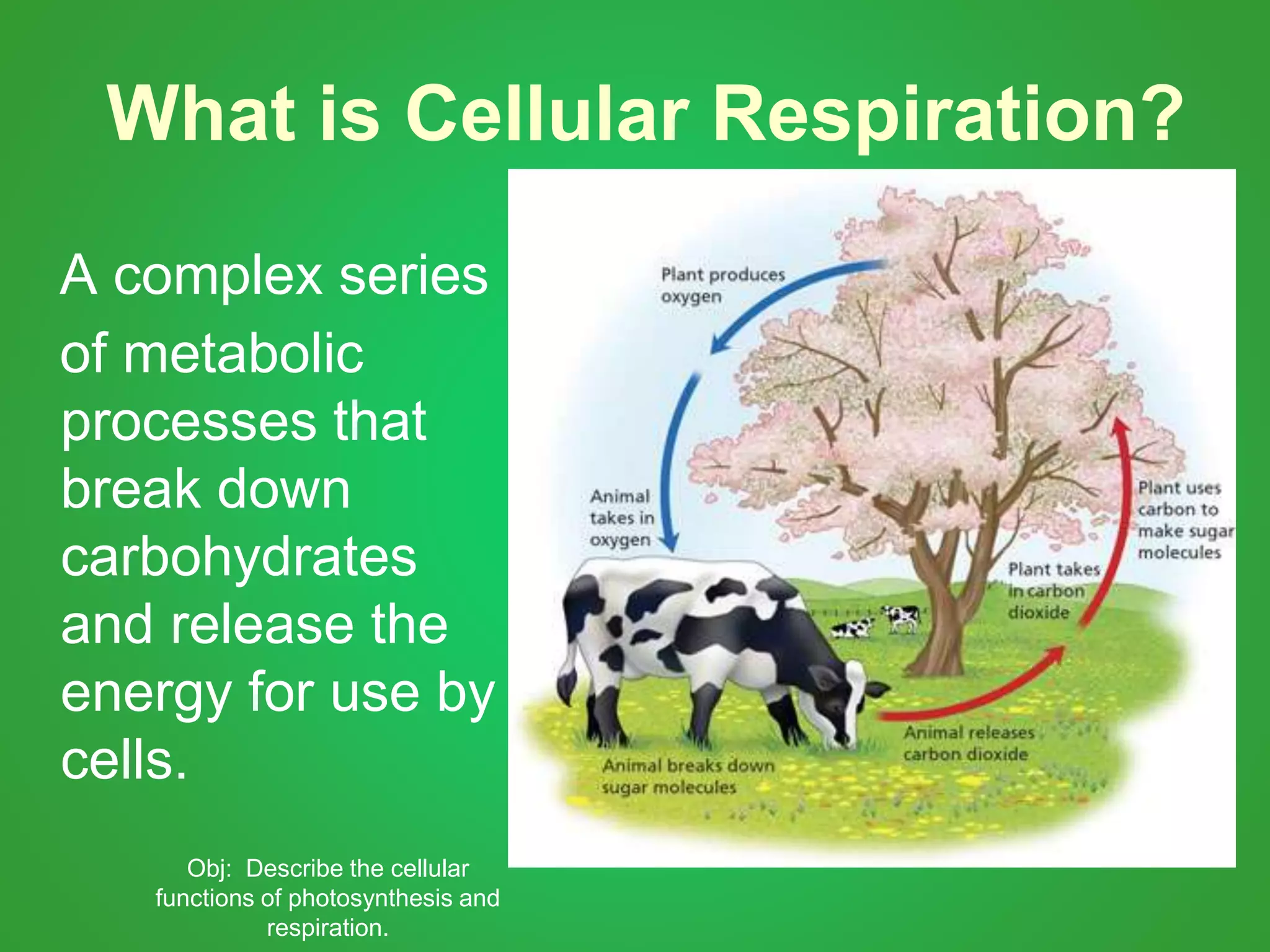
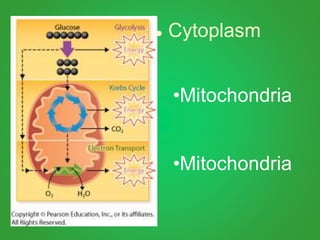
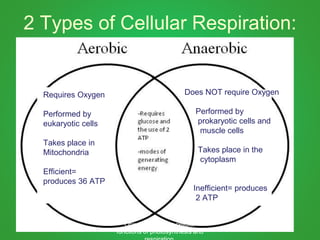
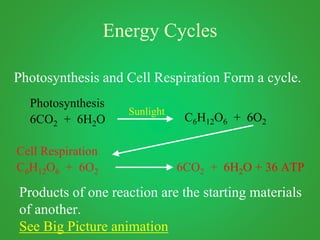
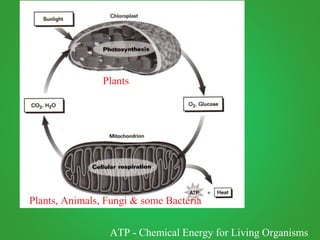
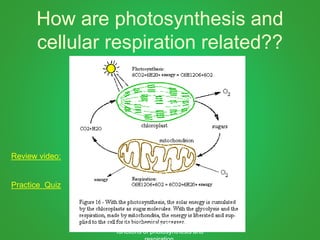
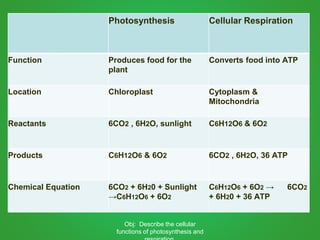
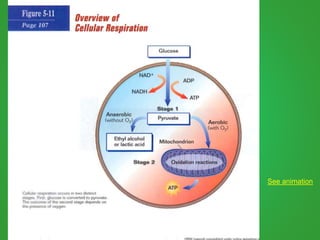
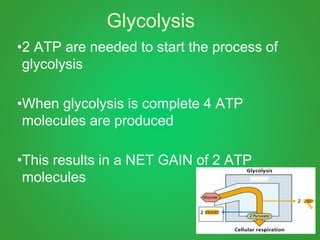
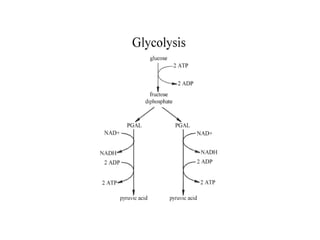
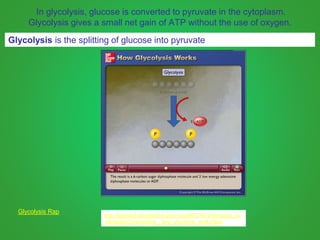
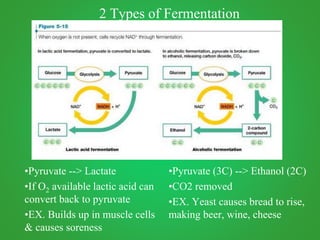
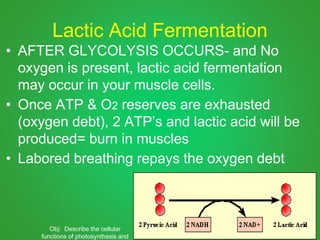
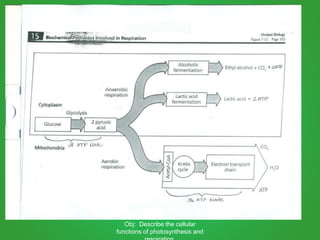
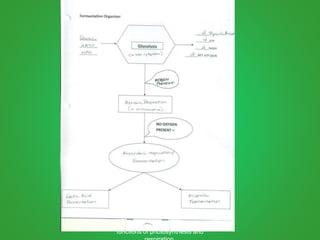
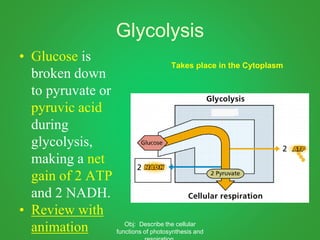
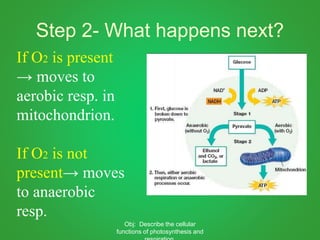
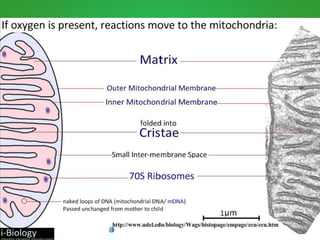
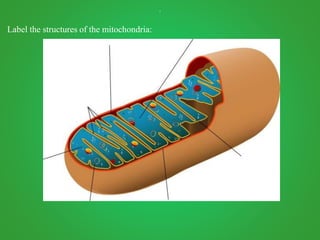
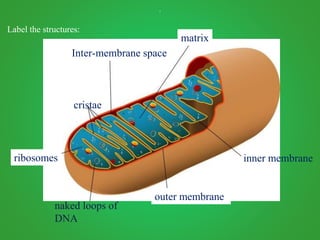
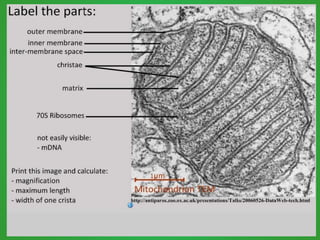
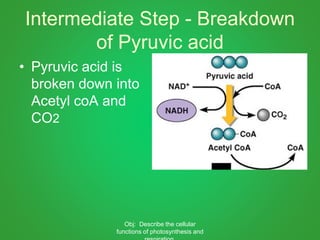
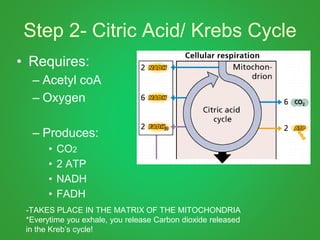
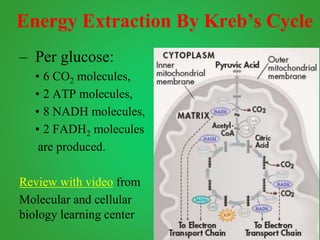
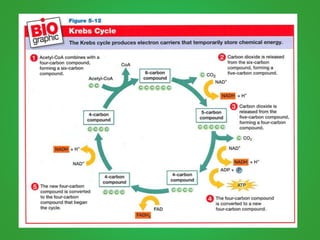
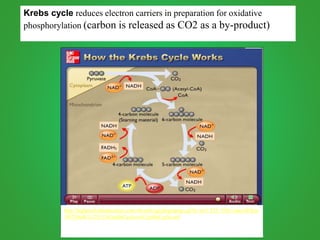
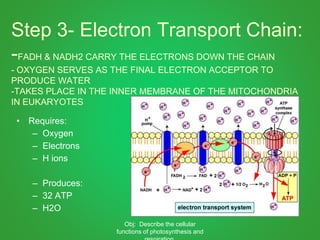
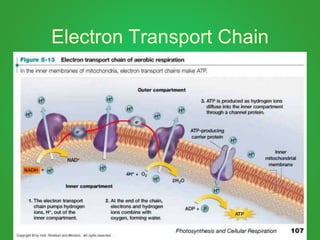
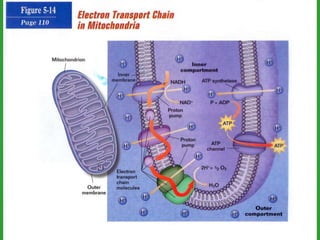
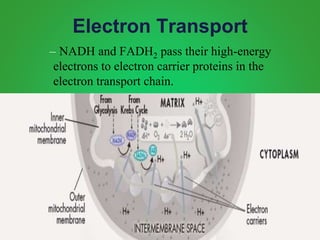
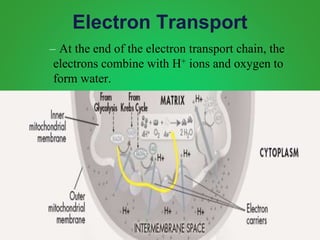
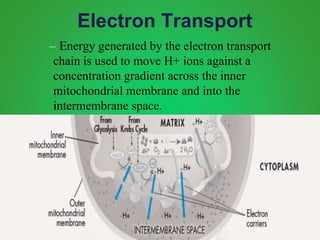
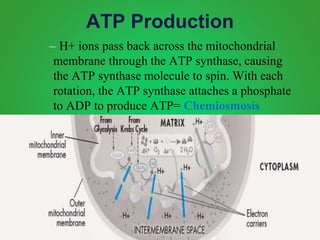
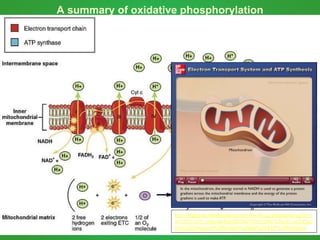
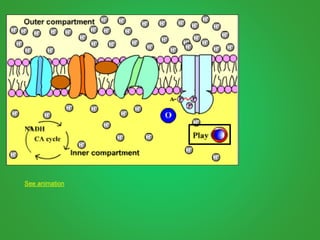
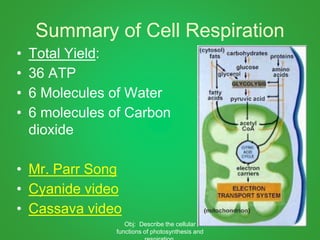
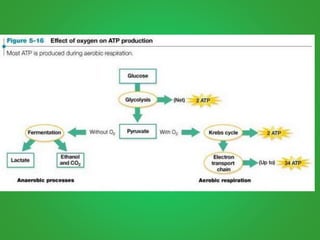
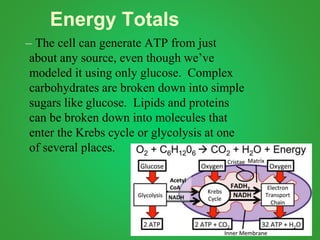
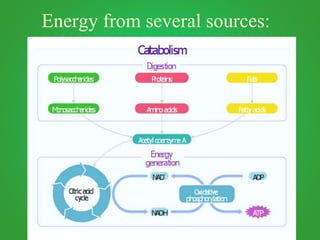
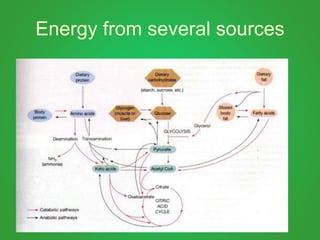
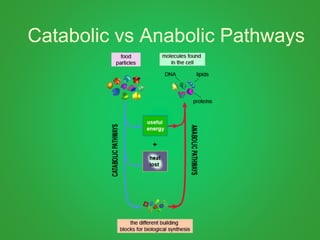
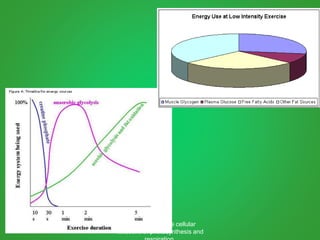
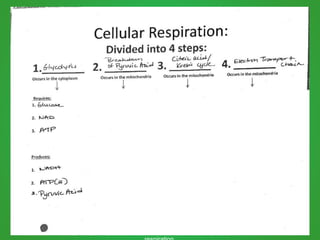
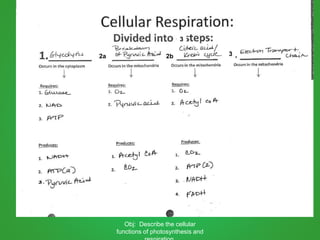
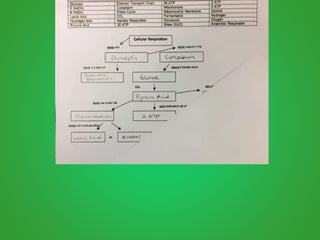
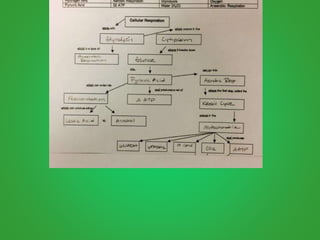
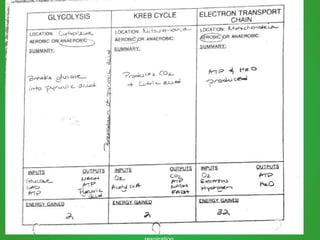
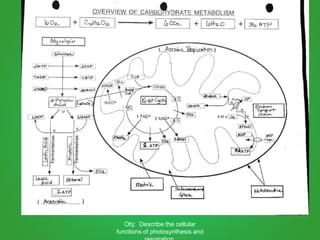
Cellular respiration involves three main stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and occurs in the cytoplasm, producing a small amount of ATP. The Krebs cycle and electron transport chain occur in the mitochondria and release more energy through the oxidation of pyruvate and other molecules, producing much more ATP through chemiosmosis. Together, these stages of cellular respiration fully break down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen to capture energy in the form of ATP.