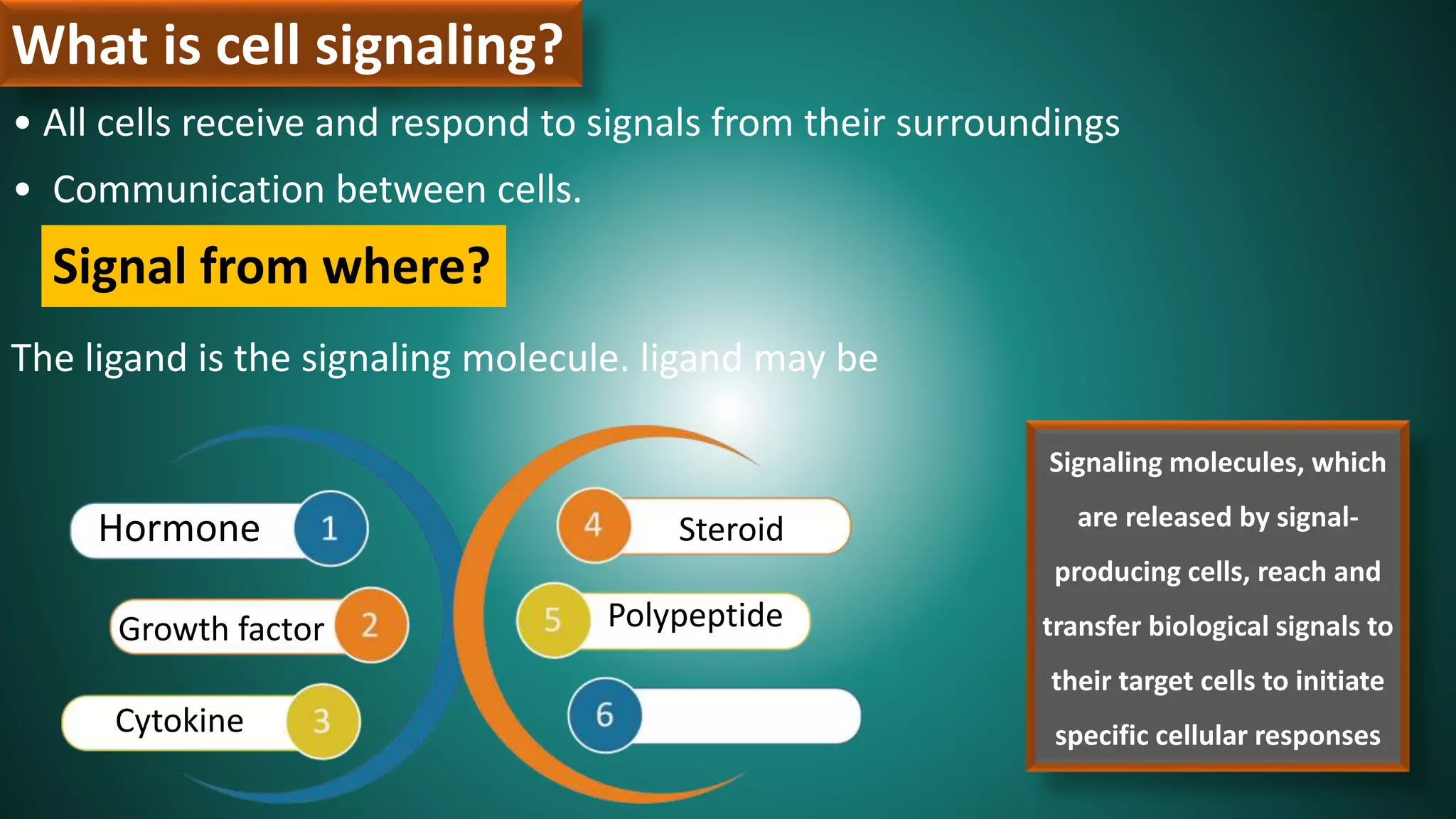
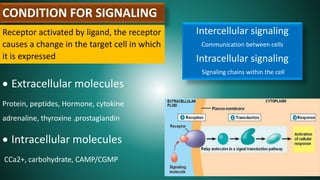
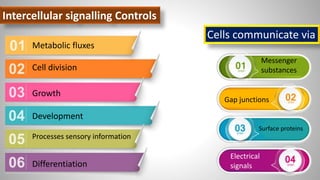
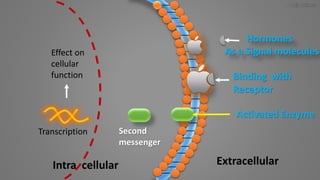
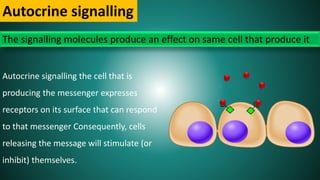
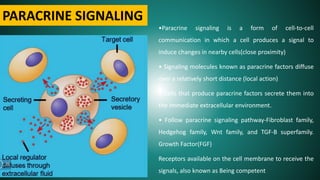
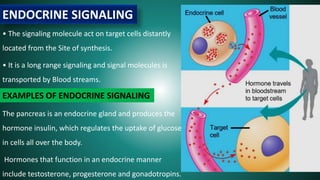
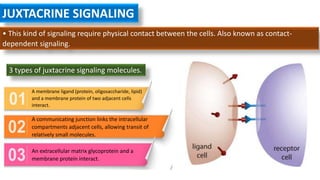
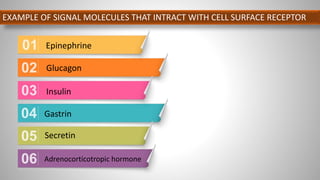
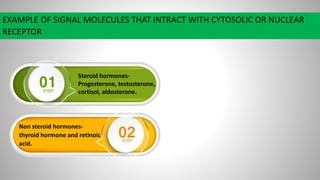
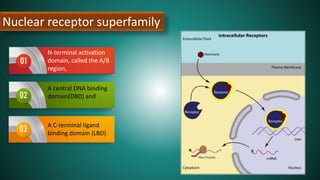
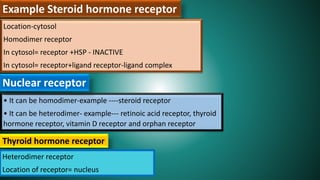
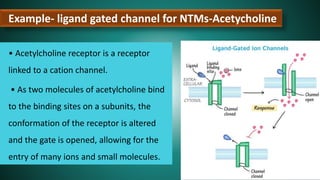
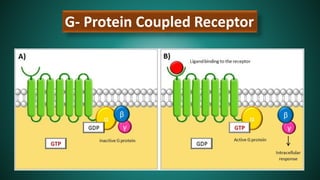
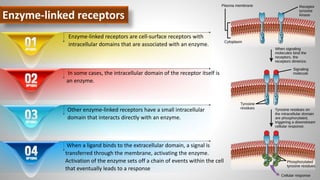
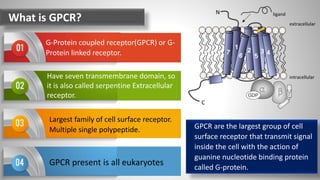
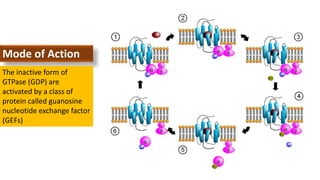
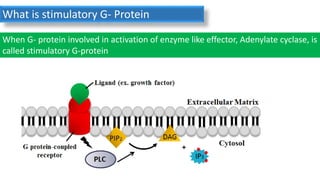
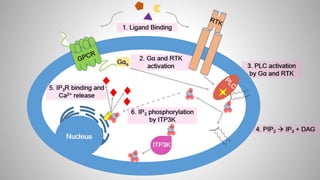
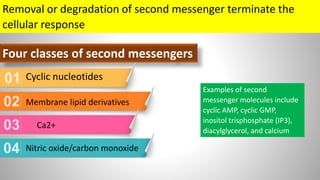
Cell signaling involves communication between cells through signaling molecules called ligands. Ligands bind to receptors on target cells and initiate cellular responses. There are several types of cell signaling depending on the location of the signaling and target cells. These include paracrine signaling between nearby cells, endocrine signaling between distant cells via the bloodstream, and autocrine signaling where cells signal themselves. The signaling molecules can be membrane-bound or secreted. Receptors are generally intracellular or cell surface proteins that receive signals and transmit them into the cell. Common signaling pathways involve G protein-coupled receptors activating intracellular secondary messengers like cyclic AMP.