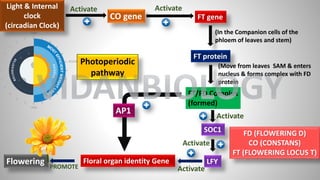
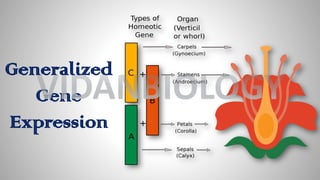
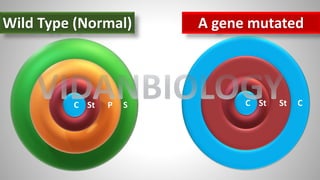
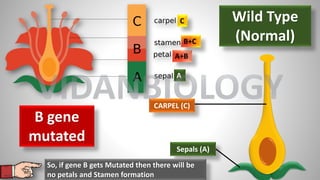
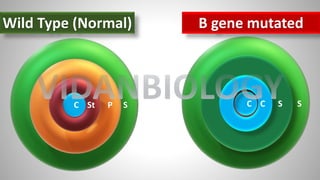
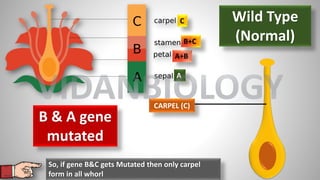
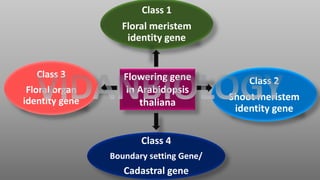
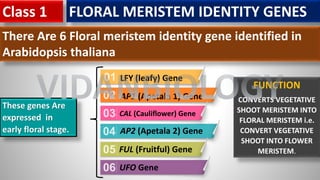
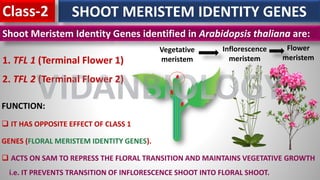
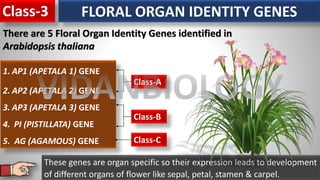
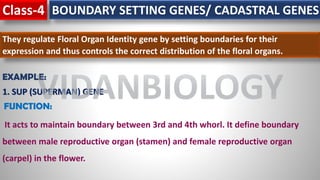
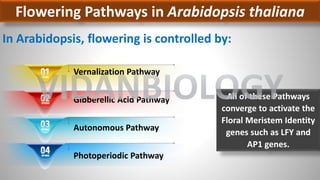
Arabidopsis thaliana is a model plant species that is used to study flowering genes. There are four classes of genes that control flowering: 1) floral meristem identity genes that convert vegetative shoot meristems into floral meristems, 2) shoot meristem identity genes that maintain vegetative growth, 3) floral organ identity genes that determine the identity of floral organs, and 4) boundary setting genes that regulate the expression of organ identity genes. Key floral organ identity genes include AP1, AP2, AP3, PI, and AG.


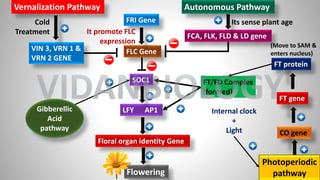
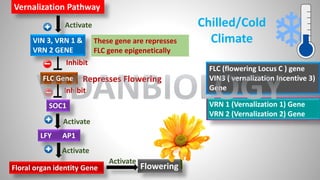
![FLC Gene
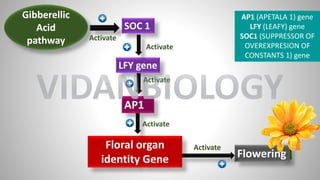
SOC1
Floral organ identity Gene
FCA, FLK, FLD & LD gene
Flowering
LFY gene
AP1
Activate
Inhibit
Activate
Activate
PROMOTE
Inhibit
Sensing
of Plant
Age
FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C)
LFY [LEAFY]
AP1[APETALA 1}
SOC1 (SUPPRESSOR OF
OVERREXPRESSION OF CONSTANTS 1)
FCA (FLOWER|NG CONTROL LOCUS A)
FLK (FLOWERING LOCUS K)
FLD (FLOWERING LOCUS D)
LD (LUMINIDEPENDENS)
PROMOTE
VIDANBIOLOGY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abcmodel-1-231022103555-f3341d20/85/ABC-Model-of-Flower-development-12-320.jpg)