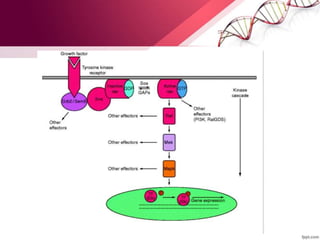
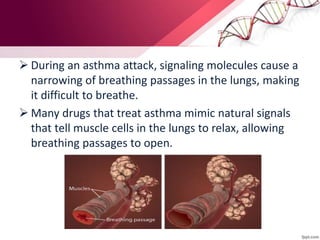
The document discusses cell signaling and diseases caused by weak cell signaling. It provides details about:
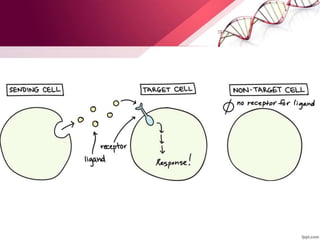
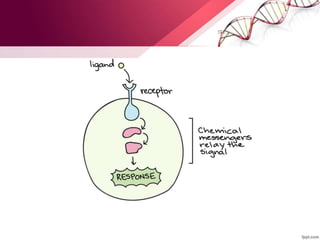
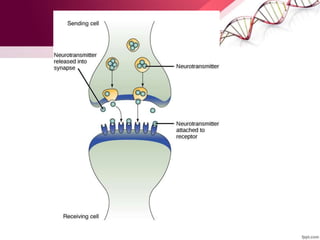
1) The process of cell signaling and how cells communicate via signaling molecules.
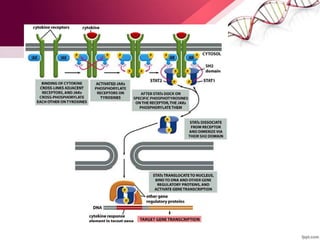
2) Key components of cell signaling pathways like receptors, ligands, and intracellular signaling cascades.
3) Examples of diseases caused by defects in cell signaling pathways like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and cancer.
4) How treatments for diseases aim to bypass problems in cell signaling pathways.