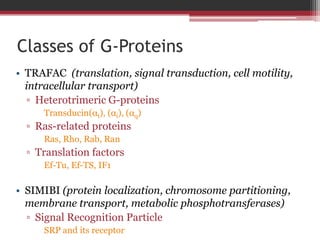
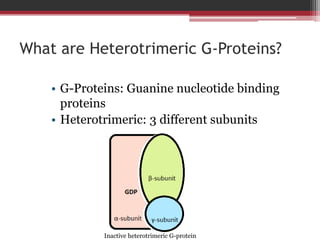
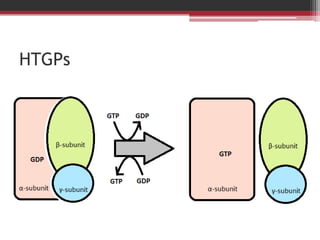
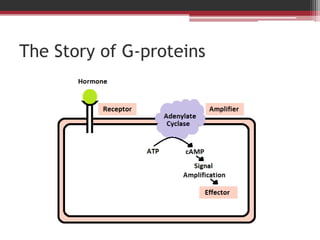
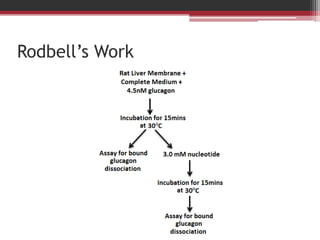
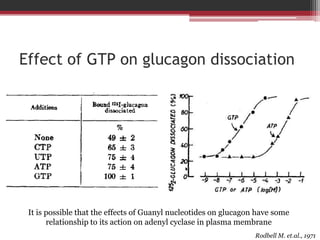
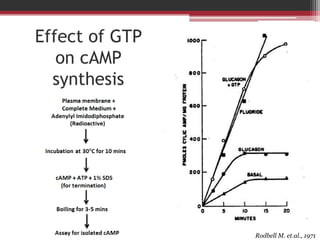
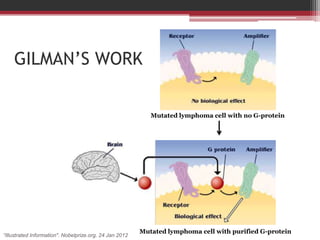
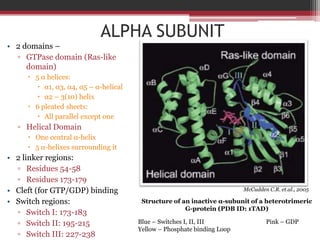
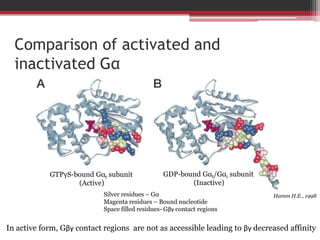
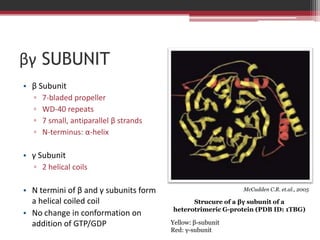
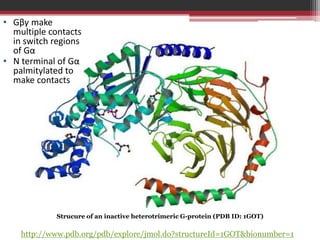
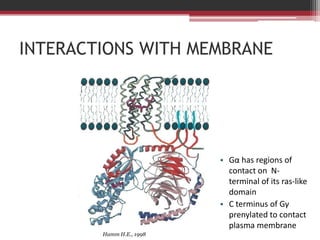
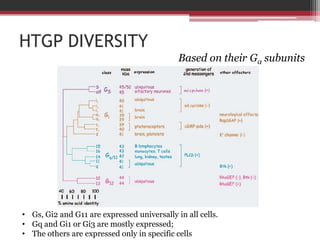
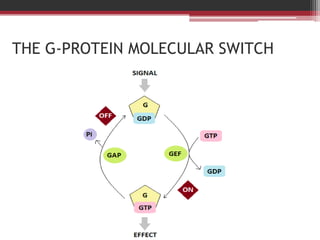
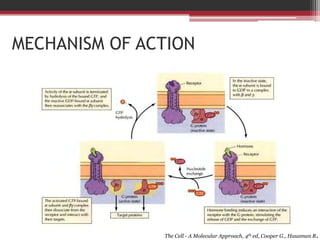
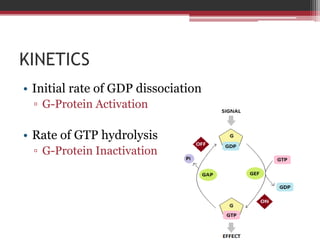
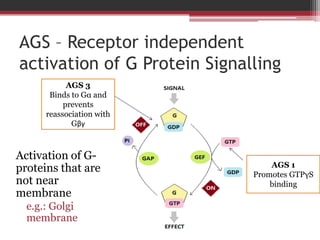
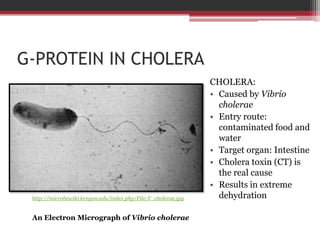
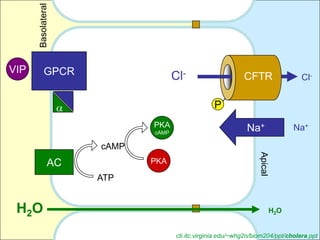
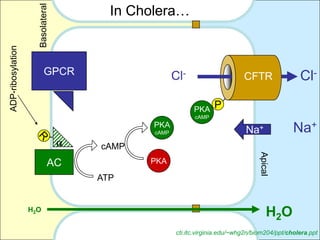
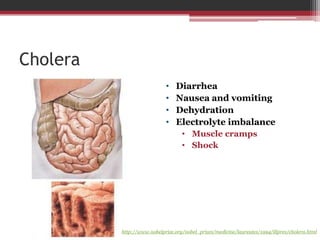
This document summarizes heterotrimeric G-proteins. It discusses that G-proteins are guanine nucleotide binding proteins composed of three subunits - alpha, beta, and gamma. The alpha subunit acts as a molecular switch cycling between an active GTP-bound form and inactive GDP-bound form. When a receptor is activated by a ligand, it causes a conformational change in the G-protein alpha subunit, activating it to turn on downstream effector molecules. The mechanism and roles of each subunit are described. Examples are given of how cholera toxin can cause disease by modifying G-protein alpha subunits and deregulating ion transport.