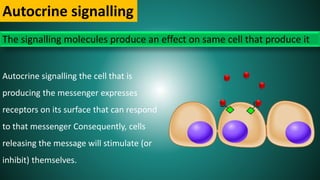
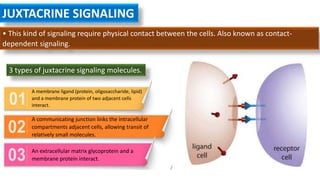
Cell signaling involves communication between cells through signaling molecules called ligands. Ligands can be proteins, peptides, hormones, or other molecules. They are released by signal-producing cells and bind to receptors on target cells to initiate responses. Signaling can occur through several methods - paracrine signaling involves local cell-to-cell communication, endocrine signaling uses hormones to target distant cells, and autocrine signaling allows cells to stimulate themselves. Receptors are proteins that receive signals, and can be intracellular or cell-surface receptors. Intracellular receptors interact with hydrophobic ligands that enter the cell, while cell-surface receptors have an extracellular ligand-binding domain and transduce signals across the membrane.